Yuehe Chen
Divide-Then-Align: Honest Alignment based on the Knowledge Boundary of RAG
May 27, 2025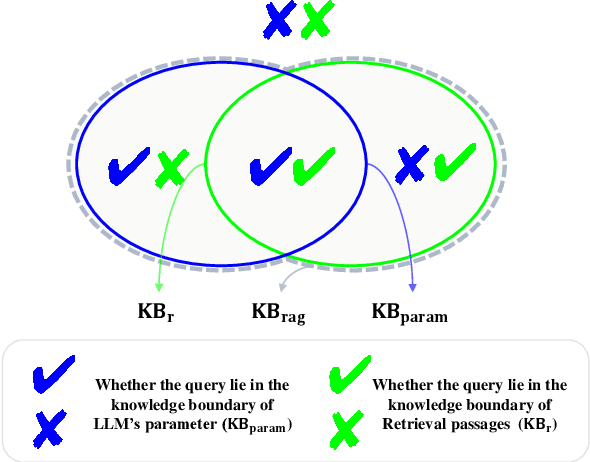
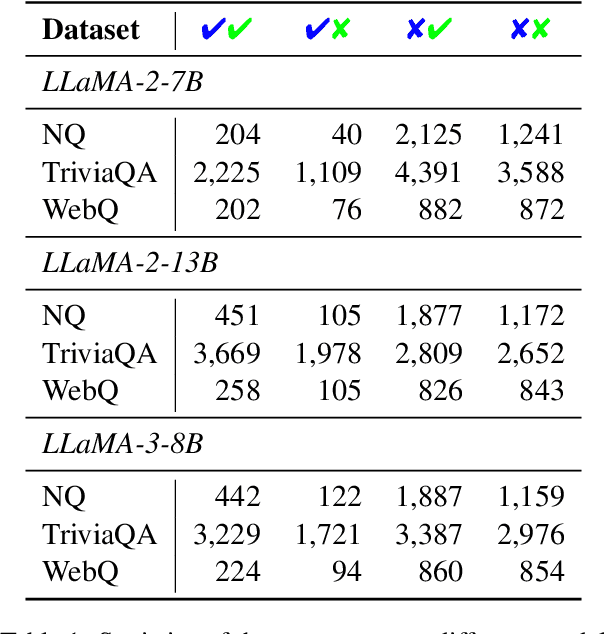
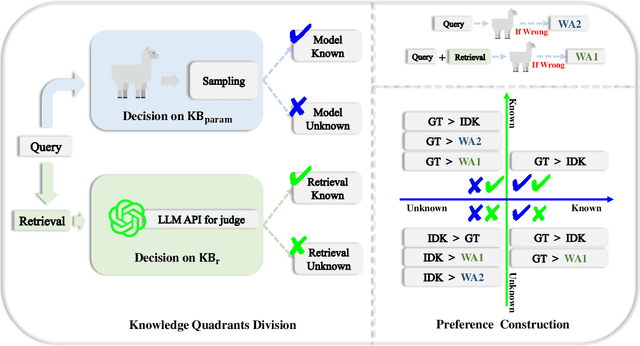
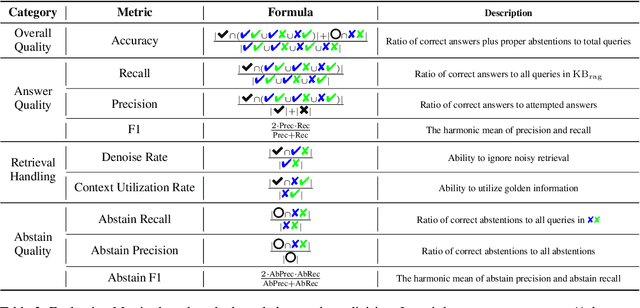
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) augmented with retrieval systems have significantly advanced natural language processing tasks by integrating external knowledge sources, enabling more accurate and contextually rich responses. To improve the robustness of such systems against noisy retrievals, Retrieval-Augmented Fine-Tuning (RAFT) has emerged as a widely adopted method. However, RAFT conditions models to generate answers even in the absence of reliable knowledge. This behavior undermines their reliability in high-stakes domains, where acknowledging uncertainty is critical. To address this issue, we propose Divide-Then-Align (DTA), a post-training approach designed to endow RAG systems with the ability to respond with "I don't know" when the query is out of the knowledge boundary of both the retrieved passages and the model's internal knowledge. DTA divides data samples into four knowledge quadrants and constructs tailored preference data for each quadrant, resulting in a curated dataset for Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). Experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that DTA effectively balances accuracy with appropriate abstention, enhancing the reliability and trustworthiness of retrieval-augmented systems.
Revisiting Modularity Maximization for Graph Clustering: A Contrastive Learning Perspective
Jun 20, 2024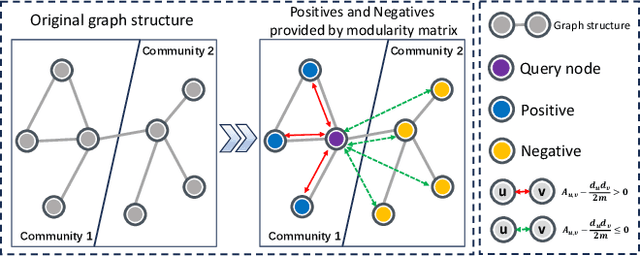
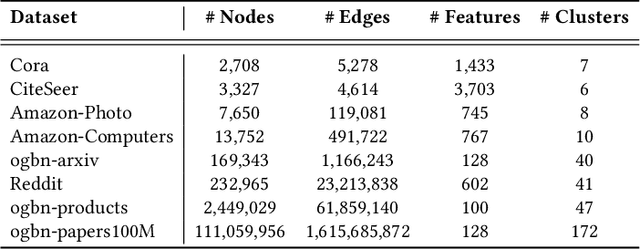
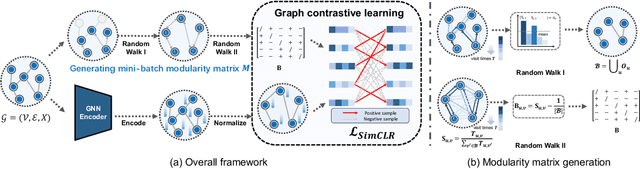
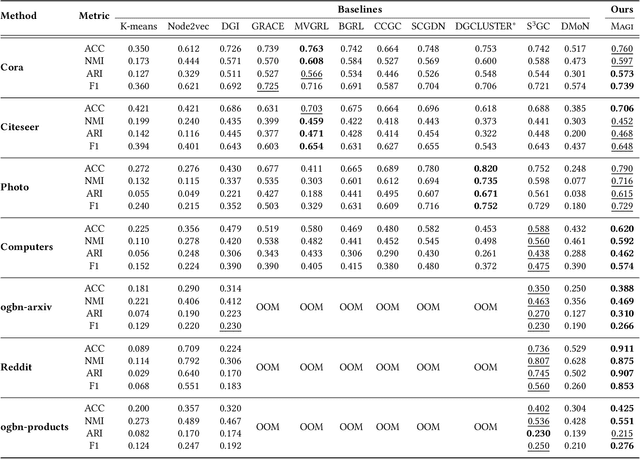
Abstract:Graph clustering, a fundamental and challenging task in graph mining, aims to classify nodes in a graph into several disjoint clusters. In recent years, graph contrastive learning (GCL) has emerged as a dominant line of research in graph clustering and advances the new state-of-the-art. However, GCL-based methods heavily rely on graph augmentations and contrastive schemes, which may potentially introduce challenges such as semantic drift and scalability issues. Another promising line of research involves the adoption of modularity maximization, a popular and effective measure for community detection, as the guiding principle for clustering tasks. Despite the recent progress, the underlying mechanism of modularity maximization is still not well understood. In this work, we dig into the hidden success of modularity maximization for graph clustering. Our analysis reveals the strong connections between modularity maximization and graph contrastive learning, where positive and negative examples are naturally defined by modularity. In light of our results, we propose a community-aware graph clustering framework, coined MAGI, which leverages modularity maximization as a contrastive pretext task to effectively uncover the underlying information of communities in graphs, while avoiding the problem of semantic drift. Extensive experiments on multiple graph datasets verify the effectiveness of MAGI in terms of scalability and clustering performance compared to state-of-the-art graph clustering methods. Notably, MAGI easily scales a sufficiently large graph with 100M nodes while outperforming strong baselines.
Make a Choice! Knowledge Base Question Answering with In-Context Learning
May 23, 2023



Abstract:Question answering over knowledge bases (KBQA) aims to answer factoid questions with a given knowledge base (KB). Due to the large scale of KB, annotated data is impossible to cover all fact schemas in KB, which poses a challenge to the generalization ability of methods that require a sufficient amount of annotated data. Recently, LLMs have shown strong few-shot performance in many NLP tasks. We expect LLM can help existing methods improve their generalization ability, especially in low-resource situations. In this paper, we present McL-KBQA, a framework that incorporates the few-shot ability of LLM into the KBQA method via ICL-based multiple choice and then improves the effectiveness of the QA tasks. Experimental results on two KBQA datasets demonstrate the competitive performance of McL-KBQA with strong improvements in generalization. We expect to explore a new way to QA tasks from KBQA in conjunction with LLM, how to generate answers normatively and correctly with strong generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge