Yann-Aël Le Borgne
Transfer Learning for Credit Card Fraud Detection: A Journey from Research to Production
Jul 20, 2021
Abstract:The dark face of digital commerce generalization is the increase of fraud attempts. To prevent any type of attacks, state of the art fraud detection systems are now embedding Machine Learning (ML) modules. The conception of such modules is only communicated at the level of research and papers mostly focus on results for isolated benchmark datasets and metrics. But research is only a part of the journey, preceded by the right formulation of the business problem and collection of data, and followed by a practical integration. In this paper, we give a wider vision of the process, on a case study of transfer learning for fraud detection, from business to research, and back to business.
Streaming Active Learning Strategies for Real-Life Credit Card Fraud Detection: Assessment and Visualization
Apr 20, 2018
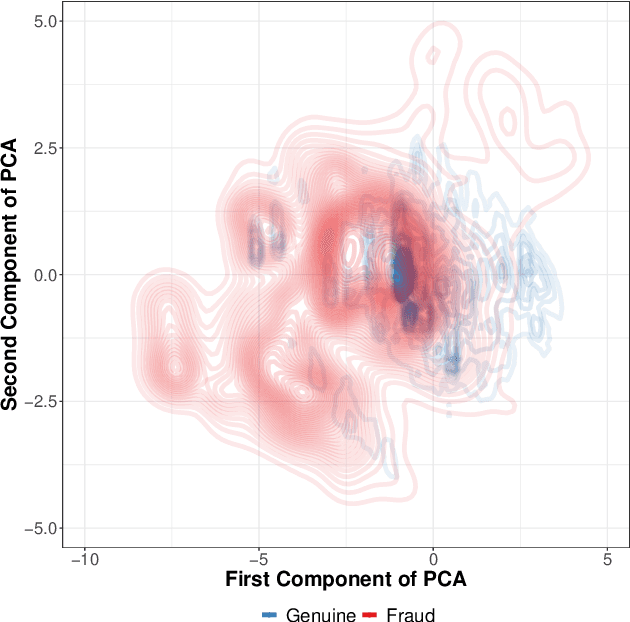

Abstract:Credit card fraud detection is a very challenging problem because of the specific nature of transaction data and the labeling process. The transaction data is peculiar because they are obtained in a streaming fashion, they are strongly imbalanced and prone to non-stationarity. The labeling is the outcome of an active learning process, as every day human investigators contact only a small number of cardholders (associated to the riskiest transactions) and obtain the class (fraud or genuine) of the related transactions. An adequate selection of the set of cardholders is therefore crucial for an efficient fraud detection process. In this paper, we present a number of active learning strategies and we investigate their fraud detection accuracies. We compare different criteria (supervised, semi-supervised and unsupervised) to query unlabeled transactions. Finally, we highlight the existence of an exploitation/exploration trade-off for active learning in the context of fraud detection, which has so far been overlooked in the literature.
Feature selection in high-dimensional dataset using MapReduce
Sep 07, 2017



Abstract:This paper describes a distributed MapReduce implementation of the minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance algorithm, a popular feature selection method in bioinformatics and network inference problems. The proposed approach handles both tall/narrow and wide/short datasets. We further provide an open source implementation based on Hadoop/Spark, and illustrate its scalability on datasets involving millions of observations or features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge