Yichen Bai
Advancing Continual Learning for Robust Deepfake Audio Classification
Jul 14, 2024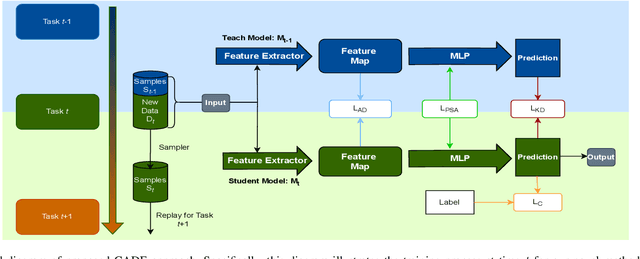
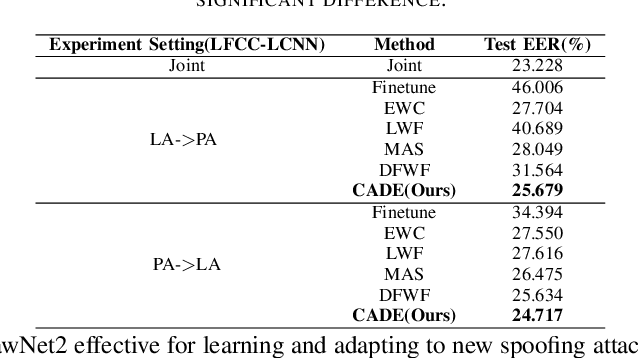
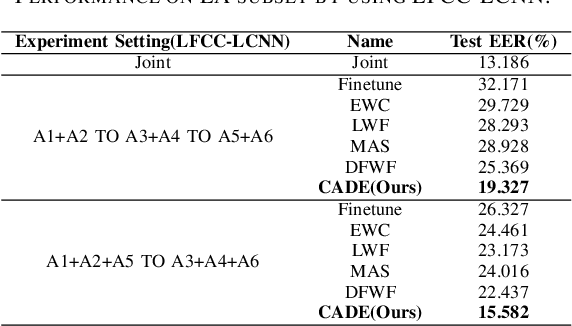
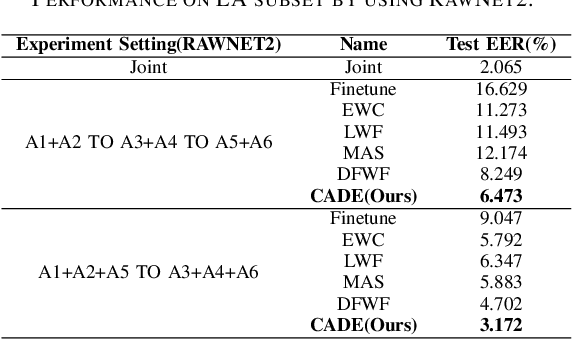
Abstract:The emergence of new spoofing attacks poses an increasing challenge to audio security. Current detection methods often falter when faced with unseen spoofing attacks. Traditional strategies, such as retraining with new data, are not always feasible due to extensive storage. This paper introduces a novel continual learning method Continual Audio Defense Enhancer (CADE). First, by utilizing a fixed memory size to store randomly selected samples from previous datasets, our approach conserves resources and adheres to privacy constraints. Additionally, we also apply two distillation losses in CADE. By distillation in classifiers, CADE ensures that the student model closely resembles that of the teacher model. This resemblance helps the model retain old information while facing unseen data. We further refine our model's performance with a novel embedding similarity loss that extends across multiple depth layers, facilitating superior positive sample alignment. Experiments conducted on the ASVspoof2019 dataset show that our proposed method outperforms the baseline methods.
ID-like Prompt Learning for Few-Shot Out-of-Distribution Detection
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection methods often exploit auxiliary outliers to train model identifying OOD samples, especially discovering challenging outliers from auxiliary outliers dataset to improve OOD detection. However, they may still face limitations in effectively distinguishing between the most challenging OOD samples that are much like in-distribution (ID) data, i.e., ID-like samples. To this end, we propose a novel OOD detection framework that discovers ID-like outliers using CLIP from the vicinity space of the ID samples, thus helping to identify these most challenging OOD samples. Then a prompt learning framework is proposed that utilizes the identified ID-like outliers to further leverage the capabilities of CLIP for OOD detection. Benefiting from the powerful CLIP, we only need a small number of ID samples to learn the prompts of the model without exposing other auxiliary outlier datasets. By focusing on the most challenging ID-like OOD samples and elegantly exploiting the capabilities of CLIP, our method achieves superior few-shot learning performance on various real-world image datasets (e.g., in 4-shot OOD detection on the ImageNet-1k dataset, our method reduces the average FPR95 by 12.16% and improves the average AUROC by 2.76%, compared to state-of-the-art methods).
Exploring and Exploiting Uncertainty for Incomplete Multi-View Classification
Apr 11, 2023Abstract:Classifying incomplete multi-view data is inevitable since arbitrary view missing widely exists in real-world applications. Although great progress has been achieved, existing incomplete multi-view methods are still difficult to obtain a trustworthy prediction due to the relatively high uncertainty nature of missing views. First, the missing view is of high uncertainty, and thus it is not reasonable to provide a single deterministic imputation. Second, the quality of the imputed data itself is of high uncertainty. To explore and exploit the uncertainty, we propose an Uncertainty-induced Incomplete Multi-View Data Classification (UIMC) model to classify the incomplete multi-view data under a stable and reliable framework. We construct a distribution and sample multiple times to characterize the uncertainty of missing views, and adaptively utilize them according to the sampling quality. Accordingly, the proposed method realizes more perceivable imputation and controllable fusion. Specifically, we model each missing data with a distribution conditioning on the available views and thus introducing uncertainty. Then an evidence-based fusion strategy is employed to guarantee the trustworthy integration of the imputed views. Extensive experiments are conducted on multiple benchmark data sets and our method establishes a state-of-the-art performance in terms of both performance and trustworthiness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge