Yuhang Tian
ActiShade: Activating Overshadowed Knowledge to Guide Multi-Hop Reasoning in Large Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:In multi-hop reasoning, multi-round retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) methods typically rely on LLM-generated content as the retrieval query. However, these approaches are inherently vulnerable to knowledge overshadowing - a phenomenon where critical information is overshadowed during generation. As a result, the LLM-generated content may be incomplete or inaccurate, leading to irrelevant retrieval and causing error accumulation during the iteration process. To address this challenge, we propose ActiShade, which detects and activates overshadowed knowledge to guide large language models (LLMs) in multi-hop reasoning. Specifically, ActiShade iteratively detects the overshadowed keyphrase in the given query, retrieves documents relevant to both the query and the overshadowed keyphrase, and generates a new query based on the retrieved documents to guide the next-round iteration. By supplementing the overshadowed knowledge during the formulation of next-round queries while minimizing the introduction of irrelevant noise, ActiShade reduces the error accumulation caused by knowledge overshadowing. Extensive experiments show that ActiShade outperforms existing methods across multiple datasets and LLMs.
Overview of the NLPCC 2025 Shared Task 4: Multi-modal, Multilingual, and Multi-hop Medical Instructional Video Question Answering Challenge
May 11, 2025Abstract:Following the successful hosts of the 1-st (NLPCC 2023 Foshan) CMIVQA and the 2-rd (NLPCC 2024 Hangzhou) MMIVQA challenges, this year, a new task has been introduced to further advance research in multi-modal, multilingual, and multi-hop medical instructional question answering (M4IVQA) systems, with a specific focus on medical instructional videos. The M4IVQA challenge focuses on evaluating models that integrate information from medical instructional videos, understand multiple languages, and answer multi-hop questions requiring reasoning over various modalities. This task consists of three tracks: multi-modal, multilingual, and multi-hop Temporal Answer Grounding in Single Video (M4TAGSV), multi-modal, multilingual, and multi-hop Video Corpus Retrieval (M4VCR) and multi-modal, multilingual, and multi-hop Temporal Answer Grounding in Video Corpus (M4TAGVC). Participants in M4IVQA are expected to develop algorithms capable of processing both video and text data, understanding multilingual queries, and providing relevant answers to multi-hop medical questions. We believe the newly introduced M4IVQA challenge will drive innovations in multimodal reasoning systems for healthcare scenarios, ultimately contributing to smarter emergency response systems and more effective medical education platforms in multilingual communities. Our official website is https://cmivqa.github.io/
RefineCoder: Iterative Improving of Large Language Models via Adaptive Critique Refinement for Code Generation
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Code generation has attracted increasing attention with the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs). Many studies have developed powerful code LLMs by synthesizing code-related instruction data and applying supervised fine-tuning. However, these methods are limited by teacher model distillation and ignore the potential of iterative refinement by self-generated code. In this paper, we propose Adaptive Critique Refinement (ACR), which enables the model to refine itself by self-generated code and external critique, rather than directly imitating the code responses of the teacher model. Concretely, ACR includes a composite scoring system with LLM-as-a-Judge to evaluate the quality of code responses and a selective critique strategy with LLM-as-a-Critic to critique self-generated low-quality code responses. We develop the RefineCoder series by iteratively applying ACR, achieving continuous performance improvement on multiple code generation benchmarks. Compared to the baselines of the same size, our proposed RefineCoder series can achieve comparable or even superior performance using less data.
FLVoogd: Robust And Privacy Preserving Federated Learning
Jun 24, 2022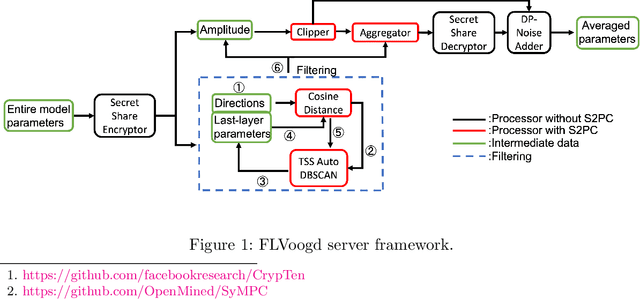


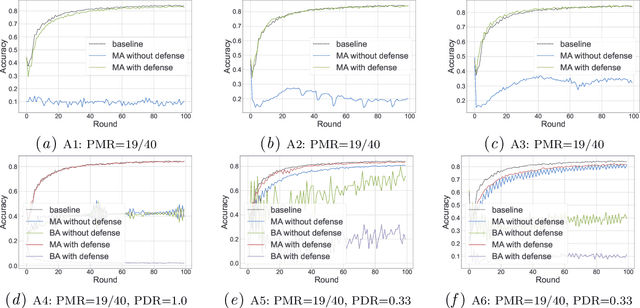
Abstract:In this work, we propose FLVoogd, an updated federated learning method in which servers and clients collaboratively eliminate Byzantine attacks while preserving privacy. In particular, servers use automatic Density-based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) combined with S2PC to cluster the benign majority without acquiring sensitive personal information. Meanwhile, clients build dual models and perform test-based distance controlling to adjust their local models toward the global one to achieve personalizing. Our framework is automatic and adaptive that servers/clients don't need to tune the parameters during the training. In addition, our framework leverages Secure Multi-party Computation (SMPC) operations, including multiplications, additions, and comparison, where costly operations, like division and square root, are not required. Evaluations are carried out on some conventional datasets from the image classification field. The result shows that FLVoogd can effectively reject malicious uploads in most scenarios; meanwhile, it avoids data leakage from the server-side.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge