Zeyang Zheng
Real-Time Roadway Obstacle Detection for Electric Scooters Using Deep Learning and Multi-Sensor Fusion
Apr 04, 2025



Abstract:The increasing adoption of electric scooters (e-scooters) in urban areas has coincided with a rise in traffic accidents and injuries, largely due to their small wheels, lack of suspension, and sensitivity to uneven surfaces. While deep learning-based object detection has been widely used to improve automobile safety, its application for e-scooter obstacle detection remains unexplored. This study introduces a novel ground obstacle detection system for e-scooters, integrating an RGB camera, and a depth camera to enhance real-time road hazard detection. Additionally, the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) measures linear vertical acceleration to identify surface vibrations, guiding the selection of six obstacle categories: tree branches, manhole covers, potholes, pine cones, non-directional cracks, and truncated domes. All sensors, including the RGB camera, depth camera, and IMU, are integrated within the Intel RealSense Camera D435i. A deep learning model powered by YOLO detects road hazards and utilizes depth data to estimate obstacle proximity. Evaluated on the seven hours of naturalistic riding dataset, the system achieves a high mean average precision (mAP) of 0.827 and demonstrates excellent real-time performance. This approach provides an effective solution to enhance e-scooter safety through advanced computer vision and data fusion. The dataset is accessible at https://zenodo.org/records/14583718, and the project code is hosted on https://github.com/Zeyang-Zheng/Real-Time-Roadway-Obstacle-Detection-for-Electric-Scooters.
Multimodal Data Integration for Sustainable Indoor Gardening: Tracking Anyplant with Time Series Foundation Model
Mar 27, 2025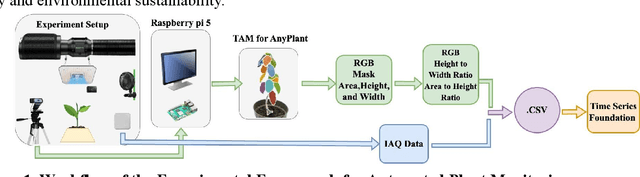
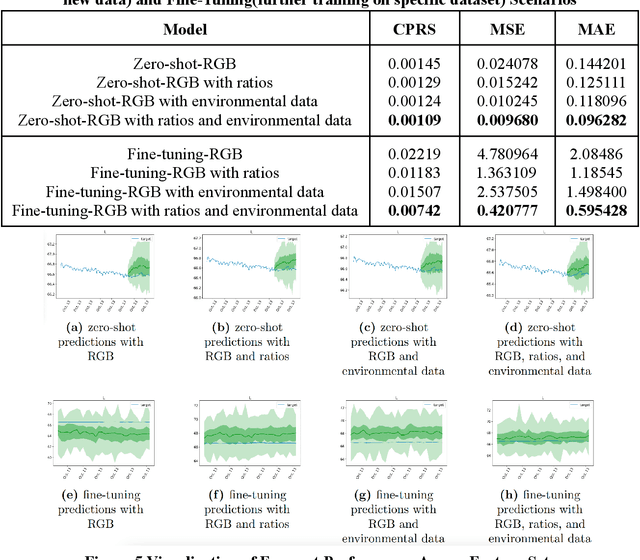
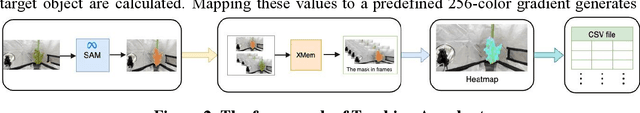
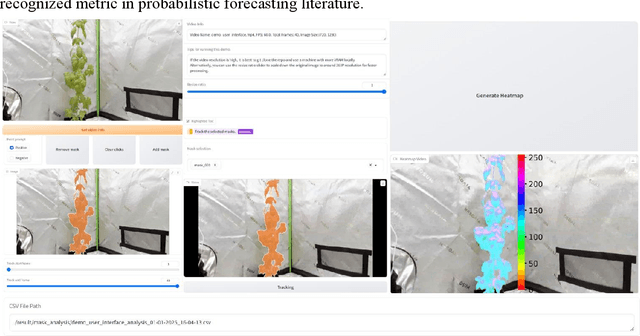
Abstract:Indoor gardening within sustainable buildings offers a transformative solution to urban food security and environmental sustainability. By 2030, urban farming, including Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) and vertical farming, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2% from 2024 to 2030, according to market reports. This growth is fueled by advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, sustainable innovations such as smart growing systems, and the rising interest in green interior design. This paper presents a novel framework that integrates computer vision, machine learning (ML), and environmental sensing for the automated monitoring of plant health and growth. Unlike previous approaches, this framework combines RGB imagery, plant phenotyping data, and environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, to predict plant water stress in a controlled growth environment. The system utilizes high-resolution cameras to extract phenotypic features, such as RGB, plant area, height, and width while employing the Lag-Llama time series model to analyze and predict water stress. Experimental results demonstrate that integrating RGB, size ratios, and environmental data significantly enhances predictive accuracy, with the Fine-tuned model achieving the lowest errors (MSE = 0.420777, MAE = 0.595428) and reduced uncertainty. These findings highlight the potential of multimodal data and intelligent systems to automate plant care, optimize resource consumption, and align indoor gardening with sustainable building management practices, paving the way for resilient, green urban spaces.
Hierarchical Forgery Classifier On Multi-modality Face Forgery Clues
Dec 30, 2022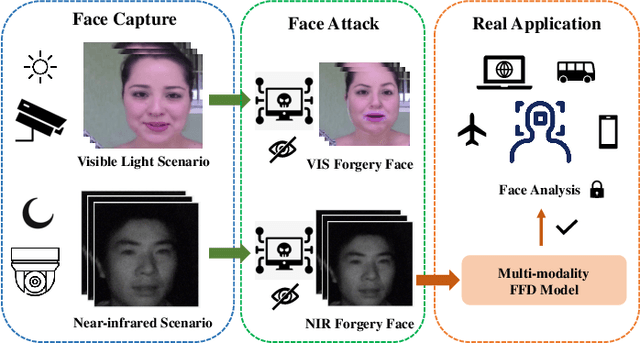
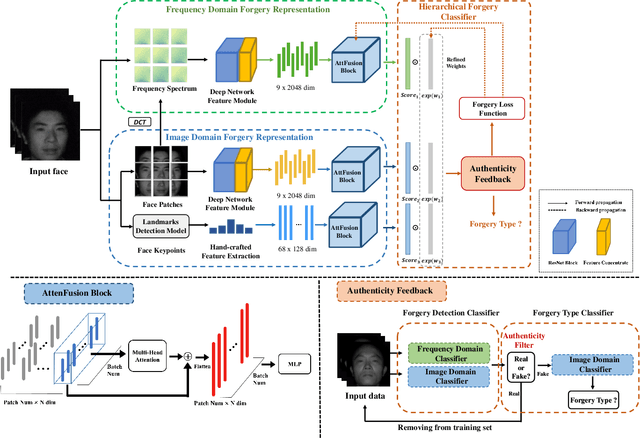

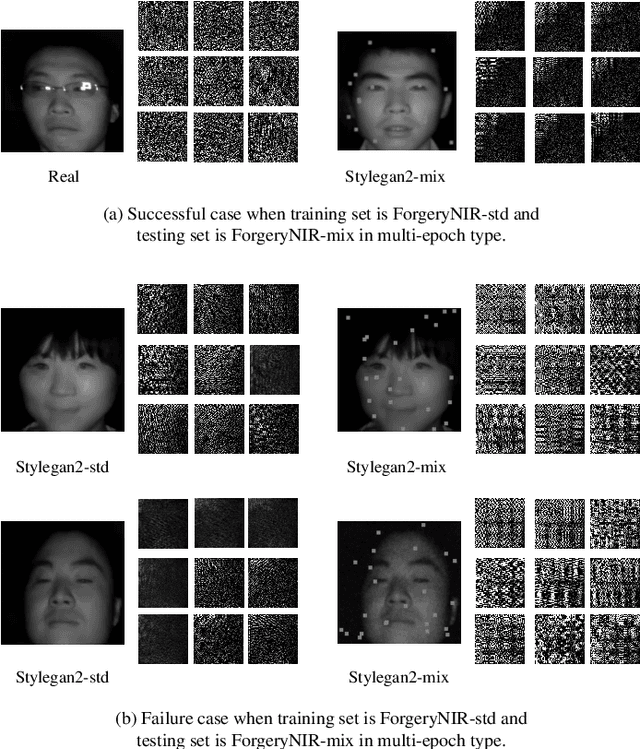
Abstract:Face forgery detection plays an important role in personal privacy and social security. With the development of adversarial generative models, high-quality forgery images become more and more indistinguishable from real to humans. Existing methods always regard as forgery detection task as the common binary or multi-label classification, and ignore exploring diverse multi-modality forgery image types, e.g. visible light spectrum and near-infrared scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel Hierarchical Forgery Classifier for Multi-modality Face Forgery Detection (HFC-MFFD), which could effectively learn robust patches-based hybrid domain representation to enhance forgery authentication in multiple-modality scenarios. The local spatial hybrid domain feature module is designed to explore strong discriminative forgery clues both in the image and frequency domain in local distinct face regions. Furthermore, the specific hierarchical face forgery classifier is proposed to alleviate the class imbalance problem and further boost detection performance. Experimental results on representative multi-modality face forgery datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed HFC-MFFD compared with state-of-the-art algorithms. The source code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/EdWhites/HFC-MFFD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge