Yicheng Zeng
In-Context Learning as Nonparametric Conditional Probability Estimation: Risk Bounds and Optimality
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates the expected excess risk of In-Context Learning (ICL) for multiclass classification. We model each task as a sequence of labeled prompt samples and a query input, where a pre-trained model estimates the conditional class probabilities of the query. The expected excess risk is defined as the average truncated Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between the predicted and ground-truth conditional class distributions, averaged over a specified family of tasks. We establish a new oracle inequality for the expected excess risk based on KL divergence in multiclass classification. This allows us to derive tight upper and lower bounds for the expected excess risk in transformer-based models, demonstrating that the ICL estimator achieves the minimax optimal rate - up to a logarithmic factor - for conditional probability estimation. From a technical standpoint, our results introduce a novel method for controlling generalization error using the uniform empirical covering entropy of the log-likelihood function class. Furthermore, we show that multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) can also perform ICL and achieve this optimal rate under specific assumptions, suggesting that transformers may not be the exclusive architecture capable of effective ICL.
Reference-Steering via Data-Driven Predictive Control for Hyper-Accurate Robotic Flying-Hopping Locomotion
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:State-of-the-art model-based control designs have been shown to be successful in realizing dynamic locomotion behaviors for robotic systems. The precision of the realized behaviors in terms of locomotion performance via fly, hopping, or walking has not yet been well investigated, despite the fact that the difference between the robot model and physical hardware is doomed to produce inaccurate trajectory tracking. To address this inaccuracy, we propose a referencing-steering method to bridge the model-to-real gap by establishing a data-driven input-output (DD-IO) model on top of the existing model-based design. The DD-IO model takes the reference tracking trajectories as the input and the realized tracking trajectory as the output. By utilizing data-driven predictive control, we steer the reference input trajectories online so that the realized output ones match the actual desired ones. We demonstrate our method on the robot PogoX to realize hyper-accurate hopping and flying behaviors in both simulation and hardware. This data-driven reference-steering approach is straightforward to apply to general robotic systems for performance improvement via hyper-accurate trajectory tracking.
STRIDE: An Open-Source, Low-Cost, and Versatile Bipedal Robot Platform for Research and Education
Jul 02, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present STRIDE, a Simple, Terrestrial, Reconfigurable, Intelligent, Dynamic, and Educational bipedal platform. STRIDE aims to propel bipedal robotics research and education by providing a cost-effective implementation with step-by-step instructions for building a bipedal robotic platform while providing flexible customizations via a modular and durable design. Moreover, a versatile terrain setup and a quantitative disturbance injection system are augmented to the robot platform to replicate natural terrains and push forces that can be used to evaluate legged locomotion in practical and adversarial scenarios. We demonstrate the functionalities of this platform by realizing an adaptive step-to-step dynamics based walking controller to achieve dynamic walking. Our work with the open-soured implementation shows that STRIDE is a highly versatile and durable platform that can be used in research and education to evaluate locomotion algorithms, mechanical designs, and robust and adaptative controls.
Enhancing Out-of-Distribution Detection with Multitesting-based Layer-wise Feature Fusion
Mar 16, 2024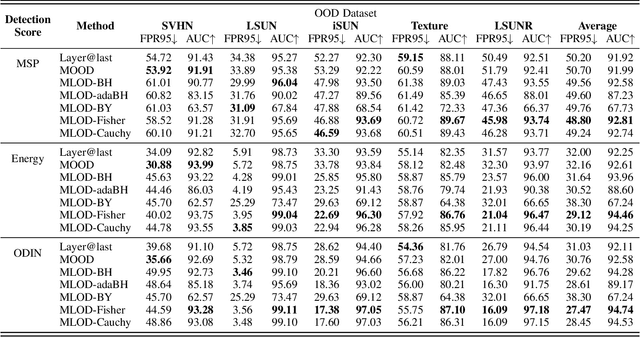
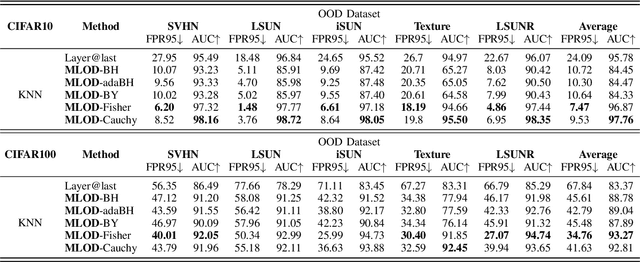
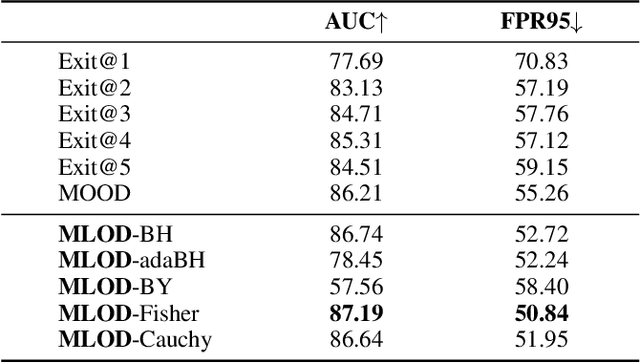
Abstract:Deploying machine learning in open environments presents the challenge of encountering diverse test inputs that differ significantly from the training data. These out-of-distribution samples may exhibit shifts in local or global features compared to the training distribution. The machine learning (ML) community has responded with a number of methods aimed at distinguishing anomalous inputs from original training data. However, the majority of previous studies have primarily focused on the output layer or penultimate layer of pre-trained deep neural networks. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, Multitesting-based Layer-wise Out-of-Distribution (OOD) Detection (MLOD), to identify distributional shifts in test samples at different levels of features through rigorous multiple testing procedure. Our approach distinguishes itself from existing methods as it does not require modifying the structure or fine-tuning of the pre-trained classifier. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed framework can seamlessly integrate with any existing distance-based inspection method while efficiently utilizing feature extractors of varying depths. Our scheme effectively enhances the performance of out-of-distribution detection when compared to baseline methods. In particular, MLOD-Fisher achieves superior performance in general. When trained using KNN on CIFAR10, MLOD-Fisher significantly lowers the false positive rate (FPR) from 24.09% to 7.47% on average compared to merely utilizing the features of the last layer.
Sketched Ridgeless Linear Regression: The Role of Downsampling
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:Overparametrization often helps improve the generalization performance. This paper proposes a dual view of overparametrization suggesting that downsampling may also help generalize. Motivated by this dual view, we characterize two out-of-sample prediction risks of the sketched ridgeless least square estimator in the proportional regime $m\asymp n \asymp p$, where $m$ is the sketching size, $n$ the sample size, and $p$ the feature dimensionality. Our results reveal the statistical role of downsampling. Specifically, downsampling does not always hurt the generalization performance, and may actually help improve it in some cases. We identify the optimal sketching sizes that minimize the out-of-sample prediction risks, and find that the optimally sketched estimator has stabler risk curves that eliminates the peaks of those for the full-sample estimator. We then propose a practical procedure to empirically identify the optimal sketching size. Finally, we extend our results to cover central limit theorems and misspecified models. Numerical studies strongly support our theory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge