Yuan Fan
DPMLBench: Holistic Evaluation of Differentially Private Machine Learning
May 10, 2023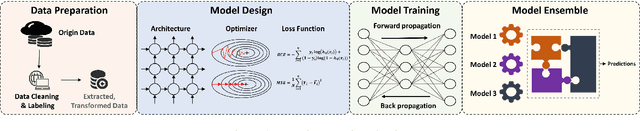
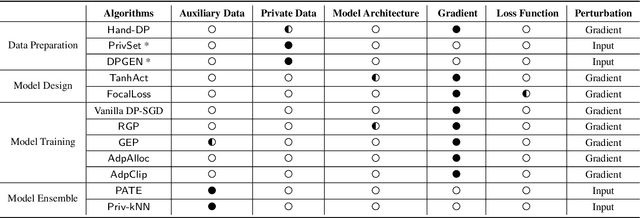
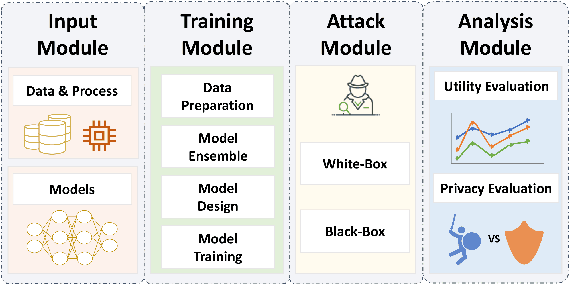
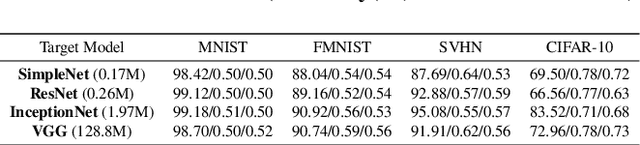
Abstract:Differential privacy (DP), as a rigorous mathematical definition quantifying privacy leakage, has become a well-accepted standard for privacy protection. Combined with powerful machine learning techniques, differentially private machine learning (DPML) is increasingly important. As the most classic DPML algorithm, DP-SGD incurs a significant loss of utility, which hinders DPML's deployment in practice. Many studies have recently proposed improved algorithms based on DP-SGD to mitigate utility loss. However, these studies are isolated and cannot comprehensively measure the performance of improvements proposed in algorithms. More importantly, there is a lack of comprehensive research to compare improvements in these DPML algorithms across utility, defensive capabilities, and generalizability. We fill this gap by performing a holistic measurement of improved DPML algorithms on utility and defense capability against membership inference attacks (MIAs) on image classification tasks. We first present a taxonomy of where improvements are located in the machine learning life cycle. Based on our taxonomy, we jointly perform an extensive measurement study of the improved DPML algorithms. We also cover state-of-the-art label differential privacy (Label DP) algorithms in the evaluation. According to our empirical results, DP can effectively defend against MIAs, and sensitivity-bounding techniques such as per-sample gradient clipping play an important role in defense. We also explore some improvements that can maintain model utility and defend against MIAs more effectively. Experiments show that Label DP algorithms achieve less utility loss but are fragile to MIAs. To support our evaluation, we implement a modular re-usable software, DPMLBench, which enables sensitive data owners to deploy DPML algorithms and serves as a benchmark tool for researchers and practitioners.
A Heterogeneous Graph Learning Model for Cyber-Attack Detection
Dec 16, 2021



Abstract:A cyber-attack is a malicious attempt by experienced hackers to breach the target information system. Usually, the cyber-attacks are characterized as hybrid TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures) and long-term adversarial behaviors, making the traditional intrusion detection methods ineffective. Most existing cyber-attack detection systems are implemented based on manually designed rules by referring to domain knowledge (e.g., threat models, threat intelligences). However, this process is lack of intelligence and generalization ability. Aiming at this limitation, this paper proposes an intelligent cyber-attack detection method based on provenance data. To effective and efficient detect cyber-attacks from a huge number of system events in the provenance data, we firstly model the provenance data by a heterogeneous graph to capture the rich context information of each system entities (e.g., process, file, socket, etc.), and learns a semantic vector representation for each system entity. Then, we perform online cyber-attack detection by sampling a small and compact local graph from the heterogeneous graph, and classifying the key system entities as malicious or benign. We conducted a series of experiments on two provenance datasets with real cyber-attacks. The experiment results show that the proposed method outperforms other learning based detection models, and has competitive performance against state-of-the-art rule based cyber-attack detection systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge