Jun Won Choi
Resilient Sensor Fusion under Adverse Sensor Failures via Multi-Modal Expert Fusion
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Modern autonomous driving perception systems utilize complementary multi-modal sensors, such as LiDAR and cameras. Although sensor fusion architectures enhance performance in challenging environments, they still suffer significant performance drops under severe sensor failures, such as LiDAR beam reduction, LiDAR drop, limited field of view, camera drop, and occlusion. This limitation stems from inter-modality dependencies in current sensor fusion frameworks. In this study, we introduce an efficient and robust LiDAR-camera 3D object detector, referred to as MoME, which can achieve robust performance through a mixture of experts approach. Our MoME fully decouples modality dependencies using three parallel expert decoders, which use camera features, LiDAR features, or a combination of both to decode object queries, respectively. We propose Multi-Expert Decoding (MED) framework, where each query is decoded selectively using one of three expert decoders. MoME utilizes an Adaptive Query Router (AQR) to select the most appropriate expert decoder for each query based on the quality of camera and LiDAR features. This ensures that each query is processed by the best-suited expert, resulting in robust performance across diverse sensor failure scenarios. We evaluated the performance of MoME on the nuScenes-R benchmark. Our MoME achieved state-of-the-art performance in extreme weather and sensor failure conditions, significantly outperforming the existing models across various sensor failure scenarios.
MR-Occ: Efficient Camera-LiDAR 3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction Using Hierarchical Multi-Resolution Voxel Representation
Dec 29, 2024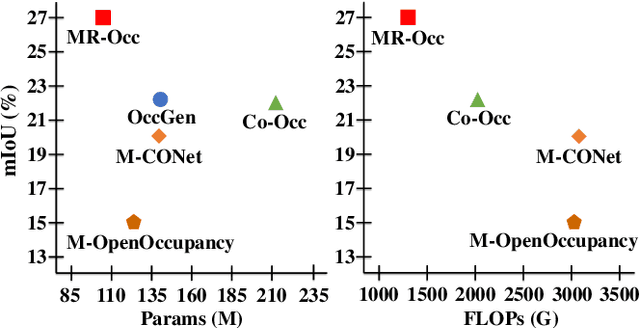
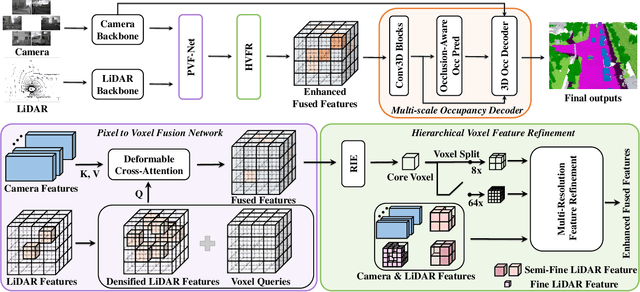
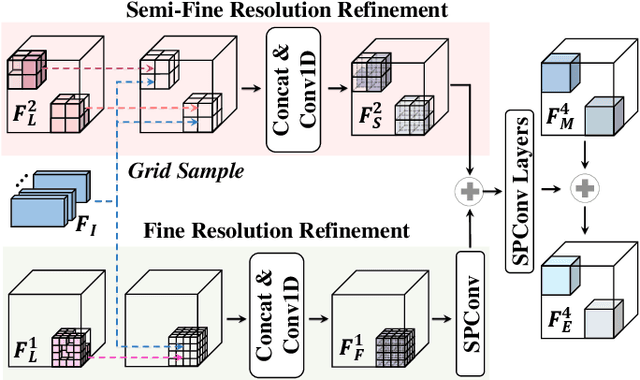
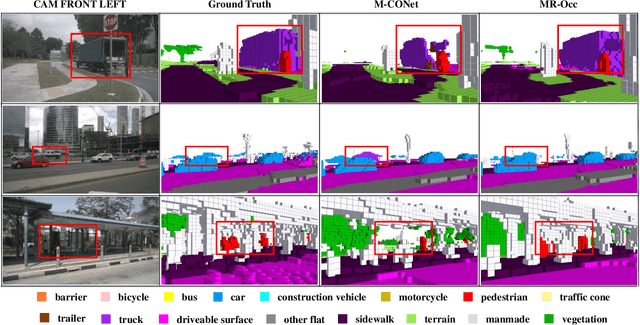
Abstract:Accurate 3D perception is essential for understanding the environment in autonomous driving. Recent advancements in 3D semantic occupancy prediction have leveraged camera-LiDAR fusion to improve robustness and accuracy. However, current methods allocate computational resources uniformly across all voxels, leading to inefficiency, and they also fail to adequately address occlusions, resulting in reduced accuracy in challenging scenarios. We propose MR-Occ, a novel approach for camera-LiDAR fusion-based 3D semantic occupancy prediction, addressing these challenges through three key components: Hierarchical Voxel Feature Refinement (HVFR), Multi-scale Occupancy Decoder (MOD), and Pixel to Voxel Fusion Network (PVF-Net). HVFR improves performance by enhancing features for critical voxels, reducing computational cost. MOD introduces an `occluded' class to better handle regions obscured from sensor view, improving accuracy. PVF-Net leverages densified LiDAR features to effectively fuse camera and LiDAR data through a deformable attention mechanism. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MR-Occ achieves state-of-the-art performance on the nuScenes-Occupancy dataset, surpassing previous approaches by +5.2% in IoU and +5.3% in mIoU while using fewer parameters and FLOPs. Moreover, MR-Occ demonstrates superior performance on the SemanticKITTI dataset, further validating its effectiveness and generalizability across diverse 3D semantic occupancy benchmarks.
JoVALE: Detecting Human Actions in Video Using Audiovisual and Language Contexts
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Video Action Detection (VAD) involves localizing and categorizing action instances in videos. Videos inherently contain various information sources, including audio, visual cues, and surrounding scene contexts. Effectively leveraging this multi-modal information for VAD is challenging, as the model must accurately focus on action-relevant cues. In this study, we introduce a novel multi-modal VAD architecture called the Joint Actor-centric Visual, Audio, Language Encoder (JoVALE). JoVALE is the first VAD method to integrate audio and visual features with scene descriptive context derived from large image captioning models. The core principle of JoVALE is the actor-centric aggregation of audio, visual, and scene descriptive contexts, where action-related cues from each modality are identified and adaptively combined. We propose a specialized module called the Actor-centric Multi-modal Fusion Network, designed to capture the joint interactions among actors and multi-modal contexts through Transformer architecture. Our evaluation conducted on three popular VAD benchmarks, AVA, UCF101-24, and JHMDB51-21, demonstrates that incorporating multi-modal information leads to significant performance gains. JoVALE achieves state-of-the-art performances. The code will be available at \texttt{https://github.com/taeiin/AAAI2025-JoVALE}.
ProtoOcc: Accurate, Efficient 3D Occupancy Prediction Using Dual Branch Encoder-Prototype Query Decoder
Dec 11, 2024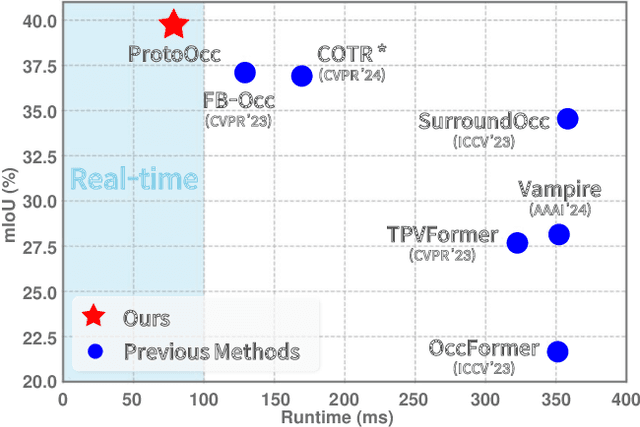
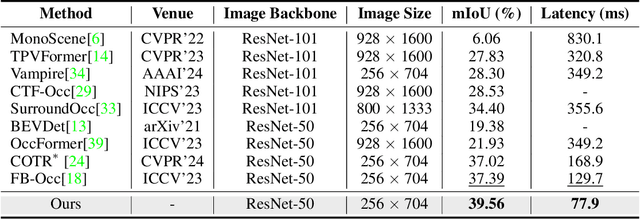
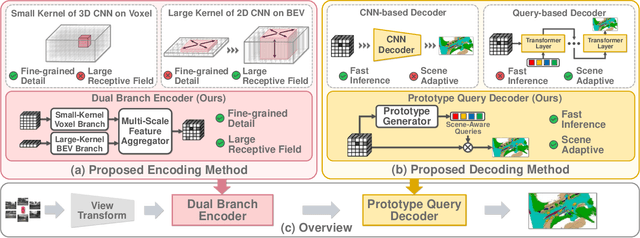
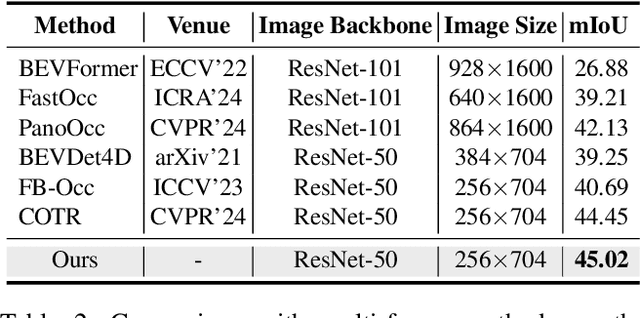
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce ProtoOcc, a novel 3D occupancy prediction model designed to predict the occupancy states and semantic classes of 3D voxels through a deep semantic understanding of scenes. ProtoOcc consists of two main components: the Dual Branch Encoder (DBE) and the Prototype Query Decoder (PQD). The DBE produces a new 3D voxel representation by combining 3D voxel and BEV representations across multiple scales through a dual branch structure. This design enhances both performance and computational efficiency by providing a large receptive field for the BEV representation while maintaining a smaller receptive field for the voxel representation. The PQD introduces Prototype Queries to accelerate the decoding process. Scene-Adaptive Prototypes are derived from the 3D voxel features of input sample, while Scene-Agnostic Prototypes are computed by applying Scene-Adaptive Prototypes to an Exponential Moving Average during the training phase. By using these prototype-based queries for decoding, we can directly predict 3D occupancy in a single step, eliminating the need for iterative Transformer decoding. Additionally, we propose the Robust Prototype Learning, which injects noise into prototype generation process and trains the model to denoise during the training phase. ProtoOcc achieves state-of-the-art performance with 45.02% mIoU on the Occ3D-nuScenes benchmark. For single-frame method, it reaches 39.56% mIoU with an inference speed of 12.83 FPS on an NVIDIA RTX 3090. Our code can be found at https://github.com/SPA-junghokim/ProtoOcc.
CRT-Fusion: Camera, Radar, Temporal Fusion Using Motion Information for 3D Object Detection
Nov 05, 2024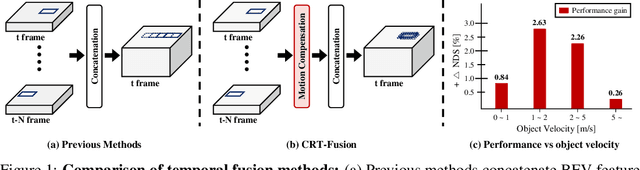
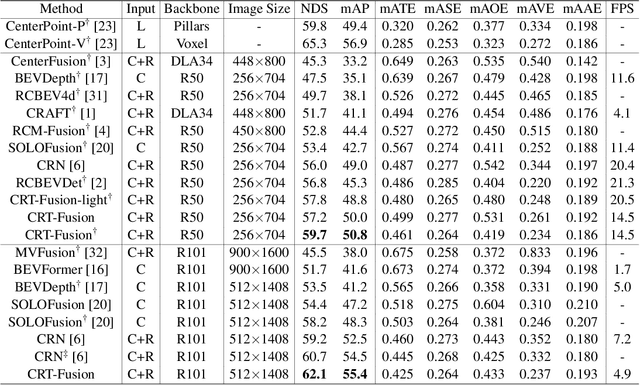
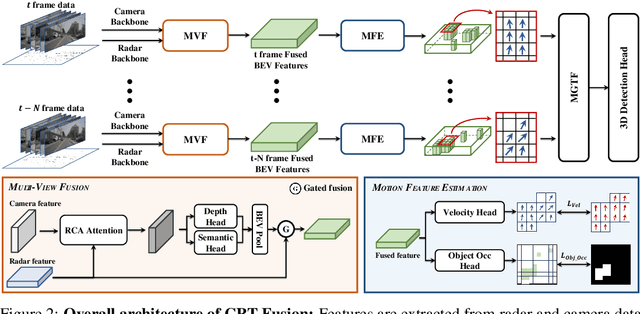
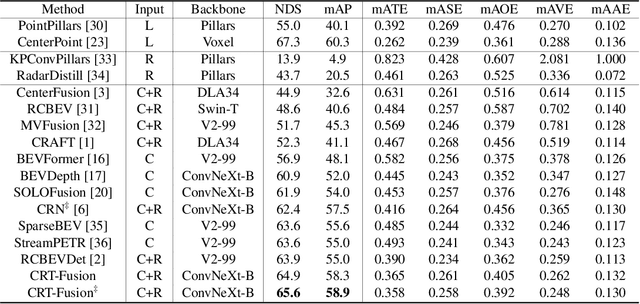
Abstract:Accurate and robust 3D object detection is a critical component in autonomous vehicles and robotics. While recent radar-camera fusion methods have made significant progress by fusing information in the bird's-eye view (BEV) representation, they often struggle to effectively capture the motion of dynamic objects, leading to limited performance in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we introduce CRT-Fusion, a novel framework that integrates temporal information into radar-camera fusion to address this challenge. Our approach comprises three key modules: Multi-View Fusion (MVF), Motion Feature Estimator (MFE), and Motion Guided Temporal Fusion (MGTF). The MVF module fuses radar and image features within both the camera view and bird's-eye view, thereby generating a more precise unified BEV representation. The MFE module conducts two simultaneous tasks: estimation of pixel-wise velocity information and BEV segmentation. Based on the velocity and the occupancy score map obtained from the MFE module, the MGTF module aligns and fuses feature maps across multiple timestamps in a recurrent manner. By considering the motion of dynamic objects, CRT-Fusion can produce robust BEV feature maps, thereby improving detection accuracy and robustness. Extensive evaluations on the challenging nuScenes dataset demonstrate that CRT-Fusion achieves state-of-the-art performance for radar-camera-based 3D object detection. Our approach outperforms the previous best method in terms of NDS by +1.7%, while also surpassing the leading approach in mAP by +1.4%. These significant improvements in both metrics showcase the effectiveness of our proposed fusion strategy in enhancing the reliability and accuracy of 3D object detection.
JARViS: Detecting Actions in Video Using Unified Actor-Scene Context Relation Modeling
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:Video action detection (VAD) is a formidable vision task that involves the localization and classification of actions within the spatial and temporal dimensions of a video clip. Among the myriad VAD architectures, two-stage VAD methods utilize a pre-trained person detector to extract the region of interest features, subsequently employing these features for action detection. However, the performance of two-stage VAD methods has been limited as they depend solely on localized actor features to infer action semantics. In this study, we propose a new two-stage VAD framework called Joint Actor-scene context Relation modeling based on Visual Semantics (JARViS), which effectively consolidates cross-modal action semantics distributed globally across spatial and temporal dimensions using Transformer attention. JARViS employs a person detector to produce densely sampled actor features from a keyframe. Concurrently, it uses a video backbone to create spatio-temporal scene features from a video clip. Finally, the fine-grained interactions between actors and scenes are modeled through a Unified Action-Scene Context Transformer to directly output the final set of actions in parallel. Our experimental results demonstrate that JARViS outperforms existing methods by significant margins and achieves state-of-the-art performance on three popular VAD datasets, including AVA, UCF101-24, and JHMDB51-21.
Distribution-Aware Robust Learning from Long-Tailed Data with Noisy Labels
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:Deep neural networks have demonstrated remarkable advancements in various fields using large, well-annotated datasets. However, real-world data often exhibit long-tailed distributions and label noise, significantly degrading generalization performance. Recent studies addressing these issues have focused on noisy sample selection methods that estimate the centroid of each class based on high-confidence samples within each target class. The performance of these methods is limited because they use only the training samples within each class for class centroid estimation, making the quality of centroids susceptible to long-tailed distributions and noisy labels. In this study, we present a robust training framework called Distribution-aware Sample Selection and Contrastive Learning (DaSC). Specifically, DaSC introduces a Distribution-aware Class Centroid Estimation (DaCC) to generate enhanced class centroids. DaCC performs weighted averaging of the features from all samples, with weights determined based on model predictions. Additionally, we propose a confidence-aware contrastive learning strategy to obtain balanced and robust representations. The training samples are categorized into high-confidence and low-confidence samples. Our method then applies Semi-supervised Balanced Contrastive Loss (SBCL) using high-confidence samples, leveraging reliable label information to mitigate class bias. For the low-confidence samples, our method computes Mixup-enhanced Instance Discrimination Loss (MIDL) to improve their representations in a self-supervised manner. Our experimental results on CIFAR and real-world noisy-label datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed DaSC compared to previous approaches.
Mask2Map: Vectorized HD Map Construction Using Bird's Eye View Segmentation Masks
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Mask2Map, a novel end-to-end online HD map construction method designed for autonomous driving applications. Our approach focuses on predicting the class and ordered point set of map instances within a scene, represented in the bird's eye view (BEV). Mask2Map consists of two primary components: the Instance-Level Mask Prediction Network (IMPNet) and the Mask-Driven Map Prediction Network (MMPNet). IMPNet generates Mask-Aware Queries and BEV Segmentation Masks to capture comprehensive semantic information globally. Subsequently, MMPNet enhances these query features using local contextual information through two submodules: the Positional Query Generator (PQG) and the Geometric Feature Extractor (GFE). PQG extracts instance-level positional queries by embedding BEV positional information into Mask-Aware Queries, while GFE utilizes BEV Segmentation Masks to generate point-level geometric features. However, we observed limited performance in Mask2Map due to inter-network inconsistency stemming from different predictions to Ground Truth (GT) matching between IMPNet and MMPNet. To tackle this challenge, we propose the Inter-network Denoising Training method, which guides the model to denoise the output affected by both noisy GT queries and perturbed GT Segmentation Masks. Our evaluation conducted on nuScenes and Argoverse2 benchmarks demonstrates that Mask2Map achieves remarkable performance improvements over previous state-of-the-art methods, with gains of 10.1% mAP and 4.1 mAP, respectively. Our code can be found at https://github.com/SehwanChoi0307/Mask2Map.
Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation Using Target-Oriented Domain Augmentation for 3D Object Detection
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:3D object detection is crucial for applications like autonomous driving and robotics. However, in real-world environments, variations in sensor data distribution due to sensor upgrades, weather changes, and geographic differences can adversely affect detection performance. Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation (SSDA) aims to mitigate these challenges by transferring knowledge from a source domain, abundant in labeled data, to a target domain where labels are scarce. This paper presents a new SSDA method referred to as Target-Oriented Domain Augmentation (TODA) specifically tailored for LiDAR-based 3D object detection. TODA efficiently utilizes all available data, including labeled data in the source domain, and both labeled data and unlabeled data in the target domain to enhance domain adaptation performance. TODA consists of two stages: TargetMix and AdvMix. TargetMix employs mixing augmentation accounting for LiDAR sensor characteristics to facilitate feature alignment between the source-domain and target-domain. AdvMix applies point-wise adversarial augmentation with mixing augmentation, which perturbs the unlabeled data to align the features within both labeled and unlabeled data in the target domain. Our experiments conducted on the challenging domain adaptation tasks demonstrate that TODA outperforms existing domain adaptation techniques designed for 3D object detection by significant margins. The code is available at: https://github.com/rasd3/TODA.
Fine-Grained Pillar Feature Encoding Via Spatio-Temporal Virtual Grid for 3D Object Detection
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Developing high-performance, real-time architectures for LiDAR-based 3D object detectors is essential for the successful commercialization of autonomous vehicles. Pillar-based methods stand out as a practical choice for onboard deployment due to their computational efficiency. However, despite their efficiency, these methods can sometimes underperform compared to alternative point encoding techniques such as Voxel-encoding or PointNet++. We argue that current pillar-based methods have not sufficiently captured the fine-grained distributions of LiDAR points within each pillar structure. Consequently, there exists considerable room for improvement in pillar feature encoding. In this paper, we introduce a novel pillar encoding architecture referred to as Fine-Grained Pillar Feature Encoding (FG-PFE). FG-PFE utilizes Spatio-Temporal Virtual (STV) grids to capture the distribution of point clouds within each pillar across vertical, temporal, and horizontal dimensions. Through STV grids, points within each pillar are individually encoded using Vertical PFE (V-PFE), Temporal PFE (T-PFE), and Horizontal PFE (H-PFE). These encoded features are then aggregated through an Attentive Pillar Aggregation method. Our experiments conducted on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that FG-PFE achieves significant performance improvements over baseline models such as PointPillar, CenterPoint-Pillar, and PillarNet, with only a minor increase in computational overhead.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge