Zhaojie Luo
Decoupling Speaker-Independent Emotions for Voice Conversion Via Source-Filter Networks
Oct 04, 2021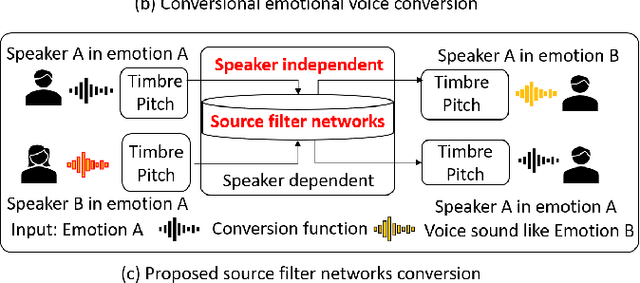
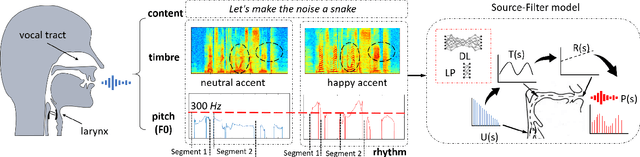
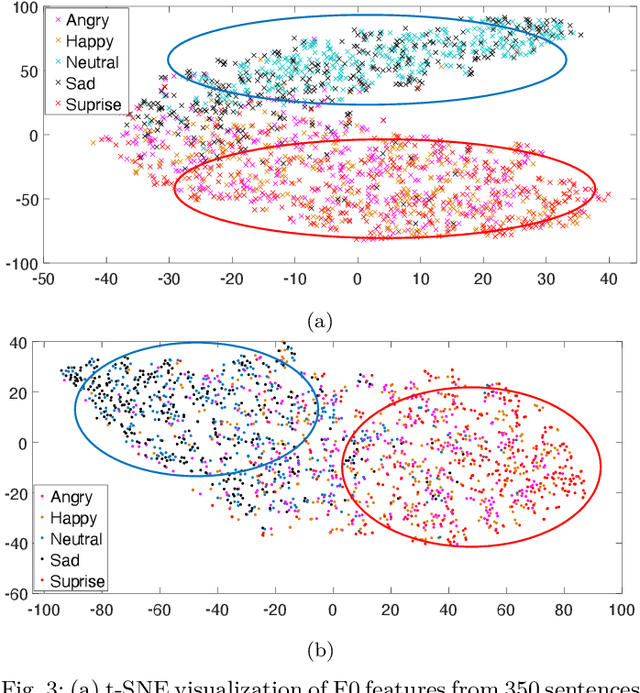
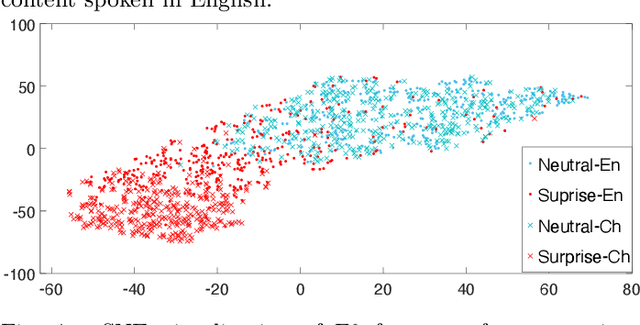
Abstract:Emotional voice conversion (VC) aims to convert a neutral voice to an emotional (e.g. happy) one while retaining the linguistic information and speaker identity. We note that the decoupling of emotional features from other speech information (such as speaker, content, etc.) is the key to achieving remarkable performance. Some recent attempts about speech representation decoupling on the neutral speech can not work well on the emotional speech, due to the more complex acoustic properties involved in the latter. To address this problem, here we propose a novel Source-Filter-based Emotional VC model (SFEVC) to achieve proper filtering of speaker-independent emotion features from both the timbre and pitch features. Our SFEVC model consists of multi-channel encoders, emotion separate encoders, and one decoder. Note that all encoder modules adopt a designed information bottlenecks auto-encoder. Additionally, to further improve the conversion quality for various emotions, a novel two-stage training strategy based on the 2D Valence-Arousal (VA) space was proposed. Experimental results show that the proposed SFEVC along with a two-stage training strategy outperforms all baselines and achieves the state-of-the-art performance in speaker-independent emotional VC with nonparallel data.
Fusion with Hierarchical Graphs for Mulitmodal Emotion Recognition
Sep 15, 2021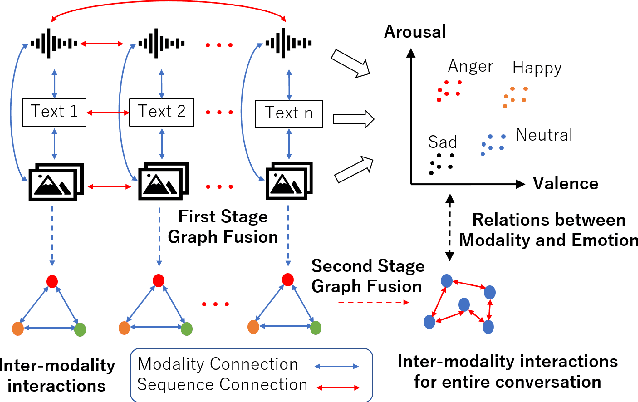
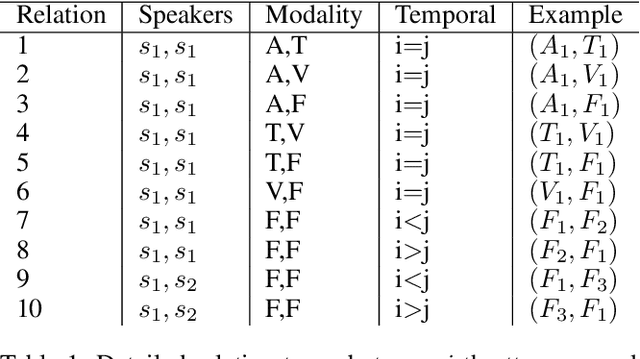
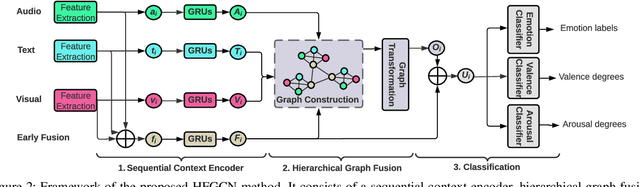
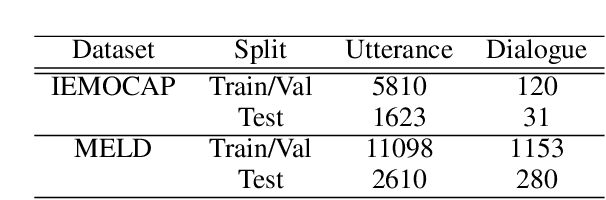
Abstract:Automatic emotion recognition (AER) based on enriched multimodal inputs, including text, speech, and visual clues, is crucial in the development of emotionally intelligent machines. Although complex modality relationships have been proven effective for AER, they are still largely underexplored because previous works predominantly relied on various fusion mechanisms with simply concatenated features to learn multimodal representations for emotion classification. This paper proposes a novel hierarchical fusion graph convolutional network (HFGCN) model that learns more informative multimodal representations by considering the modality dependencies during the feature fusion procedure. Specifically, the proposed model fuses multimodality inputs using a two-stage graph construction approach and encodes the modality dependencies into the conversation representation. We verified the interpretable capabilities of the proposed method by projecting the emotional states to a 2D valence-arousal (VA) subspace. Extensive experiments showed the effectiveness of our proposed model for more accurate AER, which yielded state-of-the-art results on two public datasets, IEMOCAP and MELD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge