Yingzhuo Sun
Semantic Communications in 6G: Coexistence, Multiple Access, and Satellite Networks
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:The exponential growth of wireless users and bandwidth constraints necessitates innovative communication paradigms for next-generation networks. Semantic Communication (SemCom) emerges as a promising solution by transmitting extracted meaning rather than raw bits, enhancing spectral efficiency and enabling intelligent resource allocation. This paper explores the integration of SemCom with conventional Bit-based Communication (BitCom) in heterogeneous networks, highlighting key challenges and opportunities. We analyze multiple access techniques, including Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA), to support coexisting SemCom and BitCom users. Furthermore, we examine multi-modal SemCom frameworks for handling diverse data types and discuss their applications in satellite networks, where semantic techniques mitigate bandwidth limitations and harsh channel conditions. Finally, we identify future directions for deploying semantic-aware systems in 6G and beyond.
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: Channel characterization and modeling
Jun 06, 2022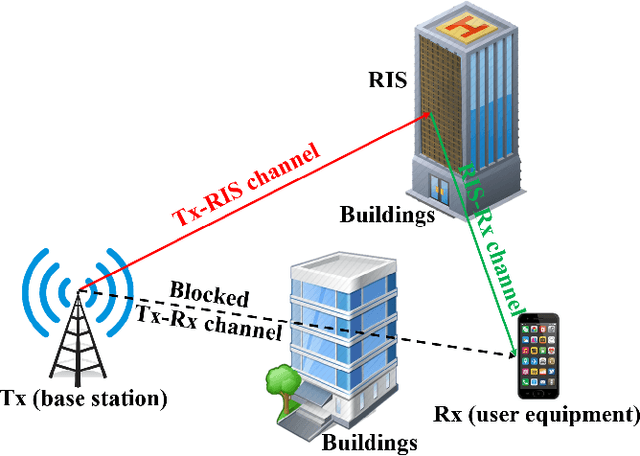
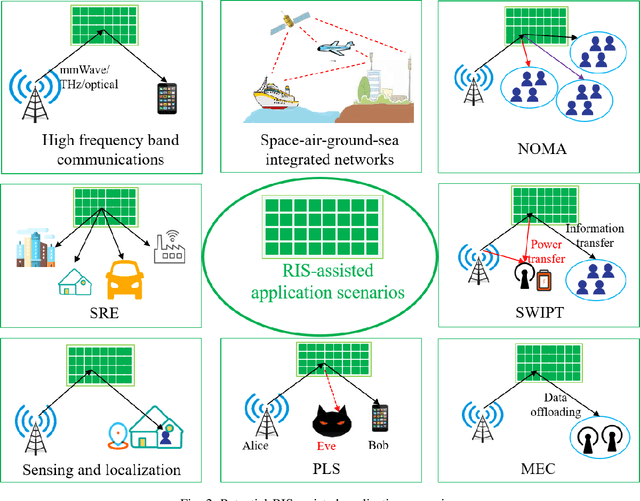
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) are two dimensional (2D) metasurfaces which can intelligently manipulate electromagnetic waves by low-cost near passive reflecting elements. RIS is viewed as a potential key technology for the sixth generation (6G) wireless communication systems mainly due to its advantages in tuning wireless signals, thus smartly controlling propagation environments. In this paper, we aim at addressing channel characterization and modeling issues of RIS-assisted wireless communication systems. At first, the concept, principle, and potential applications of RIS are given. An overview of RIS based channel measurements and experiments is presented by classifying frequency bands, scenarios, system configurations, RIS constructions, experiment purposes, and channel observations. Then, RIS based channel characteristics are studied, including reflection and transmission, Doppler effect and multipath fading mitigation, channel reciprocity, channel hardening, rank improvement, far field and near field, etc. RIS based channel modeling works are investigated, including largescale path loss models and small-scale multipath fading models. At last, future research directions related to RIS-assisted channels are also discussed.
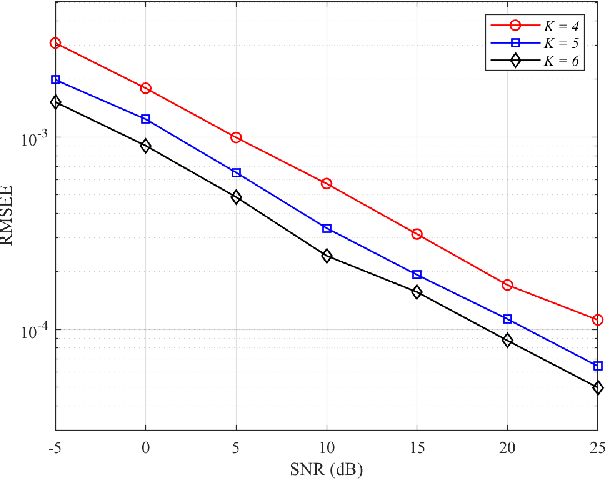
A 3D Non-Stationary Channel Model for 6G Wireless Systems Employing Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces with Practical Phase Shifts
Apr 25, 2021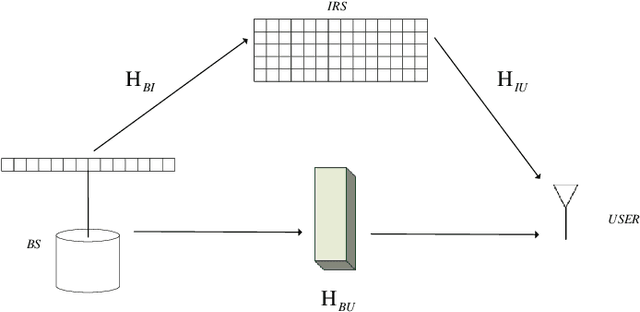
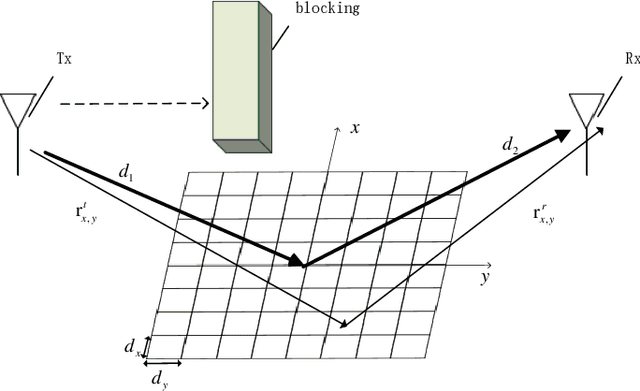
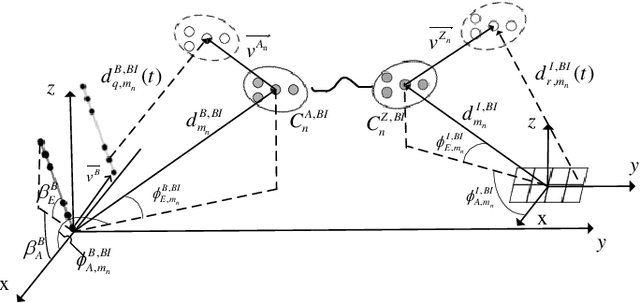
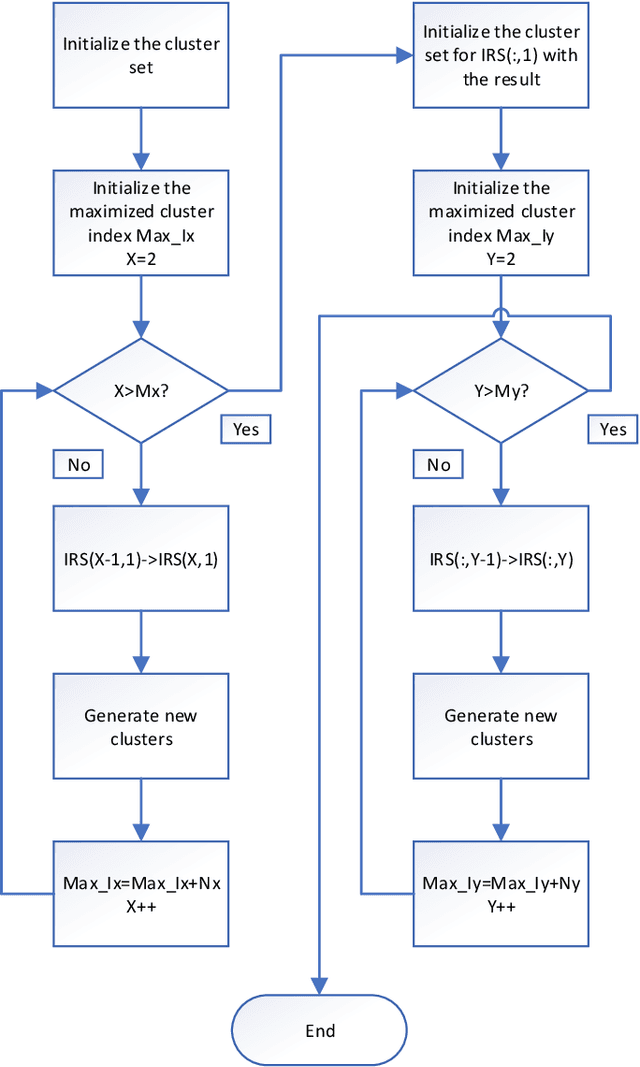
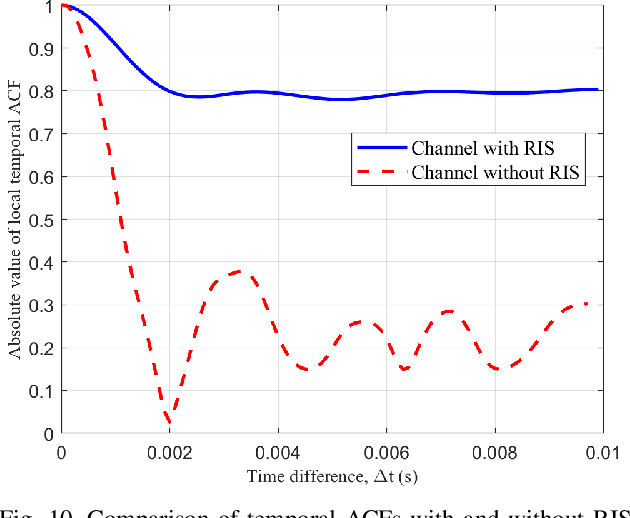
Abstract:In this paper, a three-dimensional (3D) geometry based stochastic model (GBSM) for a massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication system employing practical discrete intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) is proposed. The proposed channel model supports the scenario where both transceivers and environments move. The evolution of clusters in the space domain and the practical discrete phase shifts are considered in the channel model. The steering vector is set at the base station for the cooperation with IRS. Through studying statistical properties, the non-stationary properties are verified. We find that IRS plays a role in separating the whole channel and make the absolute value of time autocorrelation function (ACF) larger than the situation without employing IRS. Time ACF of the case using discrete phase shifts is also compared with the continuous case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge