Yuxuan Tang
TheAgentCompany: Benchmarking LLM Agents on Consequential Real World Tasks
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:We interact with computers on an everyday basis, be it in everyday life or work, and many aspects of work can be done entirely with access to a computer and the Internet. At the same time, thanks to improvements in large language models (LLMs), there has also been a rapid development in AI agents that interact with and affect change in their surrounding environments. But how performant are AI agents at helping to accelerate or even autonomously perform work-related tasks? The answer to this question has important implications for both industry looking to adopt AI into their workflows, and for economic policy to understand the effects that adoption of AI may have on the labor market. To measure the progress of these LLM agents' performance on performing real-world professional tasks, in this paper, we introduce TheAgentCompany, an extensible benchmark for evaluating AI agents that interact with the world in similar ways to those of a digital worker: by browsing the Web, writing code, running programs, and communicating with other coworkers. We build a self-contained environment with internal web sites and data that mimics a small software company environment, and create a variety of tasks that may be performed by workers in such a company. We test baseline agents powered by both closed API-based and open-weights language models (LMs), and find that with the most competitive agent, 24% of the tasks can be completed autonomously. This paints a nuanced picture on task automation with LM agents -- in a setting simulating a real workplace, a good portion of simpler tasks could be solved autonomously, but more difficult long-horizon tasks are still beyond the reach of current systems.
DMF-Net: Image-Guided Point Cloud Completion with Dual-Channel Modality Fusion and Shape-Aware Upsampling Transformer
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we study the task of a single-view image-guided point cloud completion. Existing methods have got promising results by fusing the information of image into point cloud explicitly or implicitly. However, given that the image has global shape information and the partial point cloud has rich local details, We believe that both modalities need to be given equal attention when performing modality fusion. To this end, we propose a novel dual-channel modality fusion network for image-guided point cloud completion(named DMF-Net), in a coarse-to-fine manner. In the first stage, DMF-Net takes a partial point cloud and corresponding image as input to recover a coarse point cloud. In the second stage, the coarse point cloud will be upsampled twice with shape-aware upsampling transformer to get the dense and complete point cloud. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experimental results show that DMF-Net outperforms the state-of-the-art unimodal and multimodal point cloud completion works on ShapeNet-ViPC dataset.
On A Mallows-type Model For Choices
Jul 05, 2022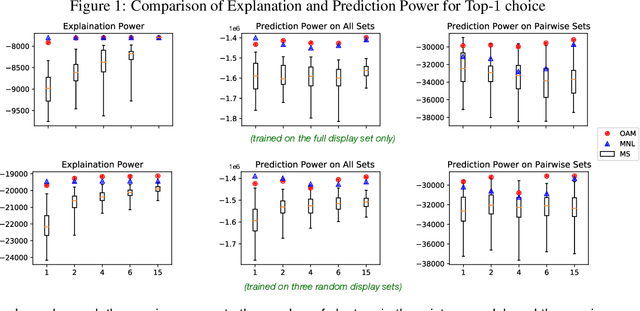

Abstract:In a preference learning setting, every participant chooses an ordered list of $k$ most preferred items among a displayed set of candidates. (The set can be different for every participant.) We identify a distance-based ranking model for the population's preferences and their (ranked) choice behavior. The ranking model resembles the Mallows model but uses a new distance function called Reverse Major Index (RMJ). We find that despite the need to sum over all permutations, the RMJ-based ranking distribution aggregates into (ranked) choice probabilities with simple closed-form expression. We develop effective methods to estimate the model parameters and showcase their generalization power using real data, especially when there is a limited variety of display sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge