Jinhong Lin
Scaling Up Audio-Synchronized Visual Animation: An Efficient Training Paradigm
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in audio-synchronized visual animation enable control of video content using audios from specific classes. However, existing methods rely heavily on expensive manual curation of high-quality, class-specific training videos, posing challenges to scaling up to diverse audio-video classes in the open world. In this work, we propose an efficient two-stage training paradigm to scale up audio-synchronized visual animation using abundant but noisy videos. In stage one, we automatically curate large-scale videos for pretraining, allowing the model to learn diverse but imperfect audio-video alignments. In stage two, we finetune the model on manually curated high-quality examples, but only at a small scale, significantly reducing the required human effort. We further enhance synchronization by allowing each frame to access rich audio context via multi-feature conditioning and window attention. To efficiently train the model, we leverage pretrained text-to-video generator and audio encoders, introducing only 1.9\% additional trainable parameters to learn audio-conditioning capability without compromising the generator's prior knowledge. For evaluation, we introduce AVSync48, a benchmark with videos from 48 classes, which is 3$\times$ more diverse than previous benchmarks. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly reduces reliance on manual curation by over 10$\times$, while generalizing to many open classes.
From Prototypes to General Distributions: An Efficient Curriculum for Masked Image Modeling
Nov 16, 2024Abstract:Masked Image Modeling (MIM) has emerged as a powerful self-supervised learning paradigm for visual representation learning, enabling models to acquire rich visual representations by predicting masked portions of images from their visible regions. While this approach has shown promising results, we hypothesize that its effectiveness may be limited by optimization challenges during early training stages, where models are expected to learn complex image distributions from partial observations before developing basic visual processing capabilities. To address this limitation, we propose a prototype-driven curriculum leagrning framework that structures the learning process to progress from prototypical examples to more complex variations in the dataset. Our approach introduces a temperature-based annealing scheme that gradually expands the training distribution, enabling more stable and efficient learning trajectories. Through extensive experiments on ImageNet-1K, we demonstrate that our curriculum learning strategy significantly improves both training efficiency and representation quality while requiring substantially fewer training epochs compared to standard Masked Auto-Encoding. Our findings suggest that carefully controlling the order of training examples plays a crucial role in self-supervised visual learning, providing a practical solution to the early-stage optimization challenges in MIM.
Accelerating Augmentation Invariance Pretraining
Oct 31, 2024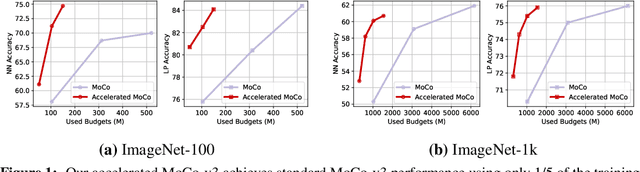
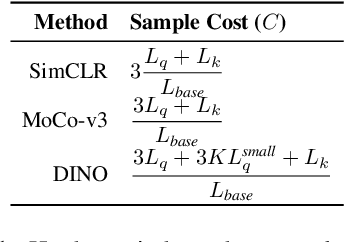
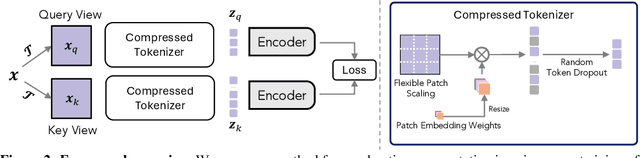
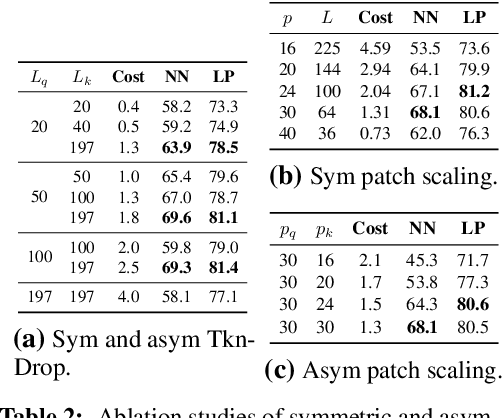
Abstract:Our work tackles the computational challenges of contrastive learning methods, particularly for the pretraining of Vision Transformers (ViTs). Despite the effectiveness of contrastive learning, the substantial computational resources required for training often hinder their practical application. To mitigate this issue, we propose an acceleration framework, leveraging ViT's unique ability to generalize across inputs of varying sequence lengths. Our method employs a mix of sequence compression strategies, including randomized token dropout and flexible patch scaling, to reduce the cost of gradient estimation and accelerate convergence. We further provide an in-depth analysis of the gradient estimation error of various acceleration strategies as well as their impact on downstream tasks, offering valuable insights into the trade-offs between acceleration and performance. We also propose a novel procedure to identify an optimal acceleration schedule to adjust the sequence compression ratios to the training progress, ensuring efficient training without sacrificing downstream performance. Our approach significantly reduces computational overhead across various self-supervised learning algorithms on large-scale datasets. In ImageNet, our method achieves speedups of 4$\times$ in MoCo, 3.3$\times$ in SimCLR, and 2.5$\times$ in DINO, demonstrating substantial efficiency gains.
Patch Ranking: Efficient CLIP by Learning to Rank Local Patches
Sep 22, 2024Abstract:Contrastive image-text pre-trained models such as CLIP have shown remarkable adaptability to downstream tasks. However, they face challenges due to the high computational requirements of the Vision Transformer (ViT) backbone. Current strategies to boost ViT efficiency focus on pruning patch tokens but fall short in addressing the multimodal nature of CLIP and identifying the optimal subset of tokens for maximum performance. To address this, we propose greedy search methods to establish a "Golden Ranking" and introduce a lightweight predictor specifically trained to approximate this Ranking. To compensate for any performance degradation resulting from token pruning, we incorporate learnable visual tokens that aid in restoring and potentially enhancing the model's performance. Our work presents a comprehensive and systematic investigation of pruning tokens within the ViT backbone of CLIP models. Through our framework, we successfully reduced 40% of patch tokens in CLIP's ViT while only suffering a minimal average accuracy loss of 0.3 across seven datasets. Our study lays the groundwork for building more computationally efficient multimodal models without sacrificing their performance, addressing a key challenge in the application of advanced vision-language models.
Extracting knowledge from features with multilevel abstraction
Dec 04, 2021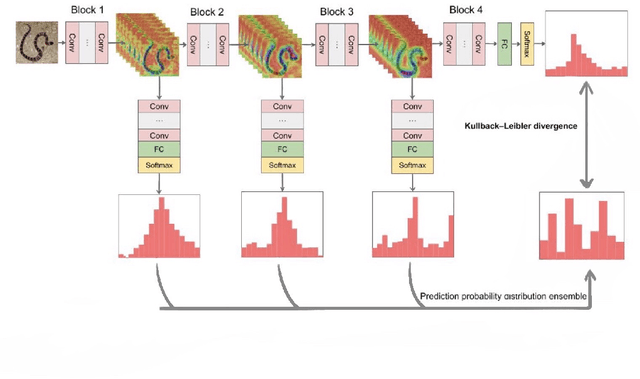
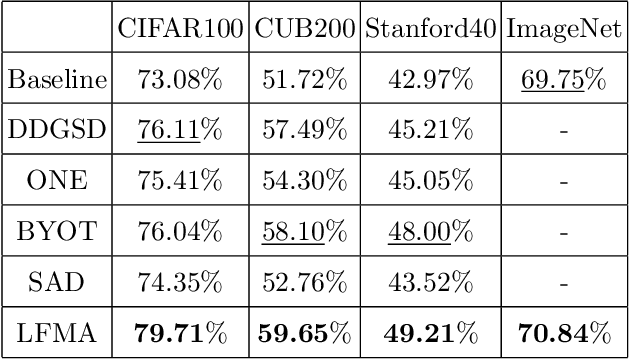
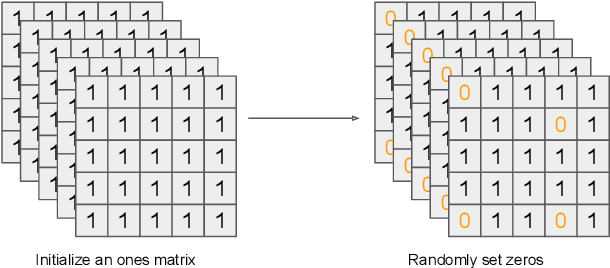
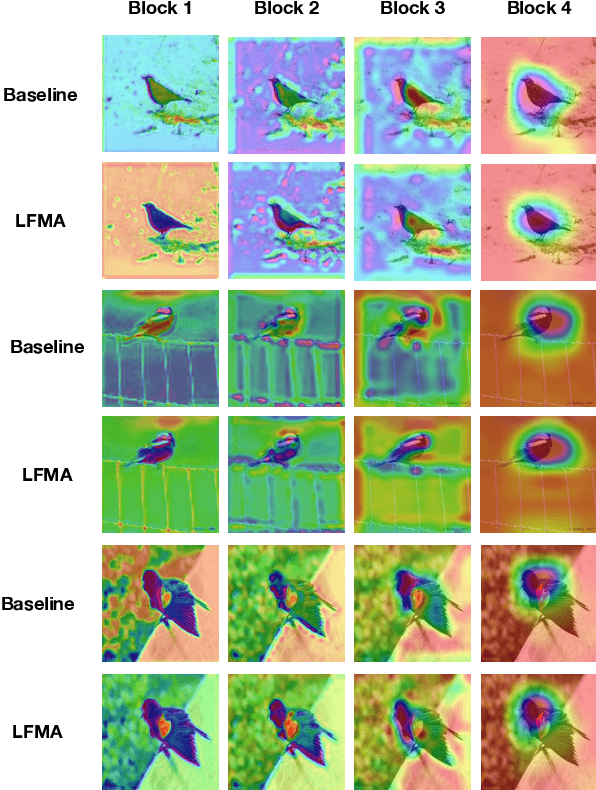
Abstract:Knowledge distillation aims at transferring the knowledge from a large teacher model to a small student model with great improvements of the performance of the student model. Therefore, the student network can replace the teacher network to deploy on low-resource devices since the higher performance, lower number of parameters and shorter inference time. Self-knowledge distillation (SKD) attracts a great attention recently that a student model itself is a teacher model distilling knowledge from. To the best of our knowledge, self knowledge distillation can be divided into two main streams: data augmentation and refined knowledge auxiliary. In this paper, we purpose a novel SKD method in a different way from the main stream methods. Our method distills knowledge from multilevel abstraction features. Experiments and ablation studies show its great effectiveness and generalization on various kinds of tasks with various kinds of model structures. Our codes have been released on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge