Zhe Song
Effective climate policies for major emission reductions of ozone precursors: Global evidence from two decades
May 20, 2025Abstract:Despite policymakers deploying various tools to mitigate emissions of ozone (O\textsubscript{3}) precursors, such as nitrogen oxides (NO\textsubscript{x}), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the effectiveness of policy combinations remains uncertain. We employ an integrated framework that couples structural break detection with machine learning to pinpoint effective interventions across the building, electricity, industrial, and transport sectors, identifying treatment effects as abrupt changes without prior assumptions about policy treatment assignment and timing. Applied to two decades of global O\textsubscript{3} precursor emissions data, we detect 78, 77, and 78 structural breaks for NO\textsubscript{x}, CO, and VOCs, corresponding to cumulative emission reductions of 0.96-0.97 Gt, 2.84-2.88 Gt, and 0.47-0.48 Gt, respectively. Sector-level analysis shows that electricity sector structural policies cut NO\textsubscript{x} by up to 32.4\%, while in buildings, developed countries combined adoption subsidies with carbon taxes to achieve 42.7\% CO reductions and developing countries used financing plus fuel taxes to secure 52.3\%. VOCs abatement peaked at 38.5\% when fossil-fuel subsidy reforms were paired with financial incentives. Finally, hybrid strategies merging non-price measures (subsidies, bans, mandates) with pricing instruments delivered up to an additional 10\% co-benefit. These findings guide the sequencing and complementarity of context-specific policy portfolios for O\textsubscript{3} precursor mitigation.
Prognosis of Rotor Parts Fly-off Based on Cascade Classification and Online Prediction Ability Index
Mar 30, 2022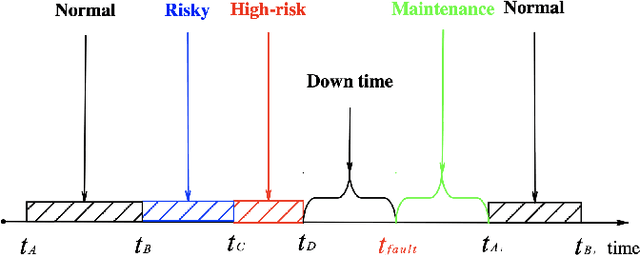
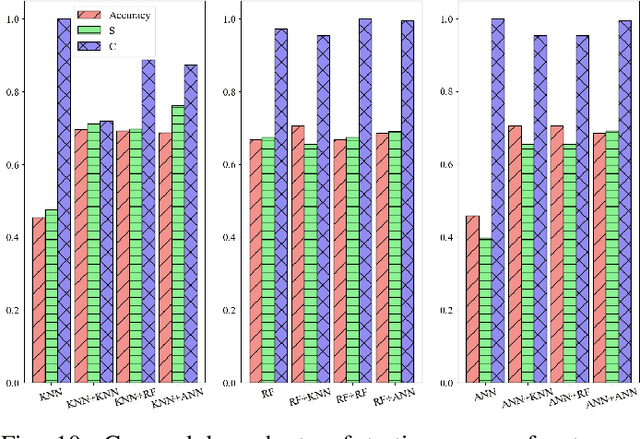
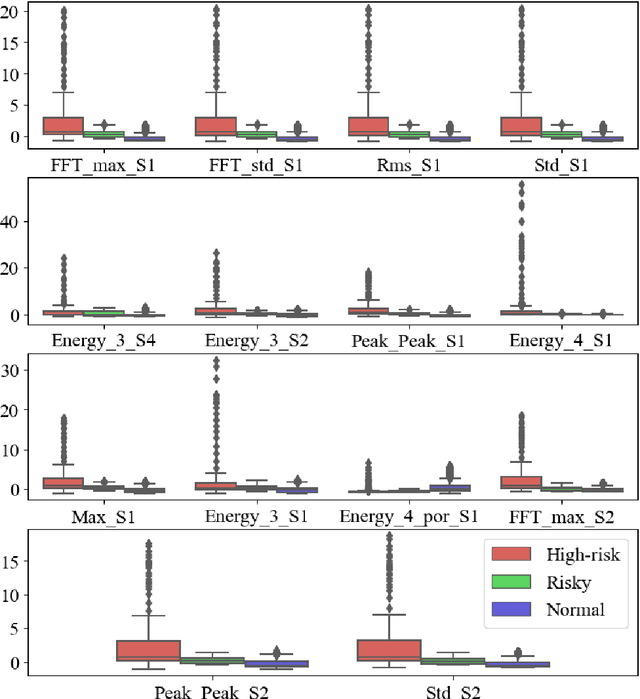
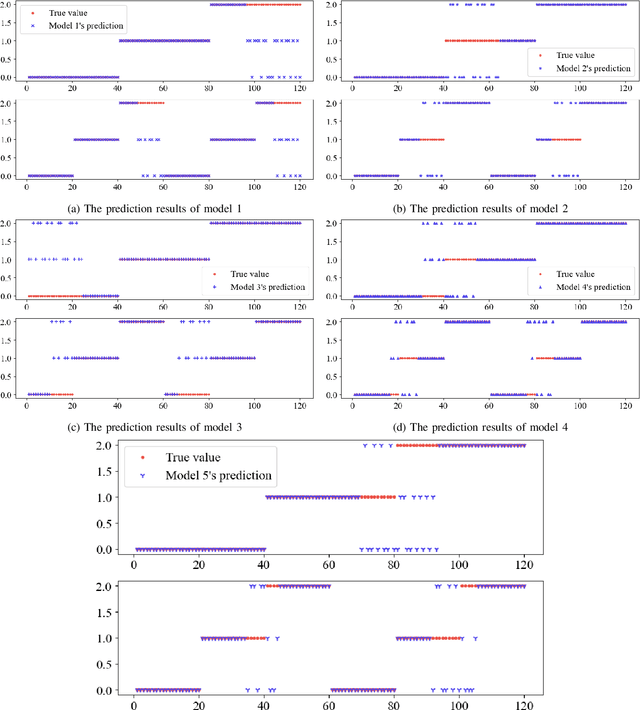
Abstract:Large rotating machines, e.g., compressors, steam turbines, gas turbines, are critical equipment in many process industries such as energy, chemical, and power generation. Due to high rotating speed and tremendous momentum of the rotor, the centrifugal force may lead to flying apart of the rotor parts, which brings a great threat to the operation safety. Early detection and prediction of potential failures could prevent the catastrophic plant downtime and economic loss. In this paper, we divide the operational states of a rotating machine into normal, risky, and high-risk ones based on the time to the moment of failure. Then a cascade classifying algorithm is proposed to predict the states in two steps, first we judge whether the machine is in normal or abnormal condition; for time periods which are predicted as abnormal we further classify them into risky or high-risk states. Moreover, traditional classification model evaluation metrics, such as confusion matrix, true-false accuracy, are static and neglect the online prediction dynamics and uneven wrong-prediction prices. An Online Prediction Ability Index (OPAI) is proposed to select prediction models with consistent online predictions and smaller close-to-downtime prediction errors. Real-world data sets and computational experiments are used to verify the effectiveness of proposed methods.
Rapid Assessments of Light-Duty Gasoline Vehicle Emissions Using On-Road Remote Sensing and Machine Learning
Oct 01, 2021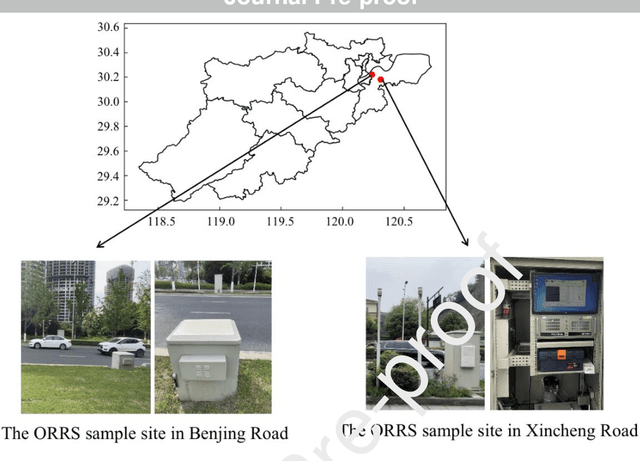
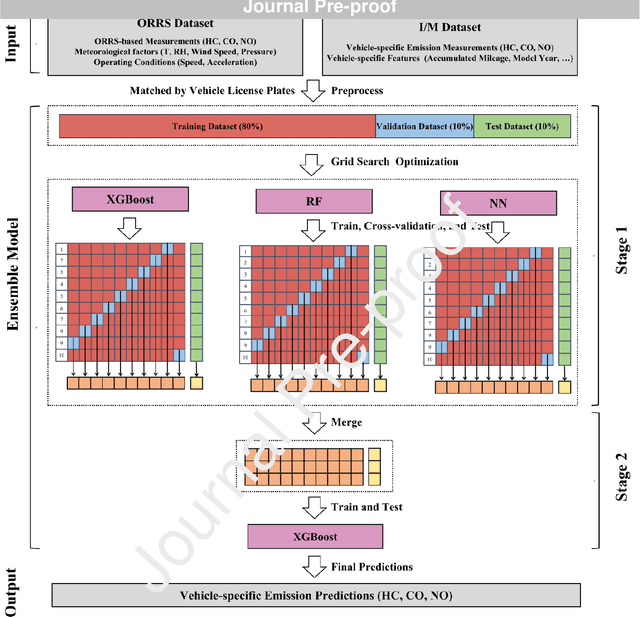
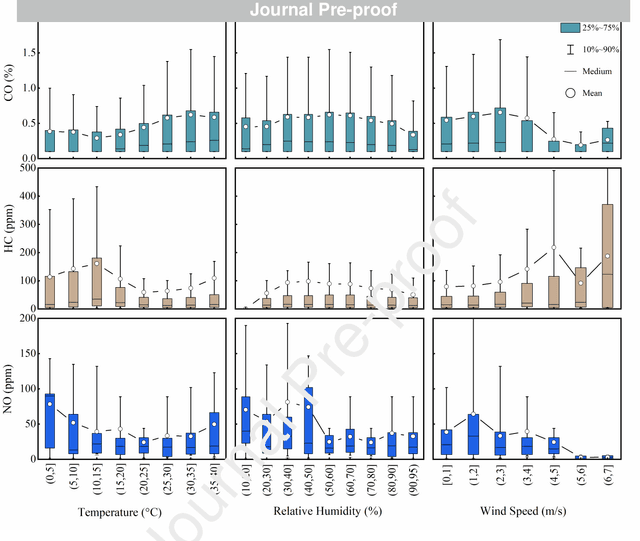
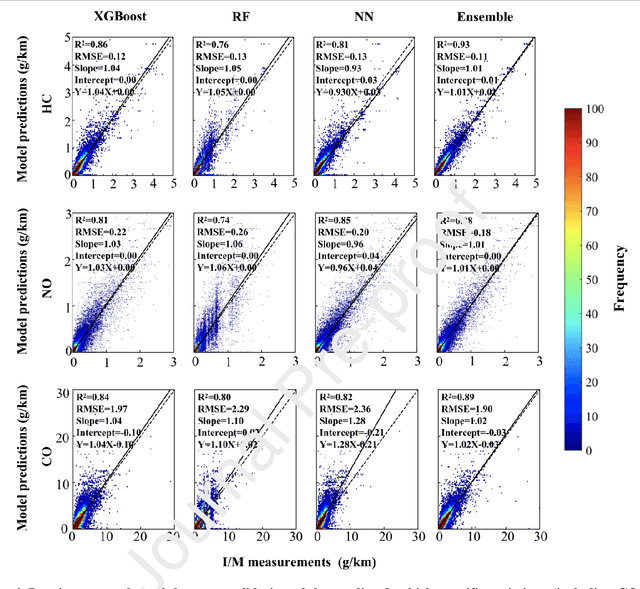
Abstract:In-time and accurate assessments of on-road vehicle emissions play a central role in urban air quality and health policymaking. However, official insight is hampered by the Inspection/Maintenance (I/M) procedure conducted in the laboratory annually. It not only has a large gap to real-world situations (e.g., meteorological conditions) but also is incapable of regular supervision. Here we build a unique dataset including 103831 light-duty gasoline vehicles, in which on-road remote sensing (ORRS) measurements are linked to the I/M records based on the vehicle identification numbers and license plates. On this basis, we develop an ensemble model framework that integrates three machining learning algorithms, including neural network (NN), extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), and random forest (RF). We demonstrate that this ensemble model could rapidly assess the vehicle-specific emissions (i.e., CO, HC, and NO). In particular, the model performs quite well for the passing vehicles under normal conditions (i.e., lower VSP (< 18 kw/t), temperature (6 ~ 32 {\deg}C), relative humidity (< 80%), and wind speed (< 5m/s)). Together with the current emission standard, we identify a large number of the dirty (2.33%) or clean (74.92%) vehicles in the real world. Our results show that the ORRS measurements, assisted by the machine-learning-based ensemble model developed here, can realize day-to-day supervision of on-road vehicle-specific emissions. This approach framework provides a valuable opportunity to reform the I/M procedures globally and mitigate urban air pollution deeply.
Enhancing Generalizability of Predictive Models with Synergy of Data and Physics
May 04, 2021
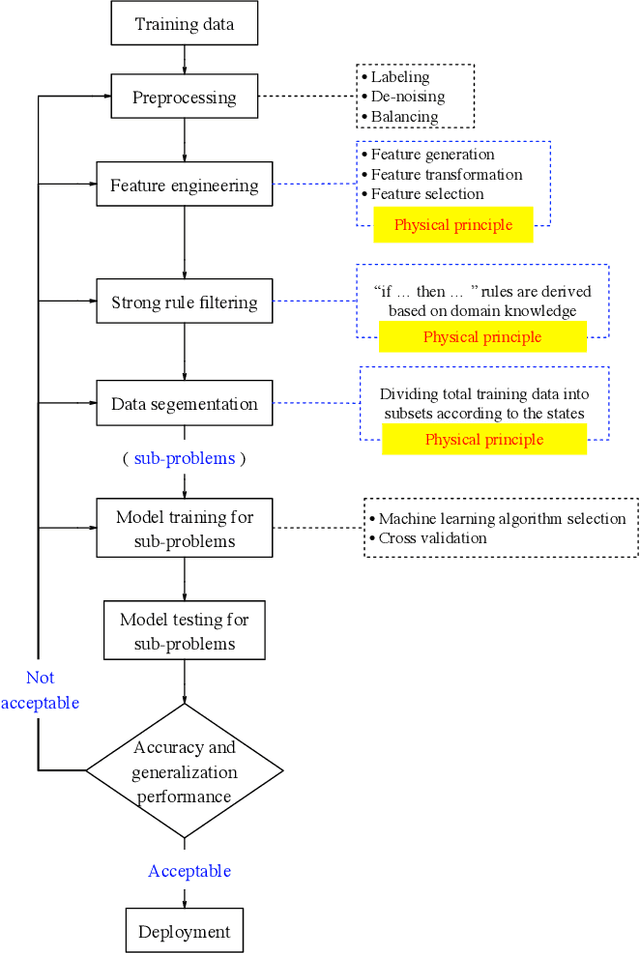
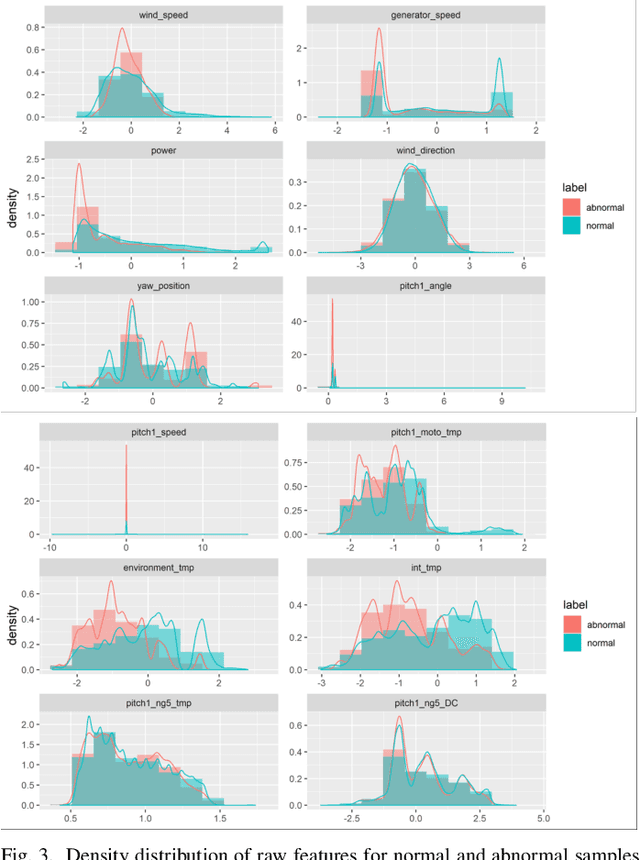
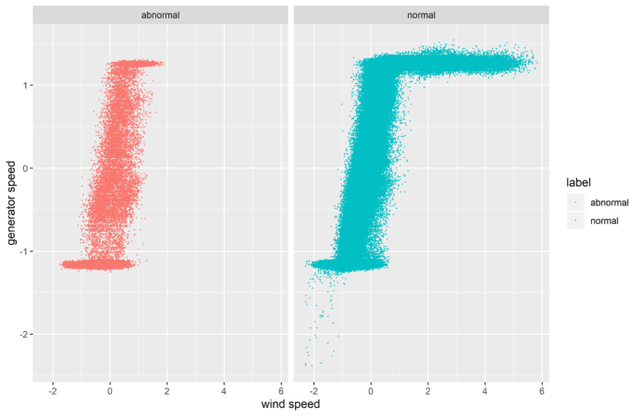
Abstract:Wind farm needs prediction models for predictive maintenance. There is a need to predict values of non-observable parameters beyond ranges reflected in available data. A prediction model developed for one machine many not perform well in another similar machine. This is usually due to lack of generalizability of data-driven models. To increase generalizability of predictive models, this research integrates the data mining with first-principle knowledge. Physics-based principles are combined with machine learning algorithms through feature engineering, strong rules and divide-and-conquer. The proposed synergy concept is illustrated with the wind turbine blade icing prediction and achieves significant prediction accuracy across different turbines. The proposed process is widely accepted by wind energy predictive maintenance practitioners because of its simplicity and efficiency. Furthermore, this paper demonstrates the importance of embedding physical principles within the machine learning process, and also highlight an important point that the need for more complex machine learning algorithms in industrial big data mining is often much less than it is in other applications, making it essential to incorporate physics and follow Less is More philosophy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge