Xiaoxia Gao
Garment Inertial Denoiser (GID): Endowing Accurate Motion Capture via Loose IMU Denoiser
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Wearable inertial motion capture (MoCap) provides a portable, occlusion-free, and privacy-preserving alternative to camera-based systems, but its accuracy depends on tightly attached sensors - an intrusive and uncomfortable requirement for daily use. Embedding IMUs into loose-fitting garments is a desirable alternative, yet sensor-body displacement introduces severe, structured, and location-dependent corruption that breaks standard inertial pipelines. We propose GID (Garment Inertial Denoiser), a lightweight, plug-and-play Transformer that factorizes loose-wear MoCap into three stages: (i) location-specific denoising, (ii) adaptive cross-wear fusion, and (iii) general pose prediction. GID uses a location-aware expert architecture, where a shared spatio-temporal backbone models global motion while per-IMU expert heads specialize in local garment dynamics, and a lightweight fusion module ensures cross-part consistency. This inductive bias enables stable training and effective learning from limited paired loose-tight IMU data. We also introduce GarMoCap, a combined public and newly collected dataset covering diverse users, motions, and garments. Experiments show that GID enables accurate, real-time denoising from single-user training and generalizes across unseen users, motions, and garment types, consistently improving state-of-the-art inertial MoCap methods when used as a drop-in module.
SuDA: Support-based Domain Adaptation for Sim2Real Motion Capture with Flexible Sensors
May 25, 2024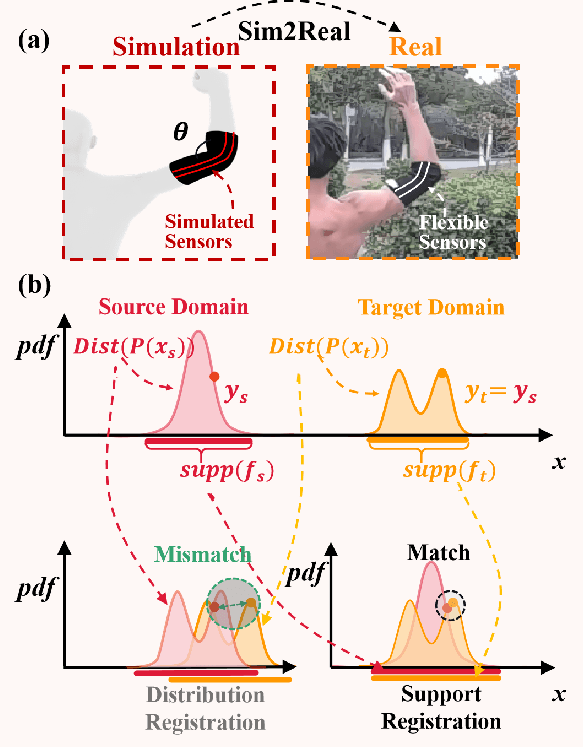
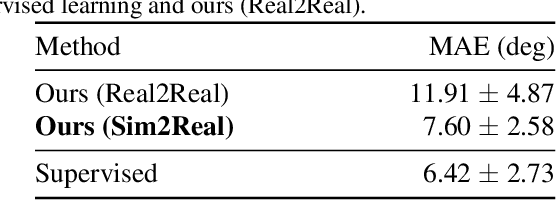
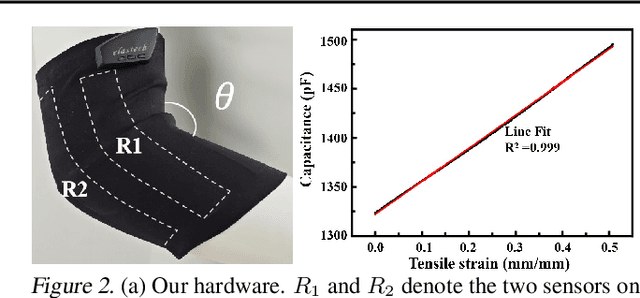
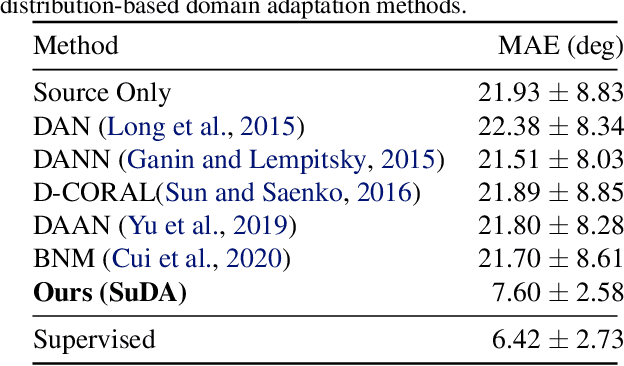
Abstract:Flexible sensors hold promise for human motion capture (MoCap), offering advantages such as wearability, privacy preservation, and minimal constraints on natural movement. However, existing flexible sensor-based MoCap methods rely on deep learning and necessitate large and diverse labeled datasets for training. These data typically need to be collected in MoCap studios with specialized equipment and substantial manual labor, making them difficult and expensive to obtain at scale. Thanks to the high-linearity of flexible sensors, we address this challenge by proposing a novel Sim2Real Mocap solution based on domain adaptation, eliminating the need for labeled data yet achieving comparable accuracy to supervised learning. Our solution relies on a novel Support-based Domain Adaptation method, namely SuDA, which aligns the supports of the predictive functions rather than the instance-dependent distributions between the source and target domains. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method andits superiority over state-of-the-art distribution-based domain adaptation methods in our task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge