Georgios Roumpos
Modeling Information Need of Users in Search Sessions
Jan 03, 2020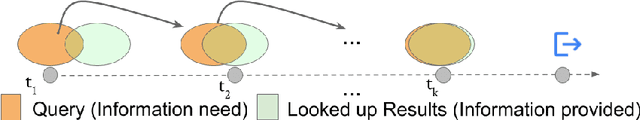
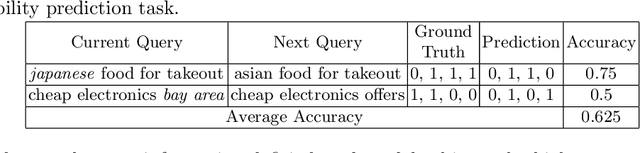

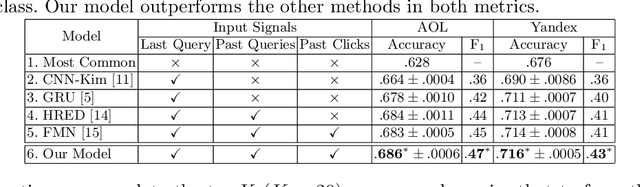
Abstract:Users issue queries to Search Engines, and try to find the desired information in the results produced. They repeat this process if their information need is not met at the first place. It is crucial to identify the important words in a query that depict the actual information need of the user and will determine the course of a search session. To this end, we propose a sequence-to-sequence based neural architecture that leverages the set of past queries issued by users, and results that were explored by them. Firstly, we employ our model for predicting the words in the current query that are important and would be retained in the next query. Additionally, as a downstream application of our model, we evaluate it on the widely popular task of next query suggestion. We show that our intuitive strategy of capturing information need can yield superior performance at these tasks on two large real-world search log datasets.
TensorFlow Estimators: Managing Simplicity vs. Flexibility in High-Level Machine Learning Frameworks
Aug 08, 2017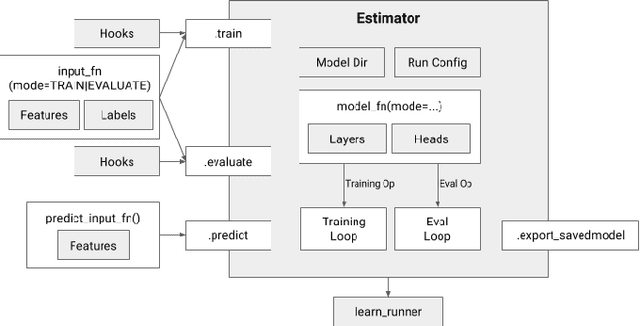
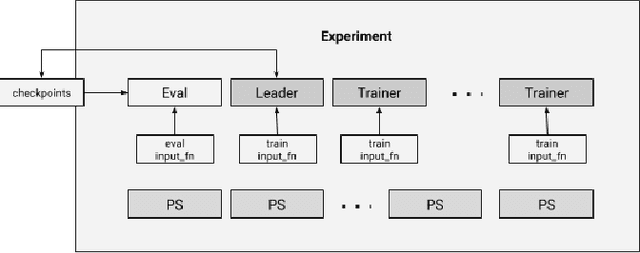
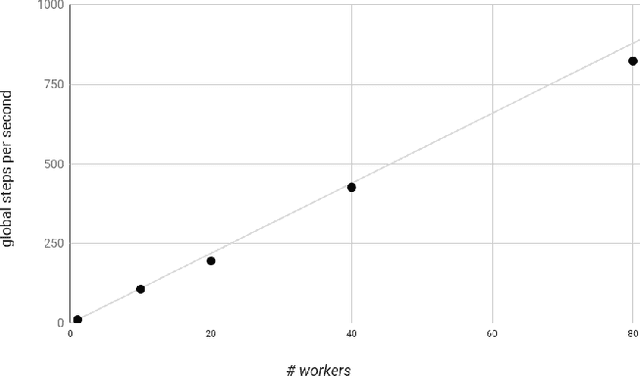
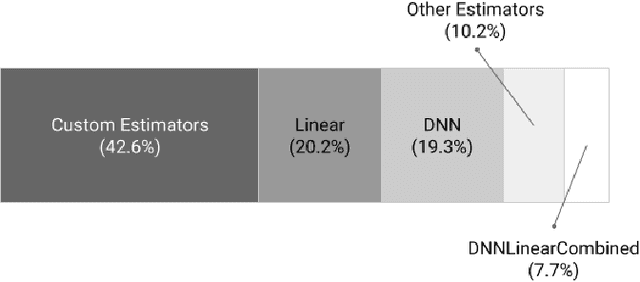
Abstract:We present a framework for specifying, training, evaluating, and deploying machine learning models. Our focus is on simplifying cutting edge machine learning for practitioners in order to bring such technologies into production. Recognizing the fast evolution of the field of deep learning, we make no attempt to capture the design space of all possible model architectures in a domain- specific language (DSL) or similar configuration language. We allow users to write code to define their models, but provide abstractions that guide develop- ers to write models in ways conducive to productionization. We also provide a unifying Estimator interface, making it possible to write downstream infrastructure (e.g. distributed training, hyperparameter tuning) independent of the model implementation. We balance the competing demands for flexibility and simplicity by offering APIs at different levels of abstraction, making common model architectures available out of the box, while providing a library of utilities designed to speed up experimentation with model architectures. To make out of the box models flexible and usable across a wide range of problems, these canned Estimators are parameterized not only over traditional hyperparameters, but also using feature columns, a declarative specification describing how to interpret input data. We discuss our experience in using this framework in re- search and production environments, and show the impact on code health, maintainability, and development speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge