Zee Fryer
Flexible text generation for counterfactual fairness probing
Jun 28, 2022

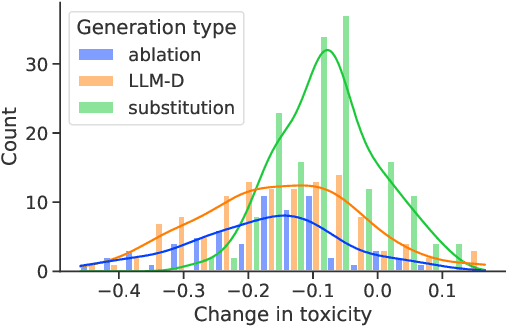
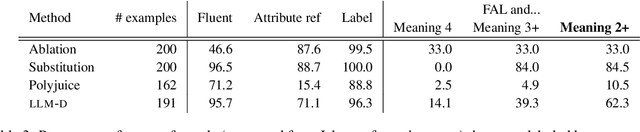
Abstract:A common approach for testing fairness issues in text-based classifiers is through the use of counterfactuals: does the classifier output change if a sensitive attribute in the input is changed? Existing counterfactual generation methods typically rely on wordlists or templates, producing simple counterfactuals that don't take into account grammar, context, or subtle sensitive attribute references, and could miss issues that the wordlist creators had not considered. In this paper, we introduce a task for generating counterfactuals that overcomes these shortcomings, and demonstrate how large language models (LLMs) can be leveraged to make progress on this task. We show that this LLM-based method can produce complex counterfactuals that existing methods cannot, comparing the performance of various counterfactual generation methods on the Civil Comments dataset and showing their value in evaluating a toxicity classifier.
Provable Hierarchical Lifelong Learning with a Sketch-based Modular Architecture
Dec 21, 2021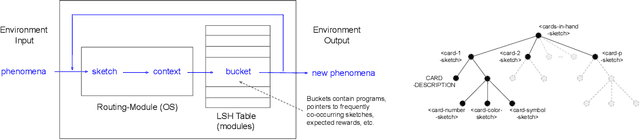

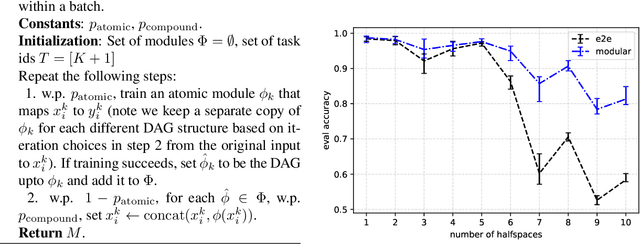
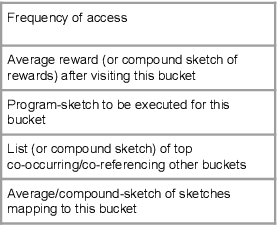
Abstract:We propose a modular architecture for the lifelong learning of hierarchically structured tasks. Specifically, we prove that our architecture is theoretically able to learn tasks that can be solved by functions that are learnable given access to functions for other, previously learned tasks as subroutines. We empirically show that some tasks that we can learn in this way are not learned by standard training methods in practice; indeed, prior work suggests that some such tasks cannot be learned by any efficient method without the aid of the simpler tasks. We also consider methods for identifying the tasks automatically, without relying on explicitly given indicators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge