Yijing Zhang
Scaling Up Audio-Synchronized Visual Animation: An Efficient Training Paradigm
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in audio-synchronized visual animation enable control of video content using audios from specific classes. However, existing methods rely heavily on expensive manual curation of high-quality, class-specific training videos, posing challenges to scaling up to diverse audio-video classes in the open world. In this work, we propose an efficient two-stage training paradigm to scale up audio-synchronized visual animation using abundant but noisy videos. In stage one, we automatically curate large-scale videos for pretraining, allowing the model to learn diverse but imperfect audio-video alignments. In stage two, we finetune the model on manually curated high-quality examples, but only at a small scale, significantly reducing the required human effort. We further enhance synchronization by allowing each frame to access rich audio context via multi-feature conditioning and window attention. To efficiently train the model, we leverage pretrained text-to-video generator and audio encoders, introducing only 1.9\% additional trainable parameters to learn audio-conditioning capability without compromising the generator's prior knowledge. For evaluation, we introduce AVSync48, a benchmark with videos from 48 classes, which is 3$\times$ more diverse than previous benchmarks. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly reduces reliance on manual curation by over 10$\times$, while generalizing to many open classes.
Revenue Optimization in Video Caching Networks with Privacy-Preserving Demand Predictions
May 09, 2025Abstract:Performance of video streaming, which accounts for most of the traffic in wireless communication, can be significantly improved by caching popular videos at the wireless edge. Determining the cache content that optimizes performance (defined via a revenue function) is thus an important task, and prediction of the future demands based on past history can make this process much more efficient. However, since practical video caching networks involve various parties (e.g., users, isp, and csp) that do not wish to reveal information such as past history to each other, privacy-preserving solutions are required. Motivated by this, we propose a proactive caching method based on users' privacy-preserving multi-slot future demand predictions -- obtained from a trained Transformer -- to optimize revenue. Specifically, we first use a privacy-preserving fl algorithm to train a Transformer to predict multi-slot future demands of the users. However, prediction accuracy is not perfect and decreases the farther into the future the prediction is done. We model the impact of prediction errors invoking the file popularities, based on which we formulate a long-term system revenue optimization to make the cache placement decisions. As the formulated problem is NP-hard, we use a greedy algorithm to efficiently obtain an approximate solution. Simulation results validate that (i) the fl solution achieves results close to the centralized (non-privacy-preserving) solution and (ii) optimization of revenue may provide different solutions than the classical chr criterion.
Personalize Your LLM: Fake it then Align it
Mar 05, 2025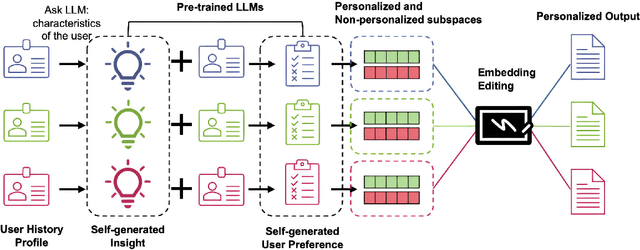

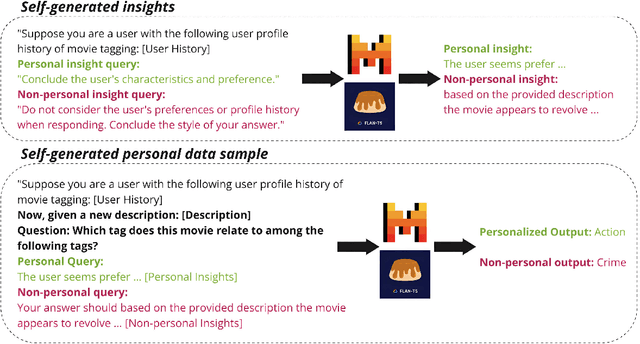

Abstract:Personalizing large language models (LLMs) is essential for delivering tailored interactions that improve user experience. Many existing personalization methods require fine-tuning LLMs for each user, rendering them prohibitively expensive for widespread adoption. Although retrieval-based approaches offer a more compute-efficient alternative, they still depend on large, high-quality datasets that are not consistently available for all users. To address this challenge, we propose CHAMELEON, a scalable and efficient personalization approach that uses (1) self-generated personal preference data and (2) representation editing to enable quick and cost-effective personalization. Our experiments on various tasks, including those from the LaMP personalization benchmark, show that CHAMELEON efficiently adapts models to personal preferences, improving instruction-tuned models and outperforms two personalization baselines by an average of 40% across two model architectures.
Is Free Self-Alignment Possible?
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Aligning pretrained language models (LMs) is a complex and resource-intensive process, often requiring access to large amounts of ground-truth preference data and substantial compute. Are these costs necessary? That is, it is possible to align using only inherent model knowledge and without additional training? We tackle this challenge with AlignEZ, a novel approach that uses (1) self-generated preference data and (2) representation editing to provide nearly cost-free alignment. During inference, AlignEZ modifies LM representations to reduce undesirable and boost desirable components using subspaces identified via self-generated preference pairs. Our experiments reveal that this nearly cost-free procedure significantly narrows the gap between base pretrained and tuned models by an average of 31.6%, observed across six datasets and three model architectures. Additionally, we explore the potential of using AlignEZ as a means of expediting more expensive alignment procedures. Our experiments show that AlignEZ improves DPO models tuned only using a small subset of ground-truth preference data. Lastly, we study the conditions under which improvement using AlignEZ is feasible, providing valuable insights into its effectiveness.
Audio-Synchronized Visual Animation
Mar 08, 2024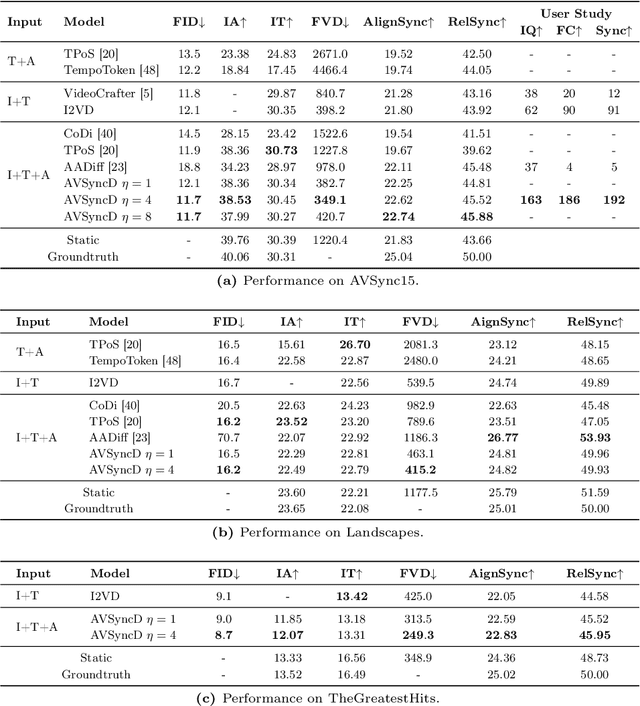
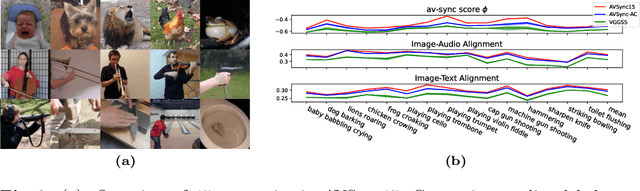
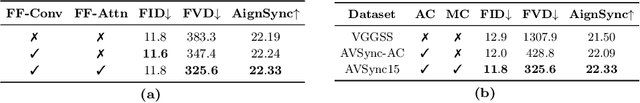
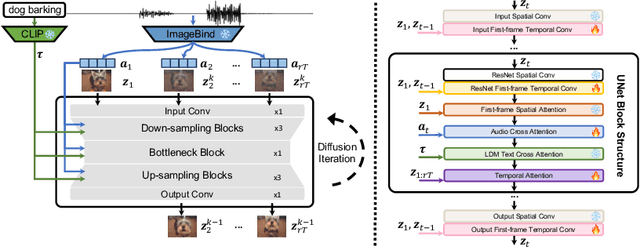
Abstract:Current visual generation methods can produce high quality videos guided by texts. However, effectively controlling object dynamics remains a challenge. This work explores audio as a cue to generate temporally synchronized image animations. We introduce Audio Synchronized Visual Animation (ASVA), a task animating a static image to demonstrate motion dynamics, temporally guided by audio clips across multiple classes. To this end, we present AVSync15, a dataset curated from VGGSound with videos featuring synchronized audio visual events across 15 categories. We also present a diffusion model, AVSyncD, capable of generating dynamic animations guided by audios. Extensive evaluations validate AVSync15 as a reliable benchmark for synchronized generation and demonstrate our models superior performance. We further explore AVSyncDs potential in a variety of audio synchronized generation tasks, from generating full videos without a base image to controlling object motions with various sounds. We hope our established benchmark can open new avenues for controllable visual generation. More videos on project webpage https://lzhangbj.github.io/projects/asva/asva.html.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge