Yiren Liu
VicSim: Enhancing Victim Simulation with Emotional and Linguistic Fidelity
Jan 06, 2025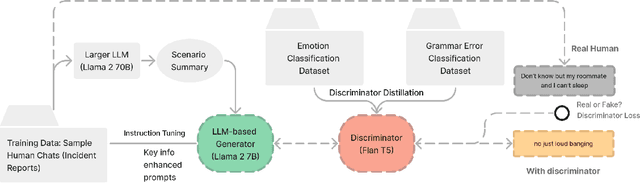



Abstract:Scenario-based training has been widely adopted in many public service sectors. Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in simulating diverse personas to create these training scenarios. However, little is known about how LLMs can be developed to simulate victims for scenario-based training purposes. In this paper, we introduce VicSim (victim simulator), a novel model that addresses three key dimensions of user simulation: informational faithfulness, emotional dynamics, and language style (e.g., grammar usage). We pioneer the integration of scenario-based victim modeling with GAN-based training workflow and key-information-based prompting, aiming to enhance the realism of simulated victims. Our adversarial training approach teaches the discriminator to recognize grammar and emotional cues as reliable indicators of synthetic content. According to evaluations by human raters, the VicSim model outperforms GPT-4 in terms of human-likeness.
Commonsense-Aware Prompting for Controllable Empathetic Dialogue Generation
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:Improving the emotional awareness of pre-trained language models is an emerging important problem for dialogue generation tasks. Although prior studies have introduced methods to improve empathetic dialogue generation, few have discussed how to incorporate commonsense knowledge into pre-trained language models for controllable dialogue generation. In this study, we propose a novel framework that improves empathetic dialogue generation using pre-trained language models by 1) incorporating commonsense knowledge through prompt verbalization, and 2) controlling dialogue generation using a strategy-driven future discriminator. We conducted experiments to reveal that both the incorporation of social commonsense knowledge and enforcement of control over generation help to improve generation performance. Finally, we discuss the implications of our study for future research.
KAER: A Knowledge Augmented Pre-Trained Language Model for Entity Resolution
Jan 12, 2023Abstract:Entity resolution has been an essential and well-studied task in data cleaning research for decades. Existing work has discussed the feasibility of utilizing pre-trained language models to perform entity resolution and achieved promising results. However, few works have discussed injecting domain knowledge to improve the performance of pre-trained language models on entity resolution tasks. In this study, we propose Knowledge Augmented Entity Resolution (KAER), a novel framework named for augmenting pre-trained language models with external knowledge for entity resolution. We discuss the results of utilizing different knowledge augmentation and prompting methods to improve entity resolution performance. Our model improves on Ditto, the existing state-of-the-art entity resolution method. In particular, 1) KAER performs more robustly and achieves better results on "dirty data", and 2) with more general knowledge injection, KAER outperforms the existing baseline models on the textual dataset and dataset from the online product domain. 3) KAER achieves competitive results on highly domain-specific datasets, such as citation datasets, requiring the injection of expert knowledge in future work.
E-commerce Query-based Generation based on User Review
Nov 11, 2020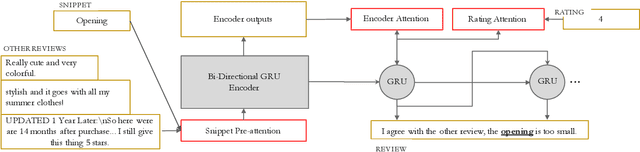
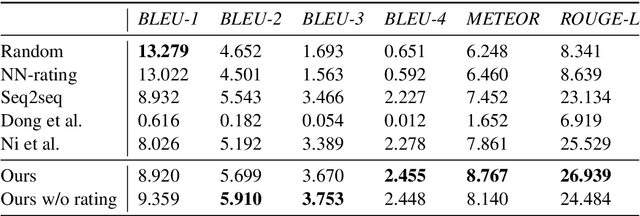
Abstract:With the increasing number of merchandise on e-commerce platforms, users tend to refer to reviews of other shoppers to decide which product they should buy. However, with so many reviews of a product, users often have to spend lots of time browsing through reviews talking about product attributes they do not care about. We want to establish a system that can automatically summarize and answer user's product specific questions. In this study, we propose a novel seq2seq based text generation model to generate answers to user's question based on reviews posted by previous users. Given a user question and/or target sentiment polarity, we extract aspects of interest and generate an answer that summarizes previous relevant user reviews. Specifically, our model performs attention between input reviews and target aspects during encoding and is conditioned on both review rating and input context during decoding. We also incorporate a pre-trained auxiliary rating classifier to improve model performance and accelerate convergence during training. Experiments using real-world e-commerce dataset show that our model achieves improvement in performance compared to previously introduced models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge