Yunzhe Wang
GraphAllocBench: A Flexible Benchmark for Preference-Conditioned Multi-Objective Policy Learning
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Preference-Conditioned Policy Learning (PCPL) in Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning (MORL) aims to approximate diverse Pareto-optimal solutions by conditioning policies on user-specified preferences over objectives. This enables a single model to flexibly adapt to arbitrary trade-offs at run-time by producing a policy on or near the Pareto front. However, existing benchmarks for PCPL are largely restricted to toy tasks and fixed environments, limiting their realism and scalability. To address this gap, we introduce GraphAllocBench, a flexible benchmark built on a novel graph-based resource allocation sandbox environment inspired by city management, which we call CityPlannerEnv. GraphAllocBench provides a rich suite of problems with diverse objective functions, varying preference conditions, and high-dimensional scalability. We also propose two new evaluation metrics -- Proportion of Non-Dominated Solutions (PNDS) and Ordering Score (OS) -- that directly capture preference consistency while complementing the widely used hypervolume metric. Through experiments with Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) and graph-aware models, we show that GraphAllocBench exposes the limitations of existing MORL approaches and paves the way for using graph-based methods such as Graph Neural Networks in complex, high-dimensional combinatorial allocation tasks. Beyond its predefined problem set, GraphAllocBench enables users to flexibly vary objectives, preferences, and allocation rules, establishing it as a versatile and extensible benchmark for advancing PCPL. Code: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/GraphAllocBench
X-Ego: Acquiring Team-Level Tactical Situational Awareness via Cross-Egocentric Contrastive Video Representation Learning
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Human team tactics emerge from each player's individual perspective and their ability to anticipate, interpret, and adapt to teammates' intentions. While advances in video understanding have improved the modeling of team interactions in sports, most existing work relies on third-person broadcast views and overlooks the synchronous, egocentric nature of multi-agent learning. We introduce X-Ego-CS, a benchmark dataset consisting of 124 hours of gameplay footage from 45 professional-level matches of the popular e-sports game Counter-Strike 2, designed to facilitate research on multi-agent decision-making in complex 3D environments. X-Ego-CS provides cross-egocentric video streams that synchronously capture all players' first-person perspectives along with state-action trajectories. Building on this resource, we propose Cross-Ego Contrastive Learning (CECL), which aligns teammates' egocentric visual streams to foster team-level tactical situational awareness from an individual's perspective. We evaluate CECL on a teammate-opponent location prediction task, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing an agent's ability to infer both teammate and opponent positions from a single first-person view using state-of-the-art video encoders. Together, X-Ego-CS and CECL establish a foundation for cross-egocentric multi-agent benchmarking in esports. More broadly, our work positions gameplay understanding as a testbed for multi-agent modeling and tactical learning, with implications for spatiotemporal reasoning and human-AI teaming in both virtual and real-world domains. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/HATS-ICT/x-ego.
Abstracting Geo-specific Terrains to Scale Up Reinforcement Learning
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) is increasingly ubiquitous in training dynamic and adaptive synthetic characters for interactive simulations on geo-specific terrains. Frameworks such as Unity's ML-Agents help to make such reinforcement learning experiments more accessible to the simulation community. Military training simulations also benefit from advances in MARL, but they have immense computational requirements due to their complex, continuous, stochastic, partially observable, non-stationary, and doctrine-based nature. Furthermore, these simulations require geo-specific terrains, further exacerbating the computational resources problem. In our research, we leverage Unity's waypoints to automatically generate multi-layered representation abstractions of the geo-specific terrains to scale up reinforcement learning while still allowing the transfer of learned policies between different representations. Our early exploratory results on a novel MARL scenario, where each side has differing objectives, indicate that waypoint-based navigation enables faster and more efficient learning while producing trajectories similar to those taken by expert human players in CSGO gaming environments. This research points out the potential of waypoint-based navigation for reducing the computational costs of developing and training MARL models for military training simulations, where geo-specific terrains and differing objectives are crucial.
Reconfigurable Robot Identification from Motion Data
Mar 15, 2024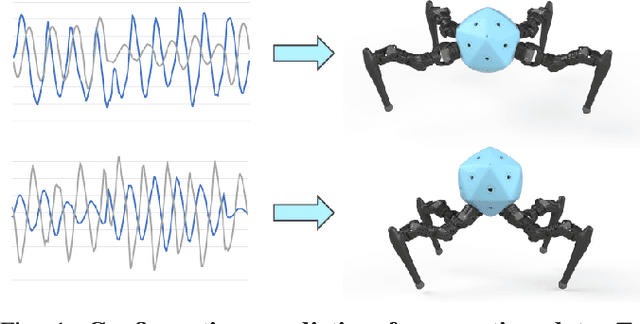
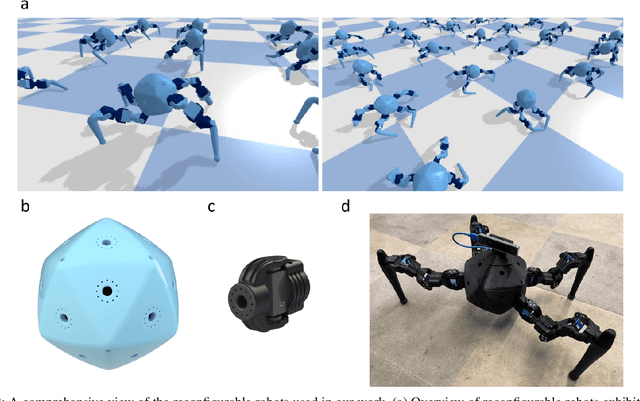
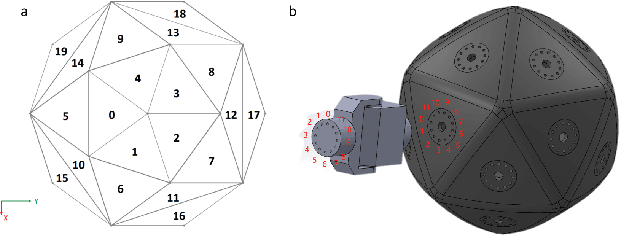
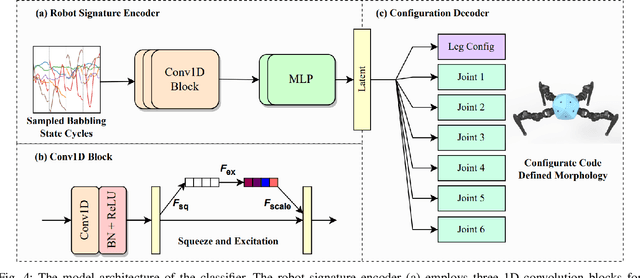
Abstract:Integrating Large Language Models (VLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) with robotic systems enables robots to process and understand complex natural language instructions and visual information. However, a fundamental challenge remains: for robots to fully capitalize on these advancements, they must have a deep understanding of their physical embodiment. The gap between AI models cognitive capabilities and the understanding of physical embodiment leads to the following question: Can a robot autonomously understand and adapt to its physical form and functionalities through interaction with its environment? This question underscores the transition towards developing self-modeling robots without reliance on external sensory or pre-programmed knowledge about their structure. Here, we propose a meta self modeling that can deduce robot morphology through proprioception (the internal sense of position and movement). Our study introduces a 12 DoF reconfigurable legged robot, accompanied by a diverse dataset of 200k unique configurations, to systematically investigate the relationship between robotic motion and robot morphology. Utilizing a deep neural network model comprising a robot signature encoder and a configuration decoder, we demonstrate the capability of our system to accurately predict robot configurations from proprioceptive signals. This research contributes to the field of robotic self-modeling, aiming to enhance understanding of their physical embodiment and adaptability in real world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge