Xiuqing Mao
CE-based white-box adversarial attacks will not work using super-fitting
May 15, 2022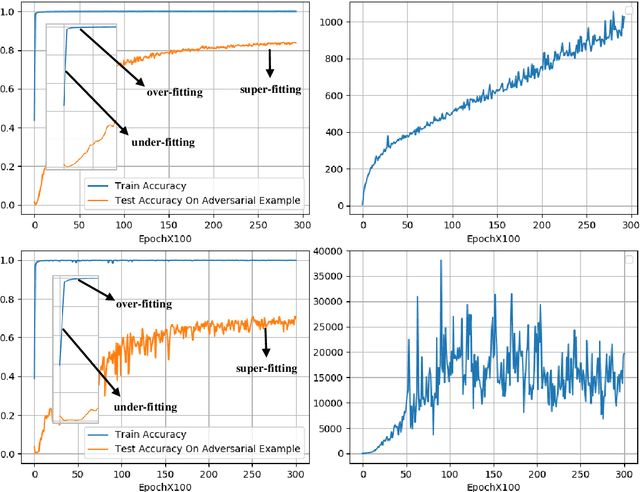
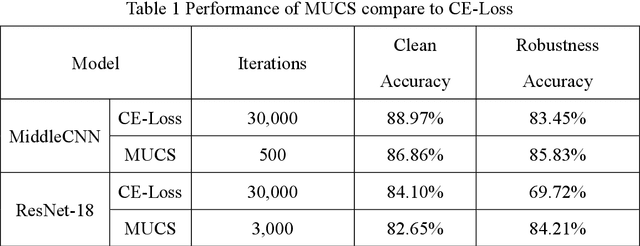
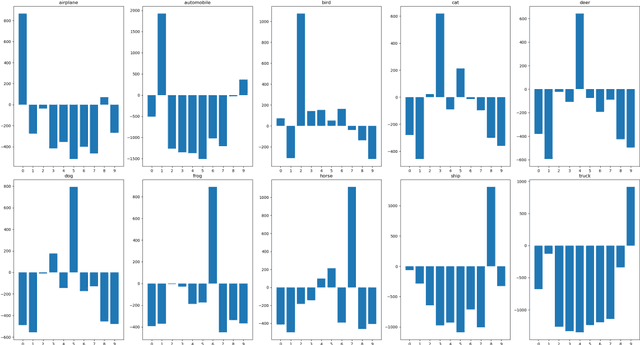
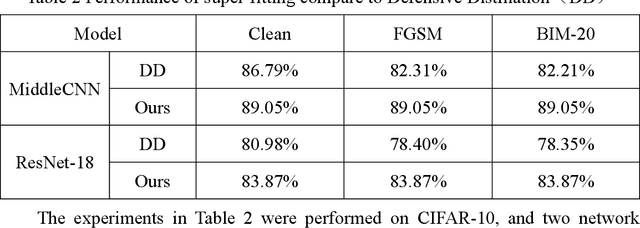
Abstract:Deep neural networks are widely used in various fields because of their powerful performance. However, recent studies have shown that deep learning models are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, i.e., adding a slight perturbation to the input will make the model obtain wrong results. This is especially dangerous for some systems with high-security requirements, so this paper proposes a new defense method by using the model super-fitting state to improve the model's adversarial robustness (i.e., the accuracy under adversarial attacks). This paper mathematically proves the effectiveness of super-fitting and enables the model to reach this state quickly by minimizing unrelated category scores (MUCS). Theoretically, super-fitting can resist any existing (even future) CE-based white-box adversarial attacks. In addition, this paper uses a variety of powerful attack algorithms to evaluate the adversarial robustness of super-fitting, and the proposed method is compared with nearly 50 defense models from recent conferences. The experimental results show that the super-fitting method in this paper can make the trained model obtain the highest adversarial robustness.
Rethinking Classifier and Adversarial Attack
May 14, 2022
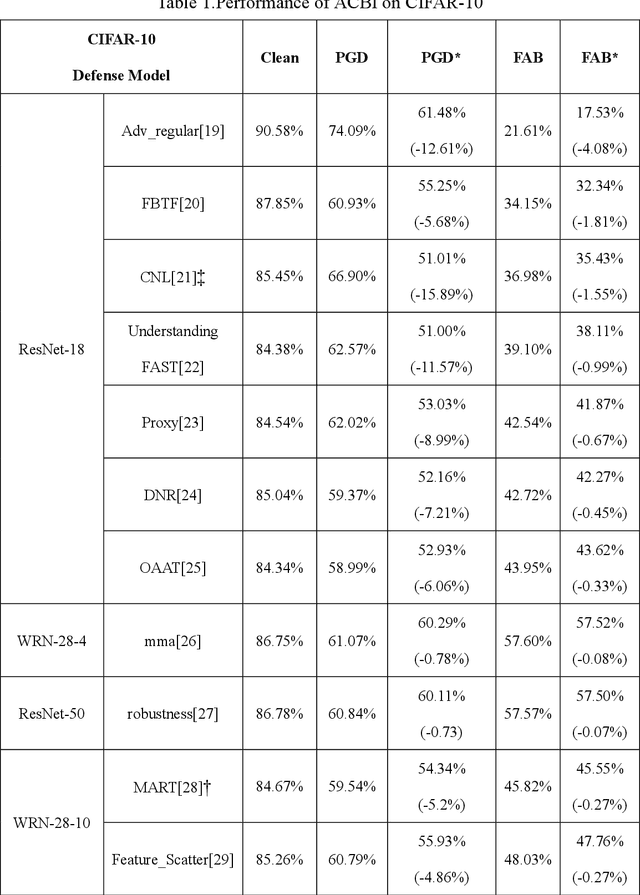
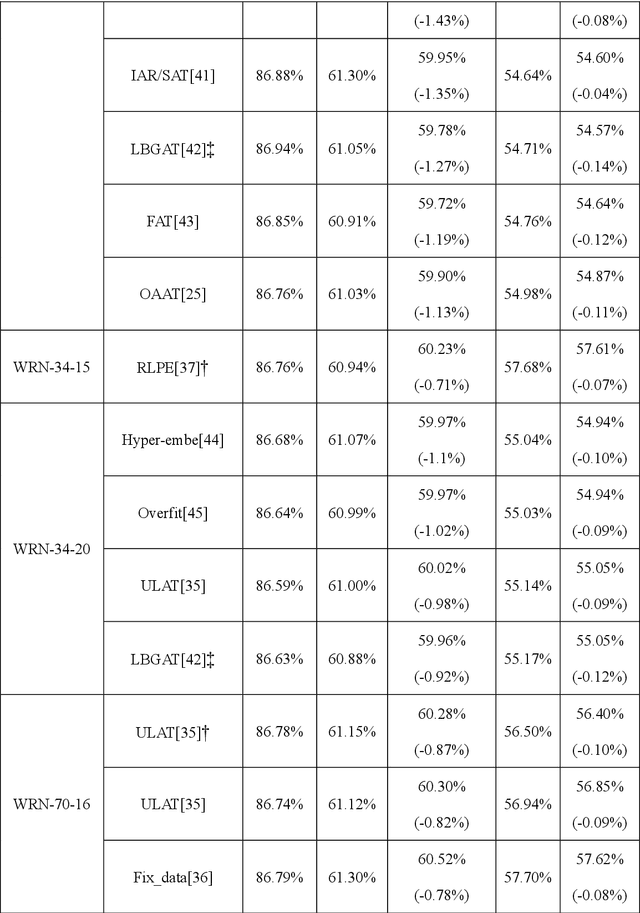
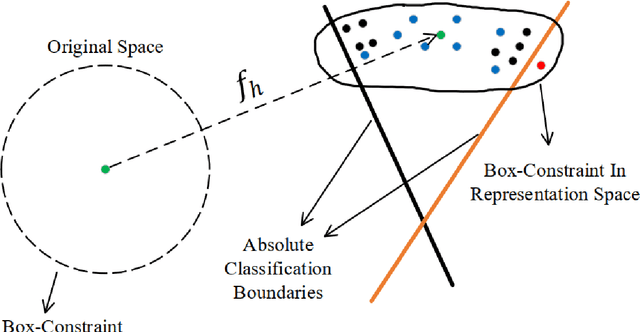
Abstract:Various defense models have been proposed to resist adversarial attack algorithms, but existing adversarial robustness evaluation methods always overestimate the adversarial robustness of these models (i.e., not approaching the lower bound of robustness). To solve this problem, this paper uses the proposed decouple space method to divide the classifier into two parts: non-linear and linear. Then, this paper defines the representation vector of the original example (and its space, i.e., the representation space) and uses the iterative optimization of Absolute Classification Boundaries Initialization (ACBI) to obtain a better attack starting point. Particularly, this paper applies ACBI to nearly 50 widely-used defense models (including 8 architectures). Experimental results show that ACBI achieves lower robust accuracy in all cases.
Metric Learning for Anti-Compression Facial Forgery Detection
Mar 15, 2021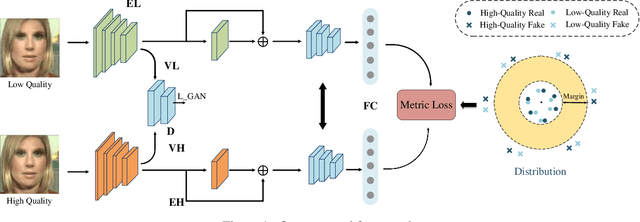
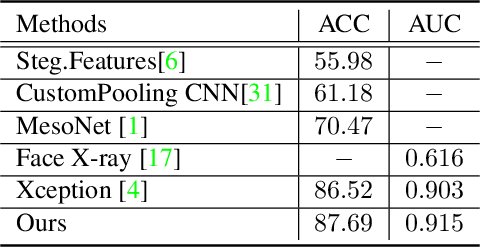
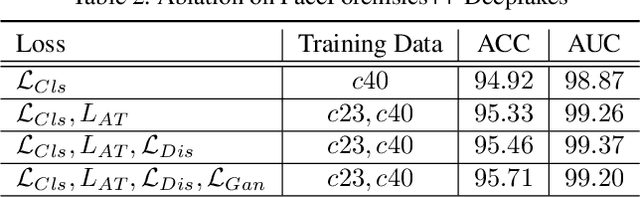
Abstract:Detecting facial forgery images and videos is an increasingly important topic in multimedia forensics. As forgery images and videos are usually compressed to different formats such as JPEG and H264 when circulating on the Internet, existing forgery-detection methods trained on uncompressed data often have significantly decreased performance in identifying them. To solve this problem, we propose a novel anti-compression facial forgery detection framework, which learns a compression-insensitive embedding feature space utilizing both original and compressed forgeries. Specifically, our approach consists of two novel ideas: (i) extracting compression-insensitive features from both uncompressed and compressed forgeries using an adversarial learning strategy; (ii) learning a robust partition by constructing a metric loss that can reduce the distance of the paired original and compressed images in the embedding space. Experimental results demonstrate that, the proposed method is highly effective in handling both compressed and uncompressed facial forgery images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge