Zakaria Haque
TensorFlow Estimators: Managing Simplicity vs. Flexibility in High-Level Machine Learning Frameworks
Aug 08, 2017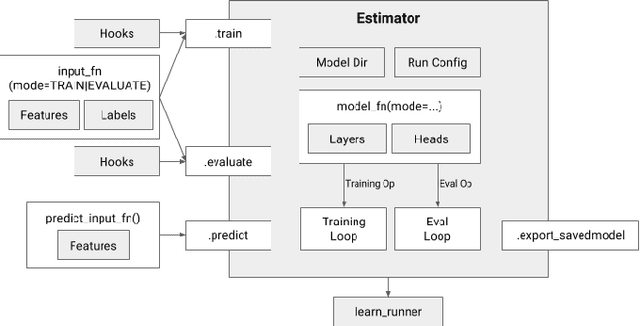
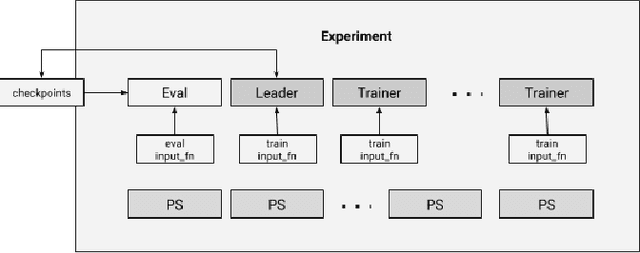
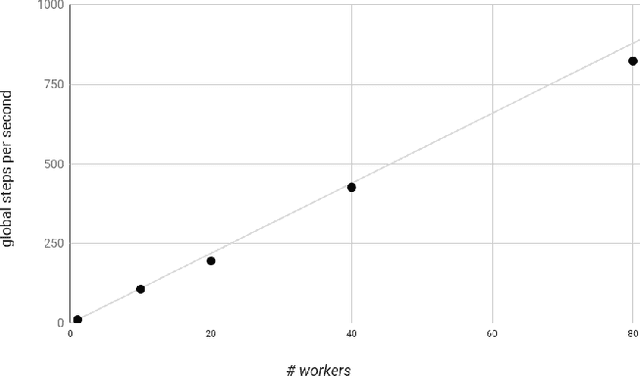
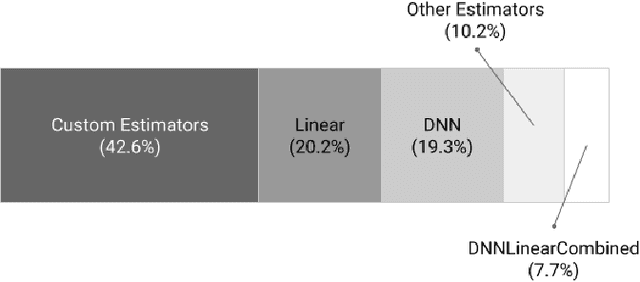
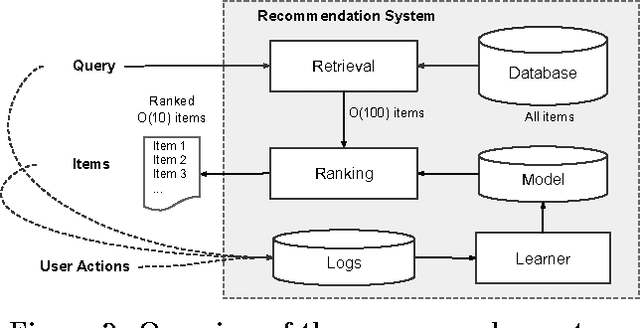
Abstract:We present a framework for specifying, training, evaluating, and deploying machine learning models. Our focus is on simplifying cutting edge machine learning for practitioners in order to bring such technologies into production. Recognizing the fast evolution of the field of deep learning, we make no attempt to capture the design space of all possible model architectures in a domain- specific language (DSL) or similar configuration language. We allow users to write code to define their models, but provide abstractions that guide develop- ers to write models in ways conducive to productionization. We also provide a unifying Estimator interface, making it possible to write downstream infrastructure (e.g. distributed training, hyperparameter tuning) independent of the model implementation. We balance the competing demands for flexibility and simplicity by offering APIs at different levels of abstraction, making common model architectures available out of the box, while providing a library of utilities designed to speed up experimentation with model architectures. To make out of the box models flexible and usable across a wide range of problems, these canned Estimators are parameterized not only over traditional hyperparameters, but also using feature columns, a declarative specification describing how to interpret input data. We discuss our experience in using this framework in re- search and production environments, and show the impact on code health, maintainability, and development speed.
Wide & Deep Learning for Recommender Systems
Jun 24, 2016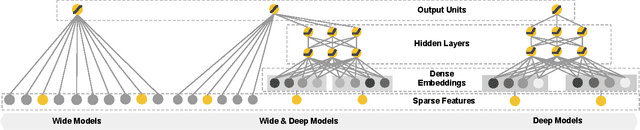
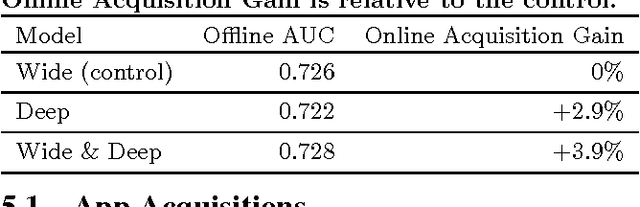

Abstract:Generalized linear models with nonlinear feature transformations are widely used for large-scale regression and classification problems with sparse inputs. Memorization of feature interactions through a wide set of cross-product feature transformations are effective and interpretable, while generalization requires more feature engineering effort. With less feature engineering, deep neural networks can generalize better to unseen feature combinations through low-dimensional dense embeddings learned for the sparse features. However, deep neural networks with embeddings can over-generalize and recommend less relevant items when the user-item interactions are sparse and high-rank. In this paper, we present Wide & Deep learning---jointly trained wide linear models and deep neural networks---to combine the benefits of memorization and generalization for recommender systems. We productionized and evaluated the system on Google Play, a commercial mobile app store with over one billion active users and over one million apps. Online experiment results show that Wide & Deep significantly increased app acquisitions compared with wide-only and deep-only models. We have also open-sourced our implementation in TensorFlow.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge