Xinle Liang
Self-supervised Cross-silo Federated Neural Architecture Search
Feb 18, 2021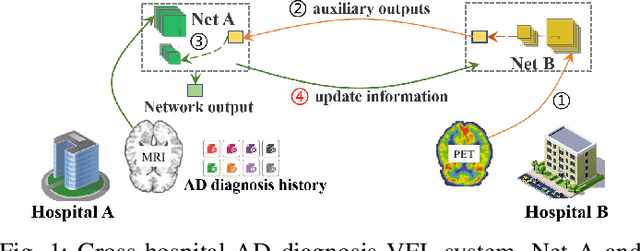
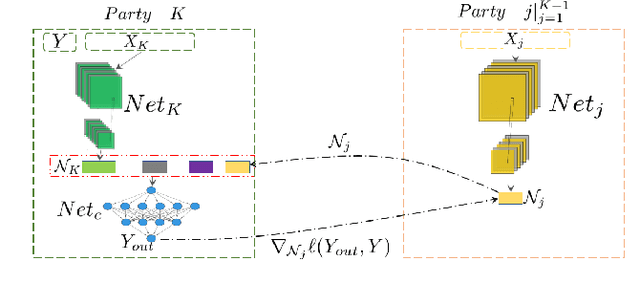
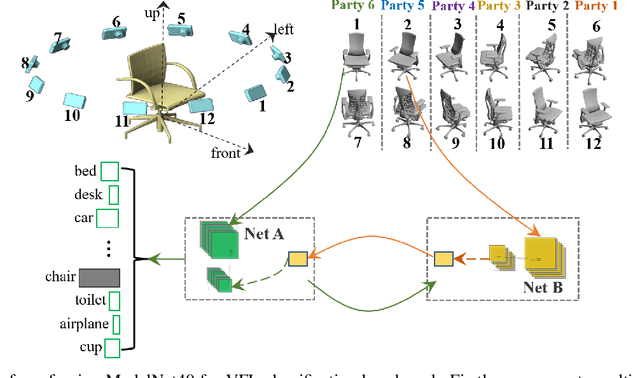
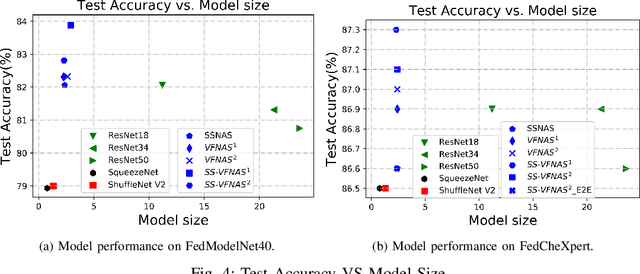
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) provides both model performance and data privacy for machine learning tasks where samples or features are distributed among different parties. In the training process of FL, no party has a global view of data distributions or model architectures of other parties. Thus the manually-designed architectures may not be optimal. In the past, Neural Architecture Search (NAS) has been applied to FL to address this critical issue. However, existing Federated NAS approaches require prohibitive communication and computation effort, as well as the availability of high-quality labels. In this work, we present Self-supervised Vertical Federated Neural Architecture Search (SS-VFNAS) for automating FL where participants hold feature-partitioned data, a common cross-silo scenario called Vertical Federated Learning (VFL). In the proposed framework, each party first conducts NAS using self-supervised approach to find a local optimal architecture with its own data. Then, parties collaboratively improve the local optimal architecture in a VFL framework with supervision. We demonstrate experimentally that our approach has superior performance, communication efficiency and privacy compared to Federated NAS and is capable of generating high-performance and highly-transferable heterogeneous architectures even with insufficient overlapping samples, providing automation for those parties without deep learning expertise.
Federated Transfer Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving
Oct 14, 2019


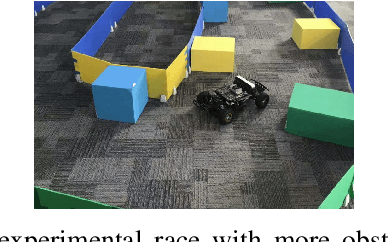
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is widely used in autonomous driving tasks and training RL models typically involves in a multi-step process: pre-training RL models on simulators, uploading the pre-trained model to real-life robots, and fine-tuning the weight parameters on robot vehicles. This sequential process is extremely time-consuming and more importantly, knowledge from the fine-tuned model stays local and can not be re-used or leveraged collaboratively. To tackle this problem, we present an online federated RL transfer process for real-time knowledge extraction where all the participant agents make corresponding actions with the knowledge learned by others, even when they are acting in very different environments. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, we constructed a real-life collision avoidance system with Microsoft Airsim simulator and NVIDIA JetsonTX2 car agents, which cooperatively learn from scratch to avoid collisions in indoor environment with obstacle objects. We demonstrate that with the proposed framework, the simulator car agents can transfer knowledge to the RC cars in real-time, with 27% increase in the average distance with obstacles and 42% decrease in the collision counts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge