Yixin Yu
Personalized Clustering via Targeted Representation Learning
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Clustering traditionally aims to reveal a natural grouping structure model from unlabeled data. However, this model may not always align with users' preference. In this paper, we propose a personalized clustering method that explicitly performs targeted representation learning by interacting with users via modicum task information (e.g., $\textit{must-link}$ or $\textit{cannot-link}$ pairs) to guide the clustering direction. We query users with the most informative pairs, i.e., those pairs most hard to cluster and those most easy to miscluster, to facilitate the representation learning in terms of the clustering preference. Moreover, by exploiting attention mechanism, the targeted representation is learned and augmented. By leveraging the targeted representation and constrained constrastive loss as well, personalized clustering is obtained. Theoretically, we verify that the risk of personalized clustering is tightly bounded, guaranteeing that active queries to users do mitigate the clustering risk. Experimentally, extensive results show that our method performs well across different clustering tasks and datasets, even with a limited number of queries.
Multi-timescale Event Detection in Nonintrusive Load Monitoring based on MDL Principle
Nov 19, 2022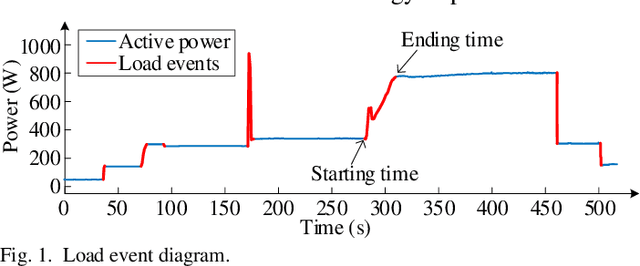
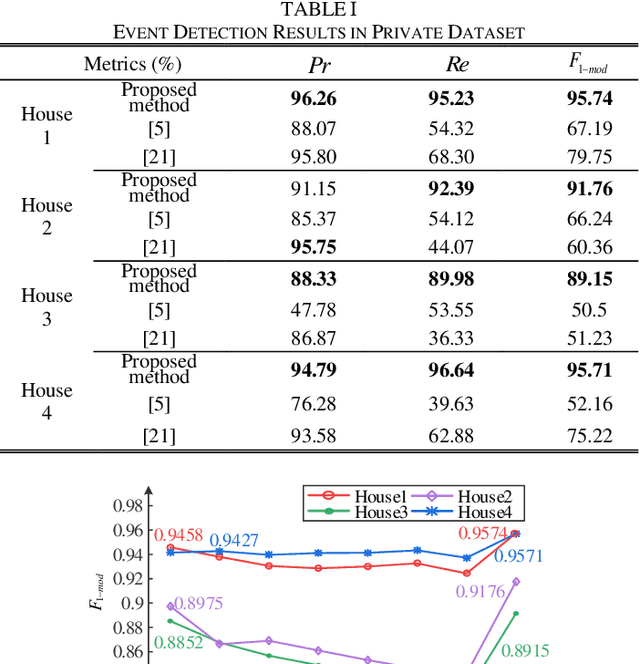
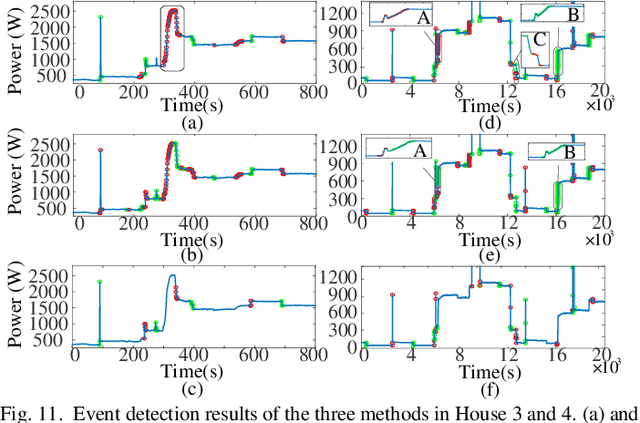
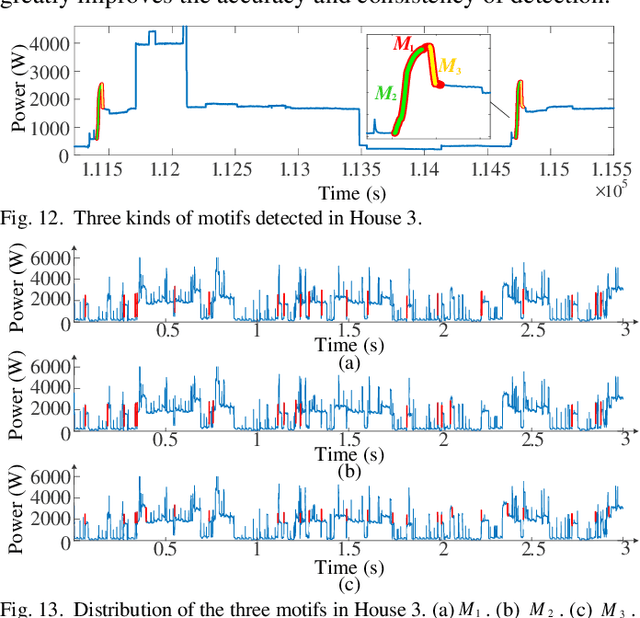
Abstract:Load event detection is the fundamental step for the event-based non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM). However, existing event detection methods with fixed parameters may fail in coping with the inherent multi-timescale characteristics of events and their event detection accuracy is easily affected by the load fluctuation. In this regard, this paper extends our previously designed two-stage event detection framework, and proposes a novel multi-timescale event detection method based on the principle of minimum description length (MDL). Following the completion of step-like event detection in the first stage, a long-transient event detection scheme with variable-length sliding window is designed for the second stage, which is intended to provide the observation and characterization of the same event at different time scales. In that, the context information in the aggregated load data is mined by motif discovery, and then based on the MDL principle, the proper observation scales are selected for different events and the corresponding detection results are determined. In the post-processing step, a load fluctuation location method based on voice activity detection (VAD) is proposed to identify and remove the unreasonable events caused by fluctuations. Based on newly proposed evaluation metrics, the comparison tests on public and private datasets demonstrate that our method achieves higher detection accuracy and integrity for events of various appliances across different scenarios.
Non-intrusive Load Monitoring based on Self-supervised Learning
Oct 09, 2022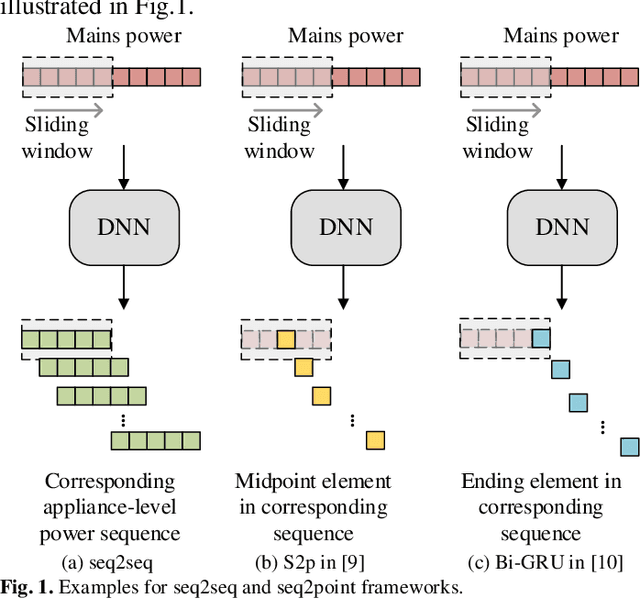
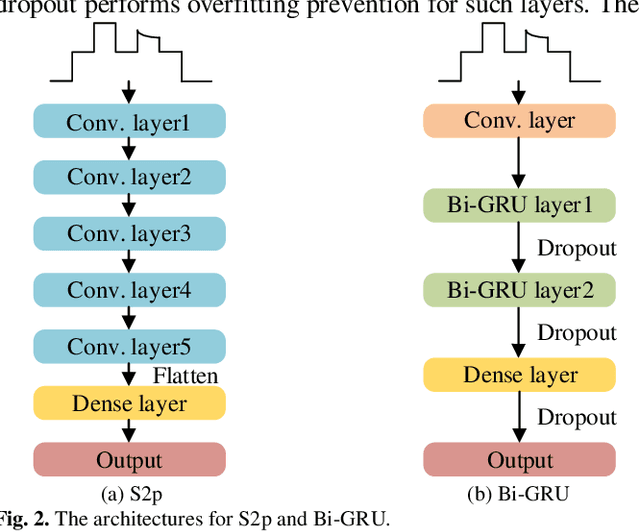
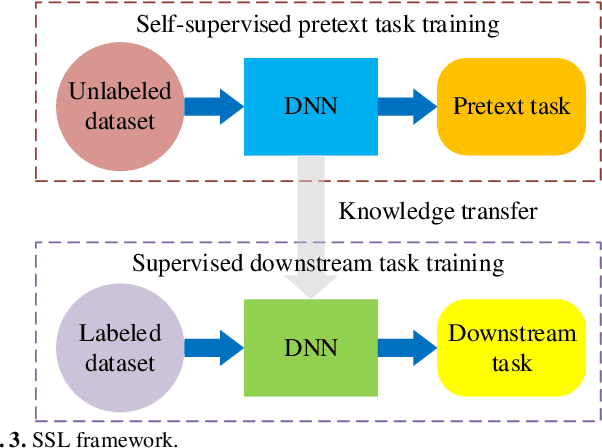
Abstract:Deep learning models for non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM) tend to require a large amount of labeled data for training. However, it is difficult to generalize the trained models to unseen sites due to different load characteristics and operating patterns of appliances between data sets. For addressing such problems, self-supervised learning (SSL) is proposed in this paper, where labeled appliance-level data from the target data set or house is not required. Initially, only the aggregate power readings from target data set are required to pre-train a general network via a self-supervised pretext task to map aggregate power sequences to derived representatives. Then, supervised downstream tasks are carried out for each appliance category to fine-tune the pre-trained network, where the features learned in the pretext task are transferred. Utilizing labeled source data sets enables the downstream tasks to learn how each load is disaggregated, by mapping the aggregate to labels. Finally, the fine-tuned network is applied to load disaggregation for the target sites. For validation, multiple experimental cases are designed based on three publicly accessible REDD, UK-DALE, and REFIT data sets. Besides, state-of-the-art neural networks are employed to perform NILM task in the experiments. Based on the NILM results in various cases, SSL generally outperforms zero-shot learning in improving load disaggregation performance without any sub-metering data from the target data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge