Yujing Liu
Dr. Assistant: Enhancing Clinical Diagnostic Inquiry via Structured Diagnostic Reasoning Data and Reinforcement Learning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSSs) provide reasoning and inquiry guidance for physicians, yet they face notable challenges, including high maintenance costs and low generalization capability. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have been widely adopted in healthcare due to their extensive knowledge reserves, retrieval, and communication capabilities. While LLMs show promise and excel at medical benchmarks, their diagnostic reasoning and inquiry skills are constrained. To mitigate this issue, we propose (1) Clinical Diagnostic Reasoning Data (CDRD) structure to capture abstract clinical reasoning logic, and a pipeline for its construction, and (2) the Dr. Assistant, a clinical diagnostic model equipped with clinical reasoning and inquiry skills. Its training involves a two-stage process: SFT, followed by RL with a tailored reward function. We also introduce a benchmark to evaluate both diagnostic reasoning and inquiry. Our experiments demonstrate that the Dr. Assistant outperforms open-source models and achieves competitive performance to closed-source models, providing an effective solution for clinical diagnostic inquiry guidance.
Noisy Node Classification by Bi-level Optimization based Multi-teacher Distillation
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:Previous graph neural networks (GNNs) usually assume that the graph data is with clean labels for representation learning, but it is not true in real applications. In this paper, we propose a new multi-teacher distillation method based on bi-level optimization (namely BO-NNC), to conduct noisy node classification on the graph data. Specifically, we first employ multiple self-supervised learning methods to train diverse teacher models, and then aggregate their predictions through a teacher weight matrix. Furthermore, we design a new bi-level optimization strategy to dynamically adjust the teacher weight matrix based on the training progress of the student model. Finally, we design a label improvement module to improve the label quality. Extensive experimental results on real datasets show that our method achieves the best results compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Adaptive Multi-Modality Prompt Learning
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:Although current prompt learning methods have successfully been designed to effectively reuse the large pre-trained models without fine-tuning their large number of parameters, they still have limitations to be addressed, i.e., without considering the adverse impact of meaningless patches in every image and without simultaneously considering in-sample generalization and out-of-sample generalization. In this paper, we propose an adaptive multi-modality prompt learning to address the above issues. To do this, we employ previous text prompt learning and propose a new image prompt learning. The image prompt learning achieves in-sample and out-of-sample generalization, by first masking meaningless patches and then padding them with the learnable parameters and the information from texts. Moreover, each of the prompts provides auxiliary information to each other, further strengthening these two kinds of generalization. Experimental results on real datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms SOTA methods, in terms of different downstream tasks.
Global Convergence of Online Identification for Mixed Linear Regression
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Mixed linear regression (MLR) is a powerful model for characterizing nonlinear relationships by utilizing a mixture of linear regression sub-models. The identification of MLR is a fundamental problem, where most of the existing results focus on offline algorithms, rely on independent and identically distributed (i.i.d) data assumptions, and provide local convergence results only. This paper investigates the online identification and data clustering problems for two basic classes of MLRs, by introducing two corresponding new online identification algorithms based on the expectation-maximization (EM) principle. It is shown that both algorithms will converge globally without resorting to the traditional i.i.d data assumptions. The main challenge in our investigation lies in the fact that the gradient of the maximum likelihood function does not have a unique zero, and a key step in our analysis is to establish the stability of the corresponding differential equation in order to apply the celebrated Ljung's ODE method. It is also shown that the within-cluster error and the probability that the new data is categorized into the correct cluster are asymptotically the same as those in the case of known parameters. Finally, numerical simulations are provided to verify the effectiveness of our online algorithms.
Toward Automated Virtual Assembly for Prefabricated Construction: Construction Sequencing through Simulated BIM
Mar 14, 2020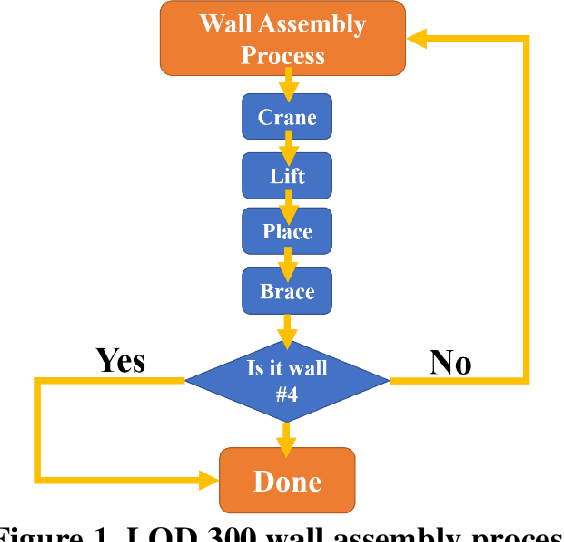
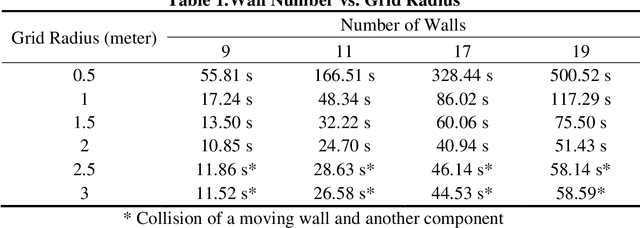
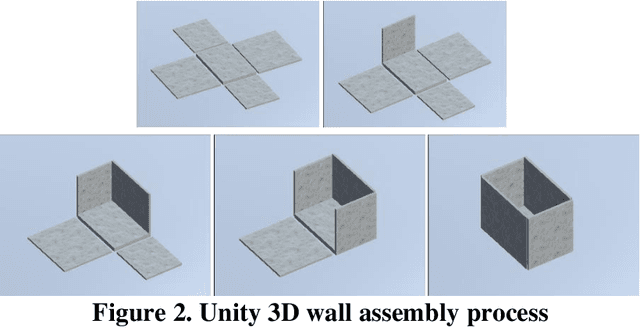
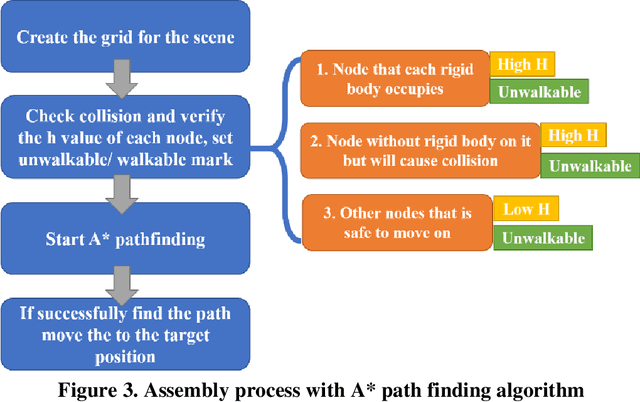
Abstract:To adhere to the stringent time and budget requirements of construction projects, contractors are utilizing prefabricated construction methods to expedite the construction process. Prefabricated construction methods require an adequate schedule and understanding by the contractors and constructors to be successful. The specificity of prefabricated construction often leads to inefficient scheduling and costly rework time. The designer, contractor, and constructors must have a strong understanding of the assembly process to experience the full benefits of the method. At the root of understanding the assembly process is visualizing how the process is intended to be performed. Currently, a virtual construction model is used to explain and better visualize the construction process. However, creating a virtual construction model is currently time consuming and requires experienced personnel. The proposed simulation of the virtual assembly will increase the automation of virtual construction modeling by implementing the data available in a building information modeling (BIM) model. This paper presents various factors (i.e., formalization of construction sequence based on the level of development (LOD)) that needs to be addressed for the development of automated virtual assembly. Two case studies are presented to demonstrate these factors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge