Zanbo Wang
Seed1.5-VL Technical Report
May 11, 2025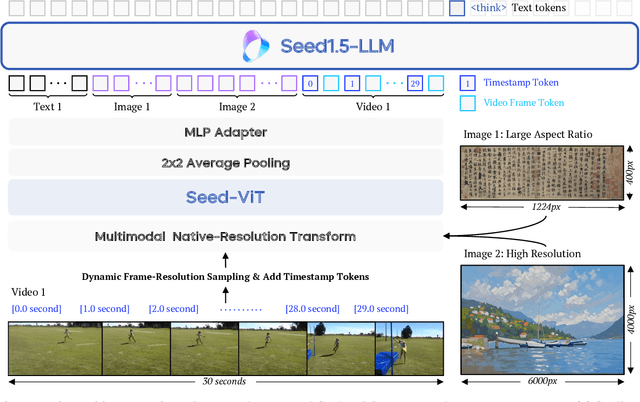

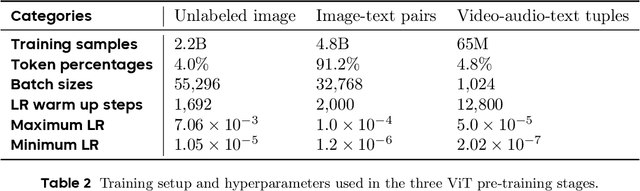
Abstract:We present Seed1.5-VL, a vision-language foundation model designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. Seed1.5-VL is composed with a 532M-parameter vision encoder and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM of 20B active parameters. Despite its relatively compact architecture, it delivers strong performance across a wide spectrum of public VLM benchmarks and internal evaluation suites, achieving the state-of-the-art performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks. Moreover, in agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, Seed1.5-VL outperforms leading multimodal systems, including OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7. Beyond visual and video understanding, it also demonstrates strong reasoning abilities, making it particularly effective for multimodal reasoning challenges such as visual puzzles. We believe these capabilities will empower broader applications across diverse tasks. In this report, we mainly provide a comprehensive review of our experiences in building Seed1.5-VL across model design, data construction, and training at various stages, hoping that this report can inspire further research. Seed1.5-VL is now accessible at https://www.volcengine.com/ (Volcano Engine Model ID: doubao-1-5-thinking-vision-pro-250428)
Exploiting Global Contextual Information for Document-level Named Entity Recognition
Jun 02, 2021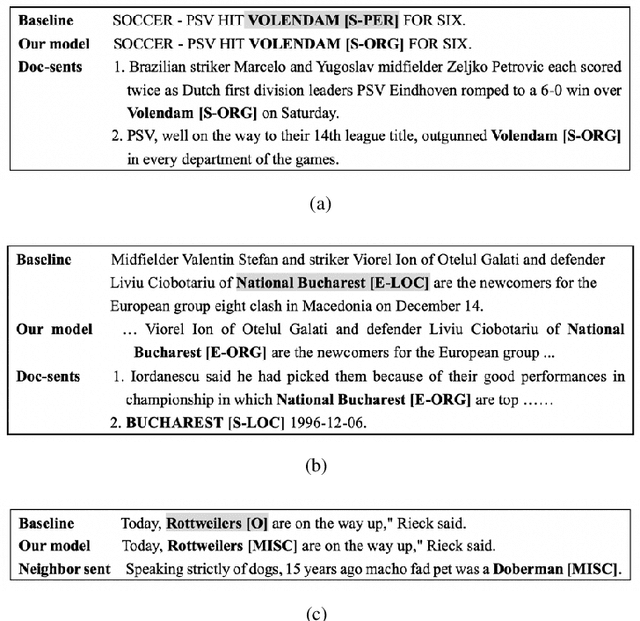
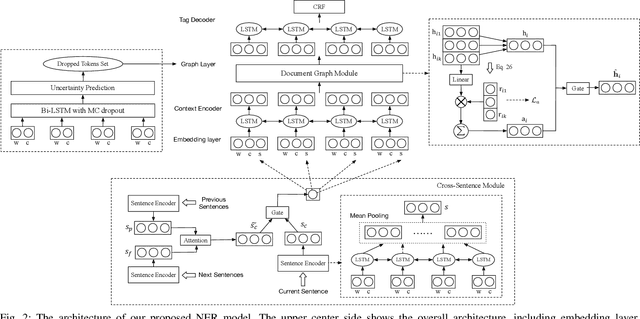

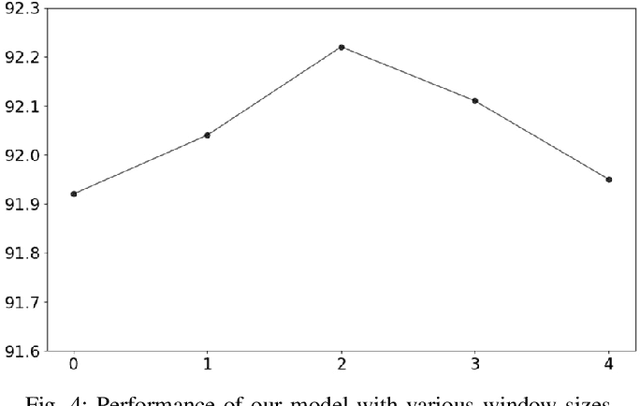
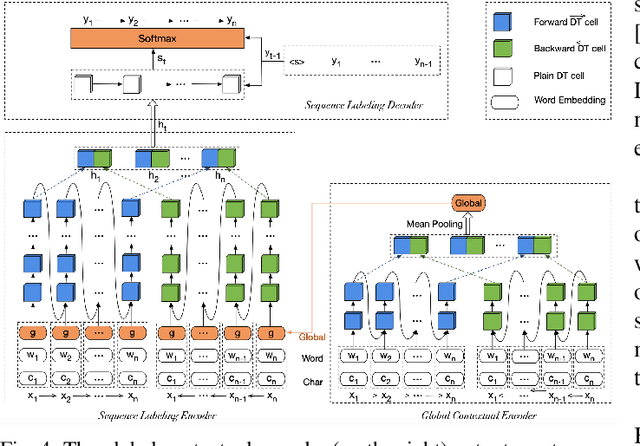
Abstract:Most existing named entity recognition (NER) approaches are based on sequence labeling models, which focus on capturing the local context dependencies. However, the way of taking one sentence as input prevents the modeling of non-sequential global context, which is useful especially when local context information is limited or ambiguous. To this end, we propose a model called Global Context enhanced Document-level NER (GCDoc) to leverage global contextual information from two levels, i.e., both word and sentence. At word-level, a document graph is constructed to model a wider range of dependencies between words, then obtain an enriched contextual representation for each word via graph neural networks (GNN). To avoid the interference of noise information, we further propose two strategies. First we apply the epistemic uncertainty theory to find out tokens whose representations are less reliable, thereby helping prune the document graph. Then a selective auxiliary classifier is proposed to effectively learn the weight of edges in document graph and reduce the importance of noisy neighbour nodes. At sentence-level, for appropriately modeling wider context beyond single sentence, we employ a cross-sentence module which encodes adjacent sentences and fuses it with the current sentence representation via attention and gating mechanisms. Extensive experiments on two benchmark NER datasets (CoNLL 2003 and Ontonotes 5.0 English dataset) demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model. Our model reaches F1 score of 92.22 (93.40 with BERT) on CoNLL 2003 dataset and 88.32 (90.49 with BERT) on Ontonotes 5.0 dataset, achieving new state-of-the-art performance.
A Survey on Recent Advances in Sequence Labeling from Deep Learning Models
Nov 13, 2020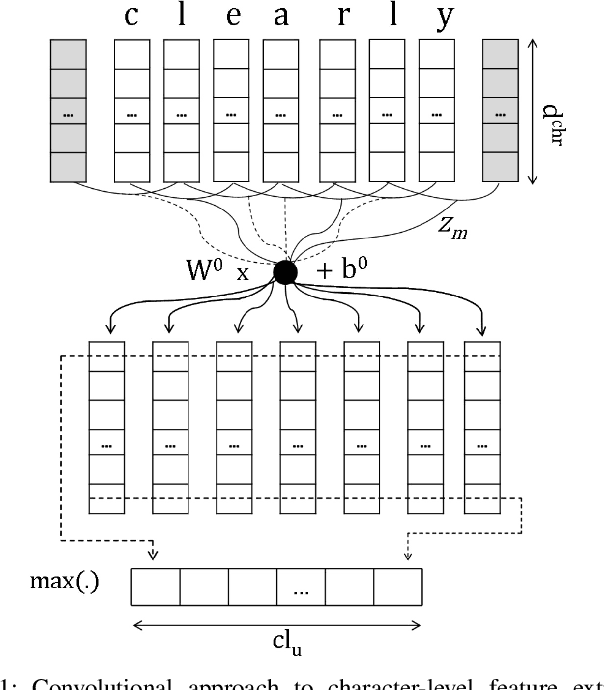
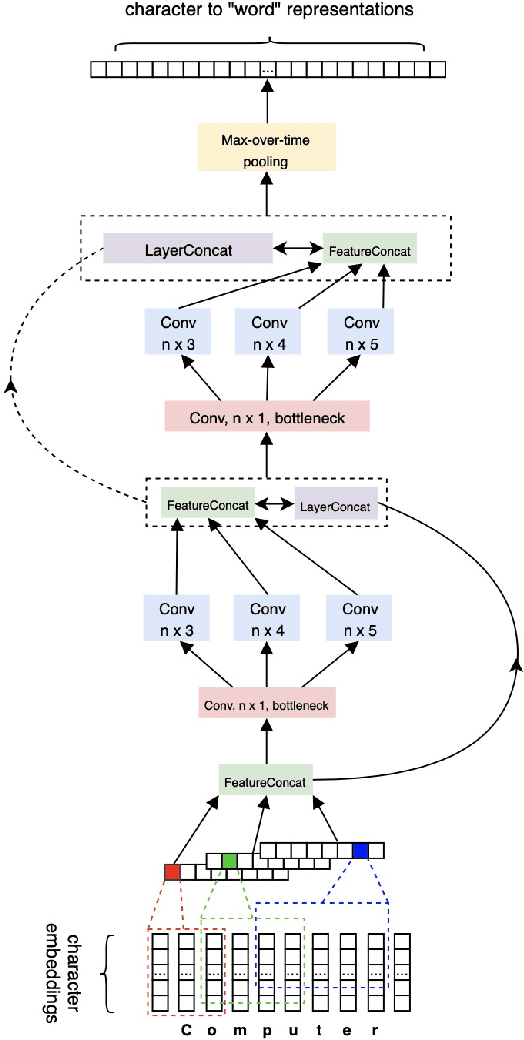
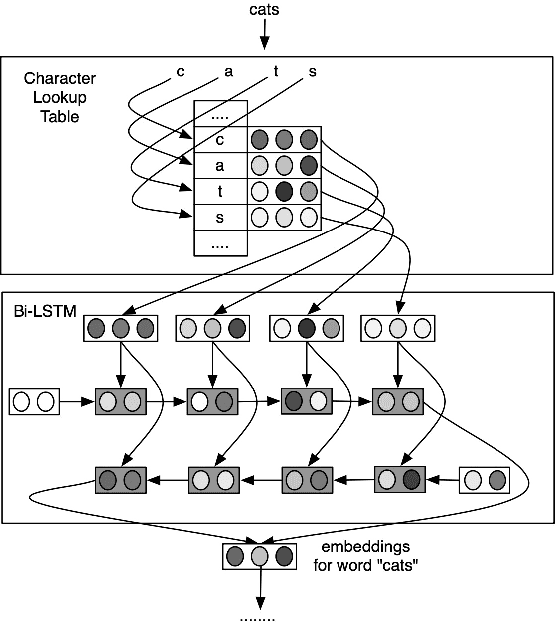
Abstract:Sequence labeling (SL) is a fundamental research problem encompassing a variety of tasks, e.g., part-of-speech (POS) tagging, named entity recognition (NER), text chunking, etc. Though prevalent and effective in many downstream applications (e.g., information retrieval, question answering, and knowledge graph embedding), conventional sequence labeling approaches heavily rely on hand-crafted or language-specific features. Recently, deep learning has been employed for sequence labeling tasks due to its powerful capability in automatically learning complex features of instances and effectively yielding the stat-of-the-art performances. In this paper, we aim to present a comprehensive review of existing deep learning-based sequence labeling models, which consists of three related tasks, e.g., part-of-speech tagging, named entity recognition, and text chunking. Then, we systematically present the existing approaches base on a scientific taxonomy, as well as the widely-used experimental datasets and popularly-adopted evaluation metrics in the SL domain. Furthermore, we also present an in-depth analysis of different SL models on the factors that may affect the performance and future directions in the SL domain.
Enhancing Neural Sequence Labeling with Position-Aware Self-Attention
Aug 24, 2019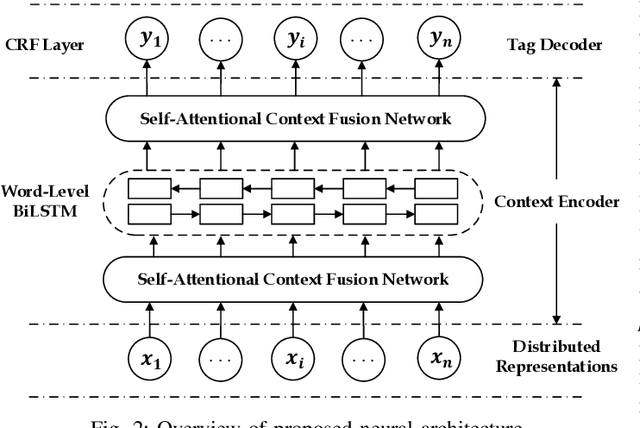
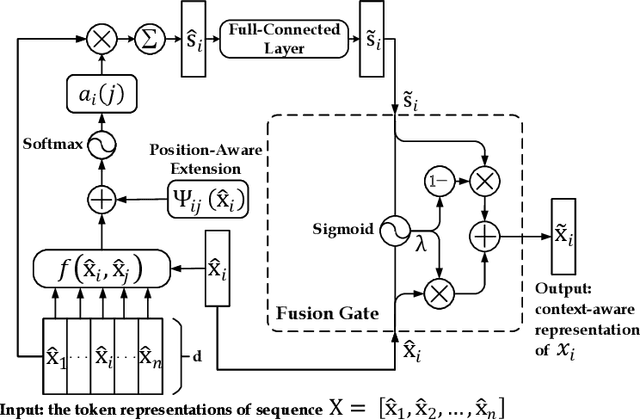
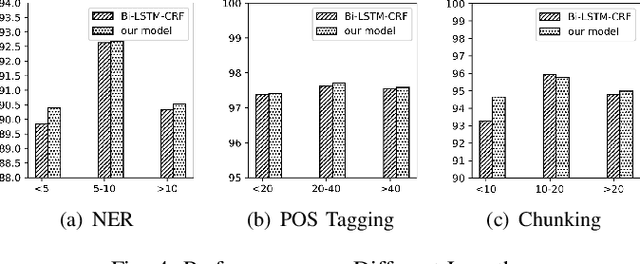
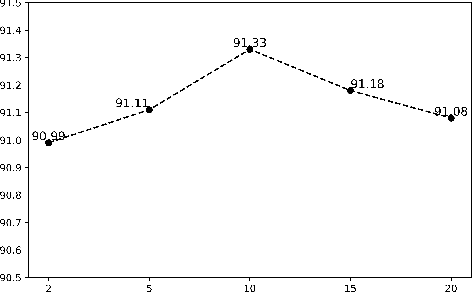
Abstract:Sequence labeling is a fundamental task in natural language processing and has been widely studied. Recently, RNN-based sequence labeling models have increasingly gained attentions. Despite superior performance achieved by learning the long short-term (i.e., successive) dependencies, the way of sequentially processing inputs might limit the ability to capture the non-continuous relations over tokens within a sentence. To tackle the problem, we focus on how to effectively model successive and discrete dependencies of each token for enhancing the sequence labeling performance. Specifically, we propose an innovative and well-designed attention-based model (called position-aware self-attention, i.e., PSA) within a neural network architecture, to explore the positional information of an input sequence for capturing the latent relations among tokens. Extensive experiments on three classical tasks in sequence labeling domain, i.e., part-of-speech (POS) tagging, named entity recognition (NER) and phrase chunking, demonstrate our proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-arts without any external knowledge, in terms of various metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge