Yunlong Gao
Learning Actionable World Models for Industrial Process Control
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:To go from (passive) process monitoring to active process control, an effective AI system must learn about the behavior of the complex system from very limited training data, forming an ad-hoc digital twin with respect to process in- and outputs that captures the consequences of actions on the process's world. We propose a novel methodology based on learning world models that disentangles process parameters in the learned latent representation, allowing for fine-grained control. Representation learning is driven by the latent factors that influence the processes through contrastive learning within a joint embedding predictive architecture. This makes changes in representations predictable from changes in inputs and vice versa, facilitating interpretability of key factors responsible for process variations, paving the way for effective control actions to keep the process within operational bounds. The effectiveness of our method is validated on the example of plastic injection molding, demonstrating practical relevance in proposing specific control actions for a notoriously unstable process.
Improve Meta-learning for Few-Shot Text Classification with All You Can Acquire from the Tasks
Oct 14, 2024
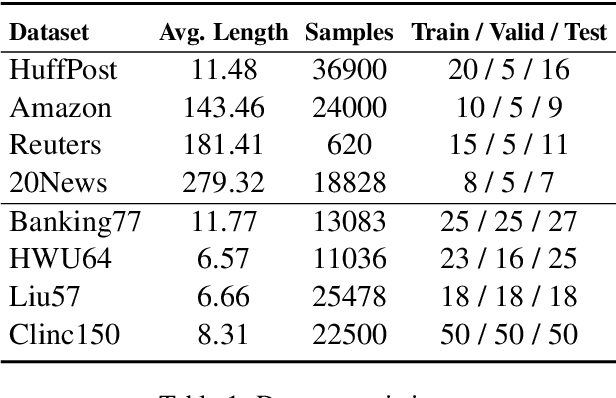

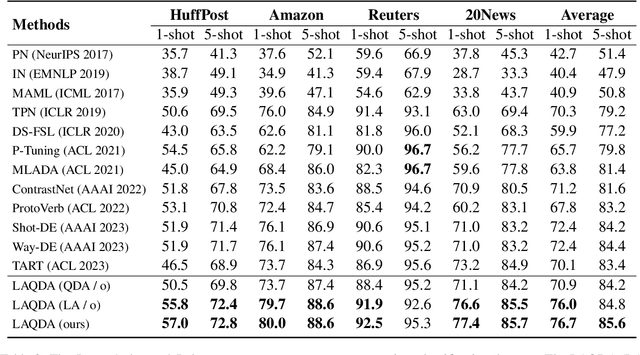
Abstract:Meta-learning has emerged as a prominent technology for few-shot text classification and has achieved promising performance. However, existing methods often encounter difficulties in drawing accurate class prototypes from support set samples, primarily due to probable large intra-class differences and small inter-class differences within the task. Recent approaches attempt to incorporate external knowledge or pre-trained language models to augment data, but this requires additional resources and thus does not suit many few-shot scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel solution to address this issue by adequately leveraging the information within the task itself. Specifically, we utilize label information to construct a task-adaptive metric space, thereby adaptively reducing the intra-class differences and magnifying the inter-class differences. We further employ the optimal transport technique to estimate class prototypes with query set samples together, mitigating the problem of inaccurate and ambiguous support set samples caused by large intra-class differences. We conduct extensive experiments on eight benchmark datasets, and our approach shows obvious advantages over state-of-the-art models across all the tasks on all the datasets. For reproducibility, all the datasets and codes are available at https://github.com/YvoGao/LAQDA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge