Yecheol Kim
Resilient Sensor Fusion under Adverse Sensor Failures via Multi-Modal Expert Fusion
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Modern autonomous driving perception systems utilize complementary multi-modal sensors, such as LiDAR and cameras. Although sensor fusion architectures enhance performance in challenging environments, they still suffer significant performance drops under severe sensor failures, such as LiDAR beam reduction, LiDAR drop, limited field of view, camera drop, and occlusion. This limitation stems from inter-modality dependencies in current sensor fusion frameworks. In this study, we introduce an efficient and robust LiDAR-camera 3D object detector, referred to as MoME, which can achieve robust performance through a mixture of experts approach. Our MoME fully decouples modality dependencies using three parallel expert decoders, which use camera features, LiDAR features, or a combination of both to decode object queries, respectively. We propose Multi-Expert Decoding (MED) framework, where each query is decoded selectively using one of three expert decoders. MoME utilizes an Adaptive Query Router (AQR) to select the most appropriate expert decoder for each query based on the quality of camera and LiDAR features. This ensures that each query is processed by the best-suited expert, resulting in robust performance across diverse sensor failure scenarios. We evaluated the performance of MoME on the nuScenes-R benchmark. Our MoME achieved state-of-the-art performance in extreme weather and sensor failure conditions, significantly outperforming the existing models across various sensor failure scenarios.
Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Target-Oriented Domain Augmentation for 3D Object Detection
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:3D object detection is crucial for applications like autonomous driving and robotics. However, in real-world environments, variations in sensor data distribution due to sensor upgrades, weather changes, and geographic differences can adversely affect detection performance. Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation (SSDA) aims to mitigate these challenges by transferring knowledge from a source domain, abundant in labeled data, to a target domain where labels are scarce. This paper presents a new SSDA method referred to as Target-Oriented Domain Augmentation (TODA) specifically tailored for LiDAR-based 3D object detection. TODA efficiently utilizes all available data, including labeled data in the source domain, and both labeled data and unlabeled data in the target domain to enhance domain adaptation performance. TODA consists of two stages: TargetMix and AdvMix. TargetMix employs mixing augmentation accounting for LiDAR sensor characteristics to facilitate feature alignment between the source-domain and target-domain. AdvMix applies point-wise adversarial augmentation with mixing augmentation, which perturbs the unlabeled data to align the features within both labeled and unlabeled data in the target domain. Our experiments conducted on the challenging domain adaptation tasks demonstrate that TODA outperforms existing domain adaptation techniques designed for 3D object detection by significant margins. The code is available at: https://github.com/rasd3/TODA.
Fine-Grained Pillar Feature Encoding Via Spatio-Temporal Virtual Grid for 3D Object Detection
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Developing high-performance, real-time architectures for LiDAR-based 3D object detectors is essential for the successful commercialization of autonomous vehicles. Pillar-based methods stand out as a practical choice for onboard deployment due to their computational efficiency. However, despite their efficiency, these methods can sometimes underperform compared to alternative point encoding techniques such as Voxel-encoding or PointNet++. We argue that current pillar-based methods have not sufficiently captured the fine-grained distributions of LiDAR points within each pillar structure. Consequently, there exists considerable room for improvement in pillar feature encoding. In this paper, we introduce a novel pillar encoding architecture referred to as Fine-Grained Pillar Feature Encoding (FG-PFE). FG-PFE utilizes Spatio-Temporal Virtual (STV) grids to capture the distribution of point clouds within each pillar across vertical, temporal, and horizontal dimensions. Through STV grids, points within each pillar are individually encoded using Vertical PFE (V-PFE), Temporal PFE (T-PFE), and Horizontal PFE (H-PFE). These encoded features are then aggregated through an Attentive Pillar Aggregation method. Our experiments conducted on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that FG-PFE achieves significant performance improvements over baseline models such as PointPillar, CenterPoint-Pillar, and PillarNet, with only a minor increase in computational overhead.
3D Dual-Fusion: Dual-Domain Dual-Query Camera-LiDAR Fusion for 3D Object Detection
Nov 24, 2022Abstract:Fusing data from cameras and LiDAR sensors is an essential technique to achieve robust 3D object detection. One key challenge in camera-LiDAR fusion involves mitigating the large domain gap between the two sensors in terms of coordinates and data distribution when fusing their features. In this paper, we propose a novel camera-LiDAR fusion architecture called, 3D Dual-Fusion, which is designed to mitigate the gap between the feature representations of camera and LiDAR data. The proposed method fuses the features of the camera-view and 3D voxel-view domain and models their interactions through deformable attention. We redesign the transformer fusion encoder to aggregate the information from the two domains. Two major changes include 1) dual query-based deformable attention to fuse the dual-domain features interactively and 2) 3D local self-attention to encode the voxel-domain queries prior to dual-query decoding. The results of an experimental evaluation show that the proposed camera-LiDAR fusion architecture achieved competitive performance on the KITTI and nuScenes datasets, with state-of-the-art performances in some 3D object detection benchmarks categories.
Joint 3D Object Detection and Tracking Using Spatio-Temporal Representation of Camera Image and LiDAR Point Clouds
Dec 15, 2021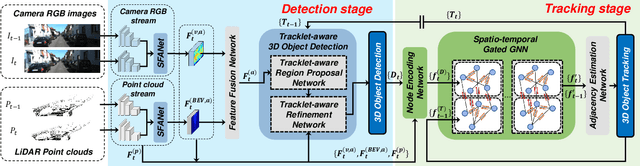
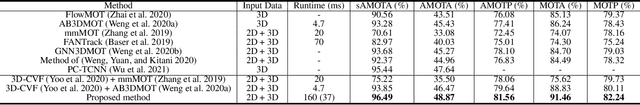
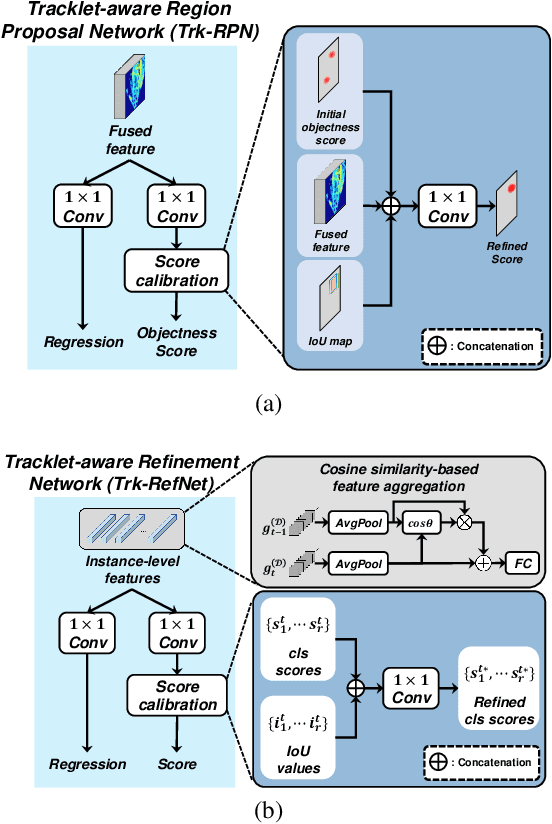
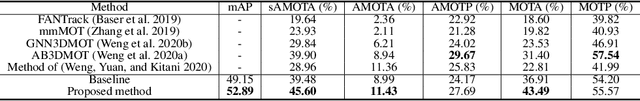
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new joint object detection and tracking (JoDT) framework for 3D object detection and tracking based on camera and LiDAR sensors. The proposed method, referred to as 3D DetecTrack, enables the detector and tracker to cooperate to generate a spatio-temporal representation of the camera and LiDAR data, with which 3D object detection and tracking are then performed. The detector constructs the spatio-temporal features via the weighted temporal aggregation of the spatial features obtained by the camera and LiDAR fusion. Then, the detector reconfigures the initial detection results using information from the tracklets maintained up to the previous time step. Based on the spatio-temporal features generated by the detector, the tracker associates the detected objects with previously tracked objects using a graph neural network (GNN). We devise a fully-connected GNN facilitated by a combination of rule-based edge pruning and attention-based edge gating, which exploits both spatial and temporal object contexts to improve tracking performance. The experiments conducted on both KITTI and nuScenes benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed 3D DetecTrack achieves significant improvements in both detection and tracking performances over baseline methods and achieves state-of-the-art performance among existing methods through collaboration between the detector and tracker.
Robust Deep Multi-modal Learning Based on Gated Information Fusion Network
Nov 02, 2018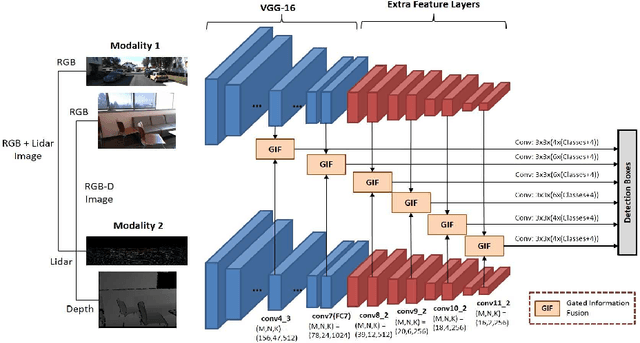
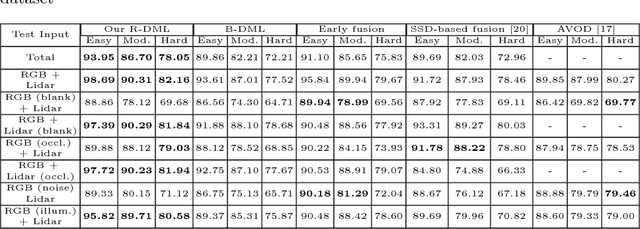
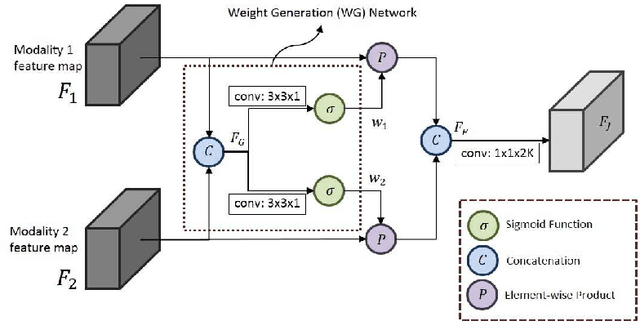
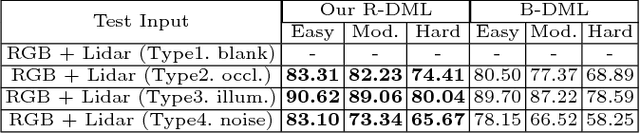
Abstract:The goal of multi-modal learning is to use complimentary information on the relevant task provided by the multiple modalities to achieve reliable and robust performance. Recently, deep learning has led significant improvement in multi-modal learning by allowing for the information fusion in the intermediate feature levels. This paper addresses a problem of designing robust deep multi-modal learning architecture in the presence of imperfect modalities. We introduce deep fusion architecture for object detection which processes each modality using the separate convolutional neural network (CNN) and constructs the joint feature map by combining the intermediate features from the CNNs. In order to facilitate the robustness to the degraded modalities, we employ the gated information fusion (GIF) network which weights the contribution from each modality according to the input feature maps to be fused. The weights are determined through the convolutional layers followed by a sigmoid function and trained along with the information fusion network in an end-to-end fashion. Our experiments show that the proposed GIF network offers the additional architectural flexibility to achieve robust performance in handling some degraded modalities, and show a significant performance improvement based on Single Shot Detector (SSD) for KITTI dataset using the proposed fusion network and data augmentation schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge