Zexiang Li
Control of a Tail-Sitter VTOL UAV Based on Recurrent Neural Networks
Apr 05, 2021
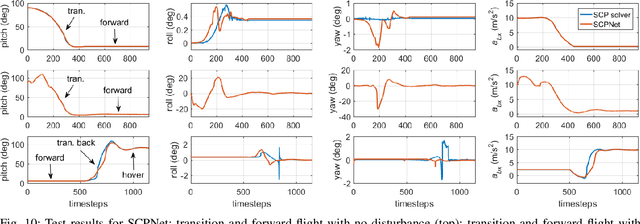
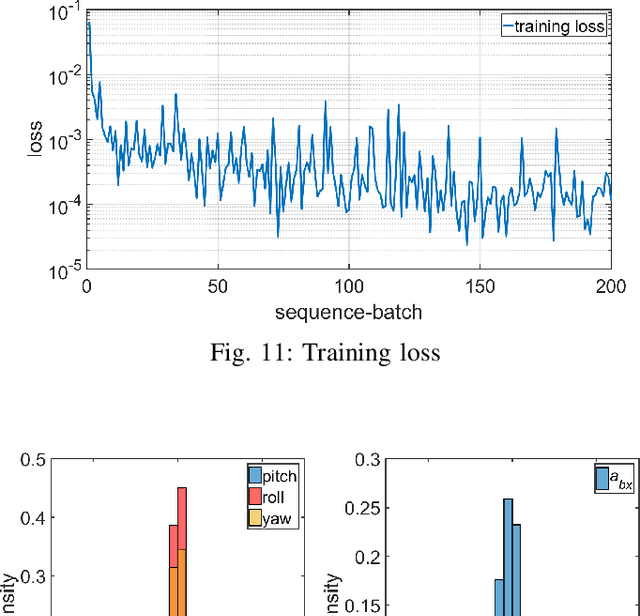
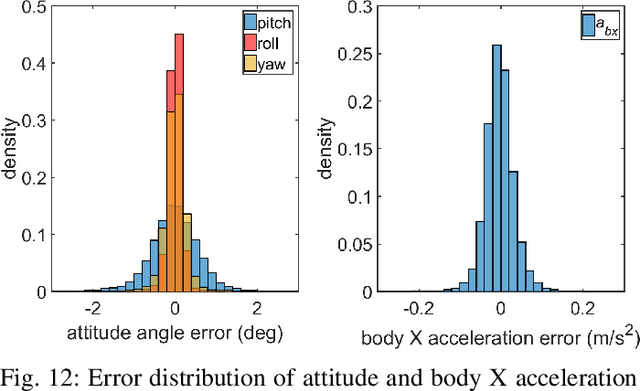
Abstract:Tail-sitter vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have the capability of hovering and performing efficient level flight with compact mechanical structures. We present a unified controller design for such UAVs, based on recurrent neural networks. An advantage of this design method is that the various flight modes (i.e., hovering, transition and level flight) of a VTOL UAV are controlled in a unified manner, as opposed to treating them separately and in the runtime switching one from another. The proposed controller consists of an outer-loop position controller and an inner-loop attitude controller. The inner-loop controller is composed of a proportional attitude controller and a loop-shaping linear angular rate controller. For the outer-loop controller, we propose a nonlinear solver to compute the desired attitude and thrust, based on the UAV dynamics and an aerodynamic model, in addition to a cascaded PID controller for the position and velocity tracking. We employ a recurrent neural network (RNN) to approximate the behavior of the nonlinear solver, which suffers from high computational complexity. The proposed RNN has negligible approximation errors, and can be implemented in real-time (e.g., 50 Hz). Moreover, the RNN generates much smoother outputs than the nonlinear solver. We provide an analysis of the stability and robustness of the overall closed-loop system. Simulation and experiments are also presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
A New Hybrid Control Architecture to Attenuate Large Horizontal Wind Disturbance for a Small-Scale Unmanned Helicopter
May 03, 2019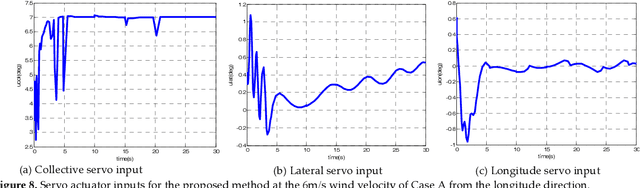
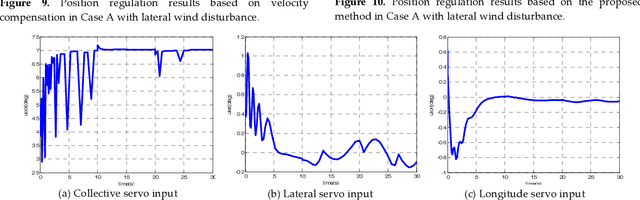
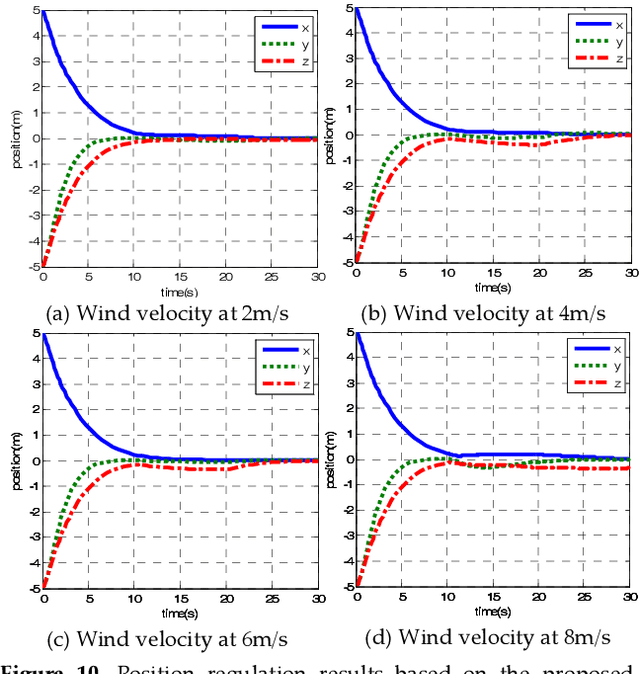
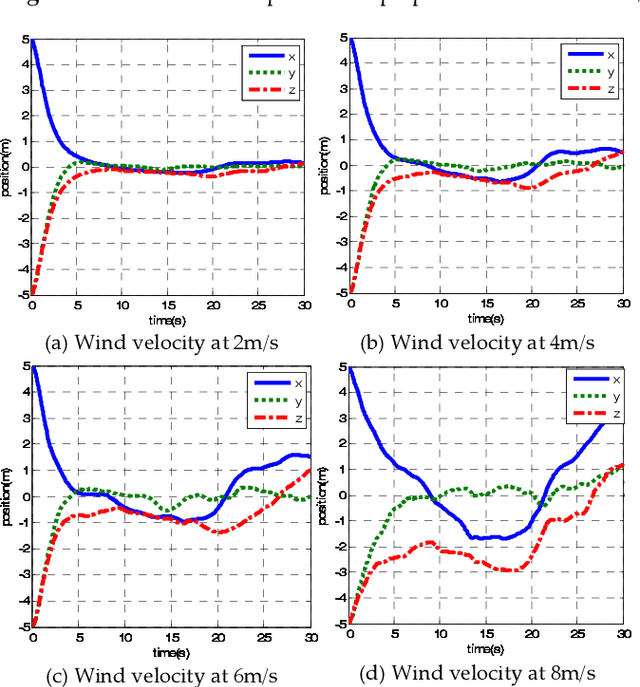
Abstract:This paper presents a novel method to attenuate large horizontal wind disturbance for a small-scale unmanned autonomous helicopter combining wind tunnel-based experimental data and a backstepping algorithm. Large horizontal wind disturbance is harmful to autonomous helicopters, especially to small ones because of their low inertia and the high cross-coupling effects among the multiple inputs. In order to achieve more accurate and faster attenuation of large wind disturbance, a new hybrid control architecture is proposed to take advantage of the direct force/moment compensation based on the wind tunnel experimental data. In this architecture, large horizontal wind disturbance is treated as an additional input to the control system instead of a small perturbation around the equilibrium state. A backstepping algorithm is then designed to guarantee the stable convergence of the hilicopter to the desired position. The proposed technique is finally evaluated in simulation on the platform, HIROBO Eagle, compared with a traditional wind velocity compensation method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge