Yikun Han
Large Language Models on Fine-grained Emotion Detection Dataset with Data Augmentation and Transfer Learning
Mar 10, 2024Abstract:This paper delves into enhancing the classification performance on the GoEmotions dataset, a large, manually annotated dataset for emotion detection in text. The primary goal of this paper is to address the challenges of detecting subtle emotions in text, a complex issue in Natural Language Processing (NLP) with significant practical applications. The findings offer valuable insights into addressing the challenges of emotion detection in text and suggest directions for future research, including the potential for a survey paper that synthesizes methods and performances across various datasets in this domain.
TinyLLM: Learning a Small Student from Multiple Large Language Models
Feb 07, 2024



Abstract:Transferring the reasoning capability from stronger large language models (LLMs) to smaller ones has been quite appealing, as smaller LLMs are more flexible to deploy with less expense. Among the existing solutions, knowledge distillation stands out due to its outstanding efficiency and generalization. However, existing methods suffer from several drawbacks, including limited knowledge diversity and the lack of rich contextual information. To solve the problems and facilitate the learning of compact language models, we propose TinyLLM, a novel knowledge distillation paradigm to learn a small student LLM from multiple large teacher LLMs. In particular, we encourage the student LLM to not only generate the correct answers but also understand the rationales behind these answers. Given that different LLMs possess diverse reasoning skills, we guide the student model to assimilate knowledge from various teacher LLMs. We further introduce an in-context example generator and a teacher-forcing Chain-of-Thought strategy to ensure that the rationales are accurate and grounded in contextually appropriate scenarios. Extensive experiments on six datasets across two reasoning tasks demonstrate the superiority of our method. Results show that TinyLLM can outperform large teacher LLMs significantly, despite having a considerably smaller model size.
When Large Language Models Meet Vector Databases: A Survey
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:This survey explores the synergistic potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vector Databases (VecDBs), a burgeoning but rapidly evolving research area. With the proliferation of LLMs comes a host of challenges, including hallucinations, outdated knowledge, prohibitive commercial application costs, and memory issues. VecDBs emerge as a compelling solution to these issues by offering an efficient means to store, retrieve, and manage the high-dimensional vector representations intrinsic to LLM operations. Through this nuanced review, we delineate the foundational principles of LLMs and VecDBs and critically analyze their integration's impact on enhancing LLM functionalities. This discourse extends into a discussion on the speculative future developments in this domain, aiming to catalyze further research into optimizing the confluence of LLMs and VecDBs for advanced data handling and knowledge extraction capabilities.
A Community Detection and Graph Neural Network Based Link Prediction Approach for Scientific Literature
Jan 04, 2024


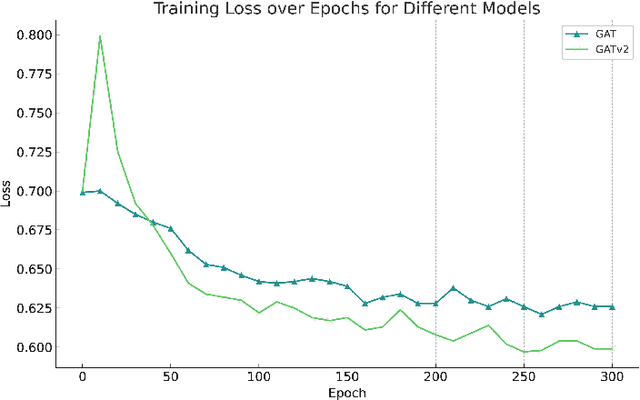
Abstract:This study introduces an innovative approach that integrates community detection algorithms with Graph Neural Network (GNN) models to enhance link prediction in scientific literature networks. We specifically focus on the utilization of the Louvain community detection algorithm to uncover latent community structures within these networks, which are then incorporated into GNN architectures to predict potential links. Our methodology demonstrates the importance of understanding community dynamics in complex networks and leverages the strengths of both community detection and GNNs to improve predictive accuracy. Through extensive experiments on bipartite graphs representing scientific collaborations and citations, our approach not only highlights the synergy between community detection and GNNs but also addresses some of the prevalent challenges in link prediction, such as scalability and resolution limits. The results suggest that incorporating community-level information can significantly enhance the performance of GNNs in link prediction tasks. This work contributes to the evolving field of network science by offering a novel perspective on integrating advanced machine learning techniques with traditional network analysis methods to better understand and predict the intricate patterns of scientific collaborations.
A Comprehensive Survey on Vector Database: Storage and Retrieval Technique, Challenge
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:A vector database is used to store high-dimensional data that cannot be characterized by traditional DBMS. Although there are not many articles describing existing or introducing new vector database architectures, the approximate nearest neighbor search problem behind vector databases has been studied for a long time, and considerable related algorithmic articles can be found in the literature. This article attempts to comprehensively review relevant algorithms to provide a general understanding of this booming research area. The basis of our framework categorises these studies by the approach of solving ANNS problem, respectively hash-based, tree-based, graph-based and quantization-based approaches. Then we present an overview of existing challenges for vector databases. Lastly, we sketch how vector databases can be combined with large language models and provide new possibilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge