Xiaoyu Geng
Tensor Robust PCA with Nonconvex and Nonlocal Regularization
Nov 04, 2022Abstract:Tensor robust principal component analysis (TRPCA) is a promising way for low-rank tensor recovery, which minimizes the convex surrogate of tensor rank by shrinking each tensor singular values equally. However, for real-world visual data, large singular values represent more signifiant information than small singular values. In this paper, we propose a nonconvex TRPCA (N-TRPCA) model based on the tensor adjustable logarithmic norm. Unlike TRPCA, our N-TRPCA can adaptively shrink small singular values more and shrink large singular values less. In addition, TRPCA assumes that the whole data tensor is of low rank. This assumption is hardly satisfied in practice for natural visual data, restricting the capability of TRPCA to recover the edges and texture details from noisy images and videos. To this end, we integrate nonlocal self-similarity into N-TRPCA, and further develop a nonconvex and nonlocal TRPCA (NN-TRPCA) model. Specifically, similar nonlocal patches are grouped as a tensor and then each group tensor is recovered by our N-TRPCA. Since the patches in one group are highly correlated, all group tensors have strong low-rank property, leading to an improvement of recovery performance. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed NN-TRPCA outperforms some existing TRPCA methods in visual data recovery. The demo code is available at https://github.com/qguo2010/NN-TRPCA.
How to Simplify Search: Classification-wise Pareto Evolution for One-shot Neural Architecture Search
Sep 14, 2021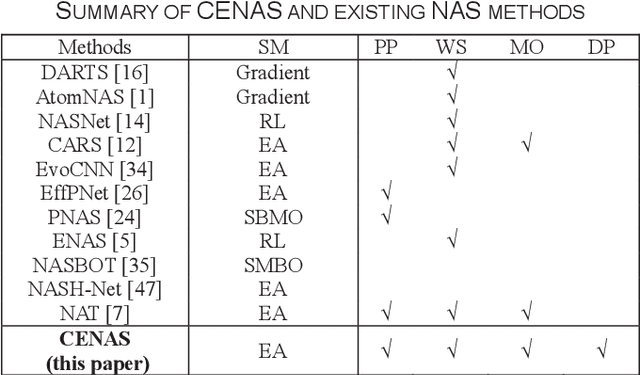
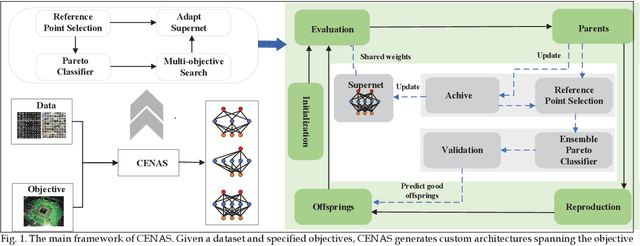
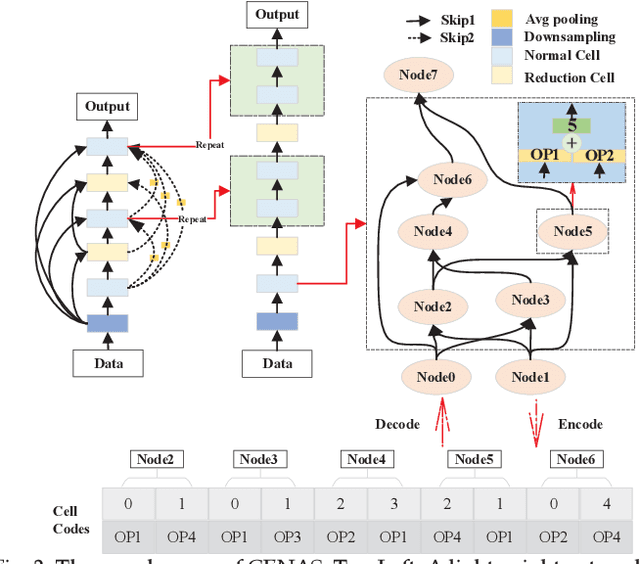
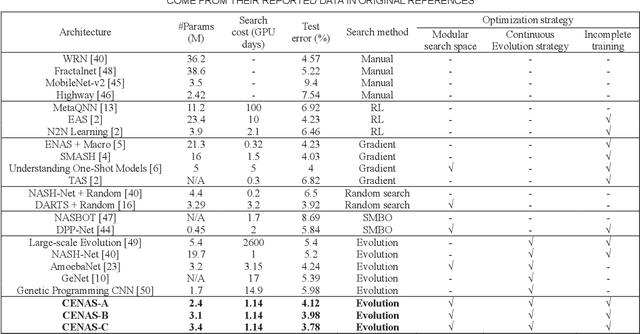
Abstract:In the deployment of deep neural models, how to effectively and automatically find feasible deep models under diverse design objectives is fundamental. Most existing neural architecture search (NAS) methods utilize surrogates to predict the detailed performance (e.g., accuracy and model size) of a candidate architecture during the search, which however is complicated and inefficient. In contrast, we aim to learn an efficient Pareto classifier to simplify the search process of NAS by transforming the complex multi-objective NAS task into a simple Pareto-dominance classification task. To this end, we propose a classification-wise Pareto evolution approach for one-shot NAS, where an online classifier is trained to predict the dominance relationship between the candidate and constructed reference architectures, instead of using surrogates to fit the objective functions. The main contribution of this study is to change supernet adaption into a Pareto classifier. Besides, we design two adaptive schemes to select the reference set of architectures for constructing classification boundary and regulate the rate of positive samples over negative ones, respectively. We compare the proposed evolution approach with state-of-the-art approaches on widely-used benchmark datasets, and experimental results indicate that the proposed approach outperforms other approaches and have found a number of neural architectures with different model sizes ranging from 2M to 6M under diverse objectives and constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge