Xiaowo Wang
Interpretable Clustering with Adaptive Heterogeneous Causal Structure Learning in Mixed Observational Data
Sep 04, 2025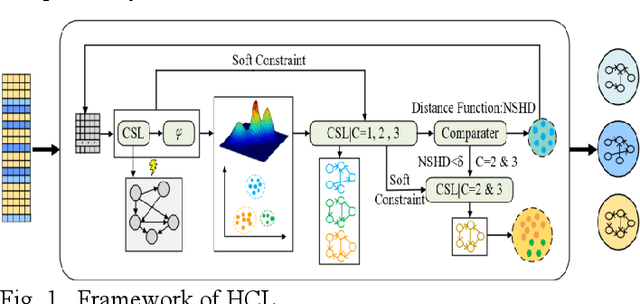
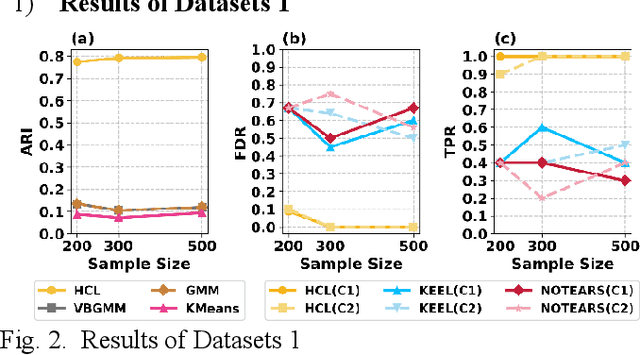
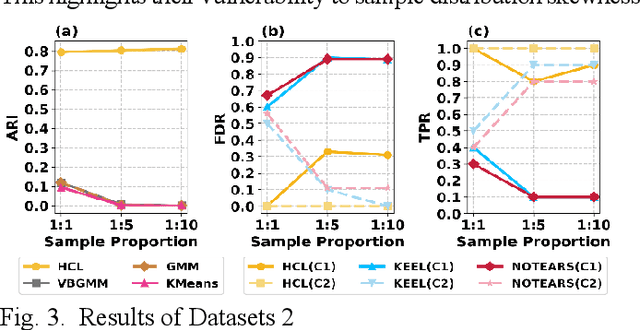
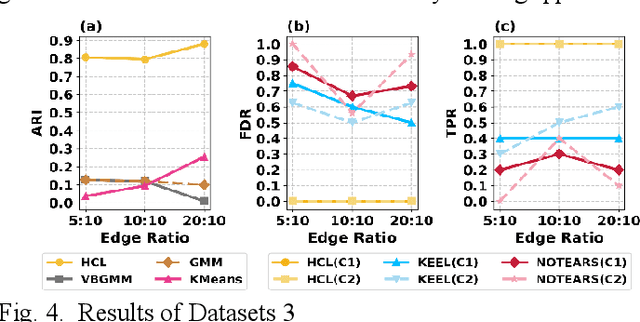
Abstract:Understanding causal heterogeneity is essential for scientific discovery in domains such as biology and medicine. However, existing methods lack causal awareness, with insufficient modeling of heterogeneity, confounding, and observational constraints, leading to poor interpretability and difficulty distinguishing true causal heterogeneity from spurious associations. We propose an unsupervised framework, HCL (Interpretable Causal Mechanism-Aware Clustering with Adaptive Heterogeneous Causal Structure Learning), that jointly infers latent clusters and their associated causal structures from mixed-type observational data without requiring temporal ordering, environment labels, interventions or other prior knowledge. HCL relaxes the homogeneity and sufficiency assumptions by introducing an equivalent representation that encodes both structural heterogeneity and confounding. It further develops a bi-directional iterative strategy to alternately refine causal clustering and structure learning, along with a self-supervised regularization that balance cross-cluster universality and specificity. Together, these components enable convergence toward interpretable, heterogeneous causal patterns. Theoretically, we show identifiability of heterogeneous causal structures under mild conditions. Empirically, HCL achieves superior performance in both clustering and structure learning tasks, and recovers biologically meaningful mechanisms in real-world single-cell perturbation data, demonstrating its utility for discovering interpretable, mechanism-level causal heterogeneity.
Non-contact Dexterous Micromanipulation with Multiple Optoelectronic Robots
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Micromanipulation systems leverage automation and robotic technologies to improve the precision, repeatability, and efficiency of various tasks at the microscale. However, current approaches are typically limited to specific objects or tasks, which necessitates the use of custom tools and specialized grasping methods. This paper proposes a novel non-contact micromanipulation method based on optoelectronic technologies. The proposed method utilizes repulsive dielectrophoretic forces generated in the optoelectronic field to drive a microrobot, enabling the microrobot to push the target object in a cluttered environment without physical contact. The non-contact feature can minimize the risks of potential damage, contamination, or adhesion while largely improving the flexibility of manipulation. The feature enables the use of a general tool for indirect object manipulation, eliminating the need for specialized tools. A series of simulation studies and real-world experiments -- including non-contact trajectory tracking, obstacle avoidance, and reciprocal avoidance between multiple microrobots -- are conducted to validate the performance of the proposed method. The proposed formulation provides a general and dexterous solution for a range of objects and tasks at the micro scale.
Weakly-supervised causal discovery based on fuzzy knowledge and complex data complementarity
May 14, 2024Abstract:Causal discovery based on observational data is important for deciphering the causal mechanism behind complex systems. However, the effectiveness of existing causal discovery methods is limited due to inferior prior knowledge, domain inconsistencies, and the challenges of high-dimensional datasets with small sample sizes. To address this gap, we propose a novel weakly-supervised fuzzy knowledge and data co-driven causal discovery method named KEEL. KEEL adopts a fuzzy causal knowledge schema to encapsulate diverse types of fuzzy knowledge, and forms corresponding weakened constraints. This schema not only lessens the dependency on expertise but also allows various types of limited and error-prone fuzzy knowledge to guide causal discovery. It can enhance the generalization and robustness of causal discovery, especially in high-dimensional and small-sample scenarios. In addition, we integrate the extended linear causal model (ELCM) into KEEL for dealing with the multi-distribution and incomplete data. Extensive experiments with different datasets demonstrate the superiority of KEEL over several state-of-the-art methods in accuracy, robustness and computational efficiency. For causal discovery in real protein signal transduction processes, KEEL outperforms the benchmark method with limited data. In summary, KEEL is effective to tackle the causal discovery tasks with higher accuracy while alleviating the requirement for extensive domain expertise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge