Yantuan Xian
Consensus-Aligned Neuron Efficient Fine-Tuning Large Language Models for Multi-Domain Machine Translation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multi-domain machine translation (MDMT) aims to build a unified model capable of translating content across diverse domains. Despite the impressive machine translation capabilities demonstrated by large language models (LLMs), domain adaptation still remains a challenge for LLMs. Existing MDMT methods such as in-context learning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning often suffer from domain shift, parameter interference and limited generalization. In this work, we propose a neuron-efficient fine-tuning framework for MDMT that identifies and updates consensus-aligned neurons within LLMs. These neurons are selected by maximizing the mutual information between neuron behavior and domain features, enabling LLMs to capture both generalizable translation patterns and domain-specific nuances. Our method then fine-tunes LLMs guided by these neurons, effectively mitigating parameter interference and domain-specific overfitting. Comprehensive experiments on three LLMs across ten German-English and Chinese-English translation domains evidence that our method consistently outperforms strong PEFT baselines on both seen and unseen domains, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Hyperspherical Graph Representation Learning via Adaptive Neighbor-Mean Alignment and Uniformity
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Graph representation learning (GRL) aims to encode structural and semantic dependencies of graph-structured data into low-dimensional embeddings. However, existing GRL methods often rely on surrogate contrastive objectives or mutual information maximization, which typically demand complex architectures, negative sampling strategies, and sensitive hyperparameter tuning. These design choices may induce over-smoothing, over-squashing, and training instability. In this work, we propose HyperGRL, a unified framework for hyperspherical graph representation learning via adaptive neighbor-mean alignment and sampling-free uniformity. HyperGRL embeds nodes on a unit hypersphere through two adversarially coupled objectives: neighbor-mean alignment and sampling-free uniformity. The alignment objective uses the mean representation of each node's local neighborhood to construct semantically grounded, stable targets that capture shared structural and feature patterns. The uniformity objective formulates dispersion via an L2-based hyperspherical regularization, encouraging globally uniform embedding distributions while preserving discriminative information. To further stabilize training, we introduce an entropy-guided adaptive balancing mechanism that dynamically regulates the interplay between alignment and uniformity without requiring manual tuning. Extensive experiments on node classification, node clustering, and link prediction demonstrate that HyperGRL delivers superior representation quality and generalization across diverse graph structures, achieving average improvements of 1.49%, 0.86%, and 0.74% over the strongest existing methods, respectively. These findings highlight the effectiveness of geometrically grounded, sampling-free contrastive objectives for graph representation learning.
Multilingual Generative Retrieval via Cross-lingual Semantic Compression
Oct 09, 2025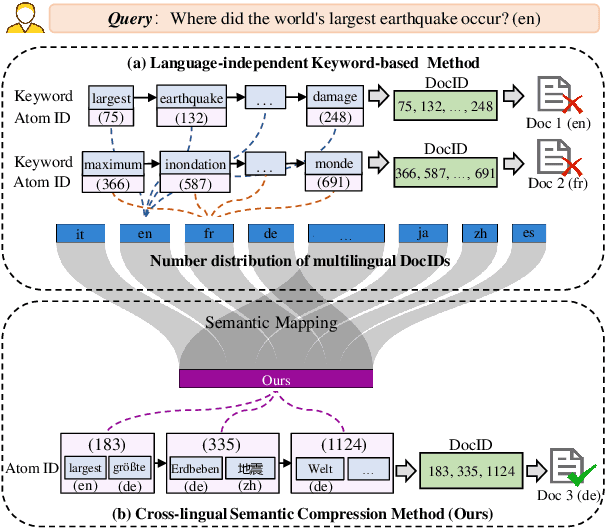
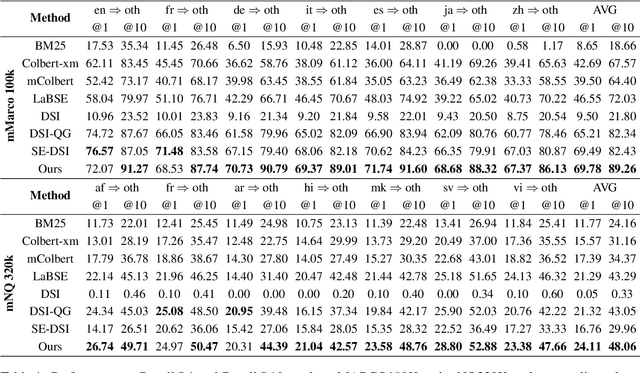
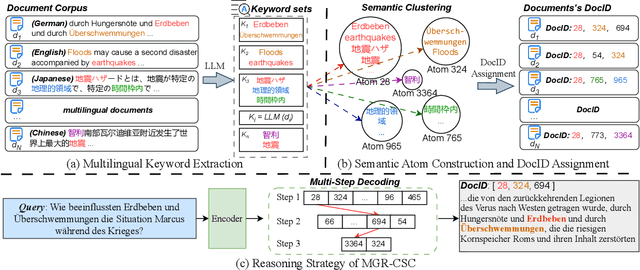

Abstract:Generative Information Retrieval is an emerging retrieval paradigm that exhibits remarkable performance in monolingual scenarios.However, applying these methods to multilingual retrieval still encounters two primary challenges, cross-lingual identifier misalignment and identifier inflation. To address these limitations, we propose Multilingual Generative Retrieval via Cross-lingual Semantic Compression (MGR-CSC), a novel framework that unifies semantically equivalent multilingual keywords into shared atoms to align semantics and compresses the identifier space, and we propose a dynamic multi-step constrained decoding strategy during retrieval. MGR-CSC improves cross-lingual alignment by assigning consistent identifiers and enhances decoding efficiency by reducing redundancy. Experiments demonstrate that MGR-CSC achieves outstanding retrieval accuracy, improving by 6.83% on mMarco100k and 4.77% on mNQ320k, while reducing document identifiers length by 74.51% and 78.2%, respectively.
Relational Prompt-based Pre-trained Language Models for Social Event Detection
Apr 12, 2024Abstract:Social Event Detection (SED) aims to identify significant events from social streams, and has a wide application ranging from public opinion analysis to risk management. In recent years, Graph Neural Network (GNN) based solutions have achieved state-of-the-art performance. However, GNN-based methods often struggle with noisy and missing edges between messages, affecting the quality of learned message embedding. Moreover, these methods statically initialize node embedding before training, which, in turn, limits the ability to learn from message texts and relations simultaneously. In this paper, we approach social event detection from a new perspective based on Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs), and present RPLM_SED (Relational prompt-based Pre-trained Language Models for Social Event Detection). We first propose a new pairwise message modeling strategy to construct social messages into message pairs with multi-relational sequences. Secondly, a new multi-relational prompt-based pairwise message learning mechanism is proposed to learn more comprehensive message representation from message pairs with multi-relational prompts using PLMs. Thirdly, we design a new clustering constraint to optimize the encoding process by enhancing intra-cluster compactness and inter-cluster dispersion, making the message representation more distinguishable. We evaluate the RPLM_SED on three real-world datasets, demonstrating that the RPLM_SED model achieves state-of-the-art performance in offline, online, low-resource, and long-tail distribution scenarios for social event detection tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge