Xiaosheng Yu
Bridging the Inter-Domain Gap through Low-Level Features for Cross-Modal Medical Image Segmentation
May 17, 2025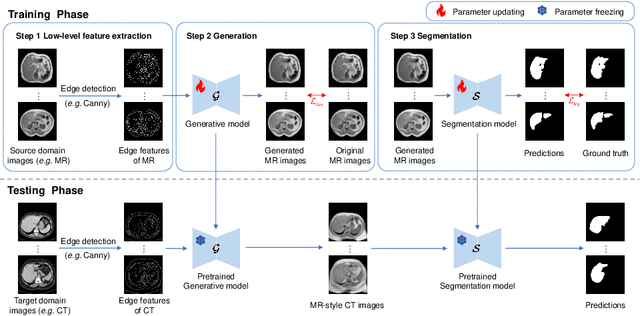
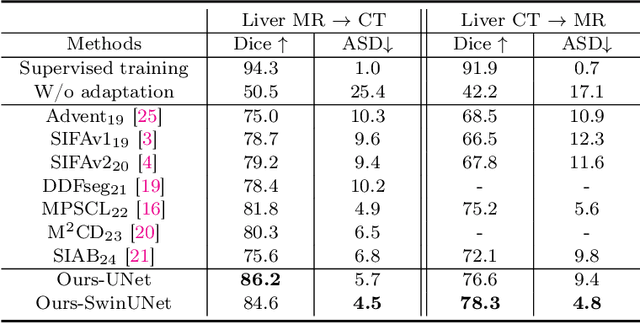
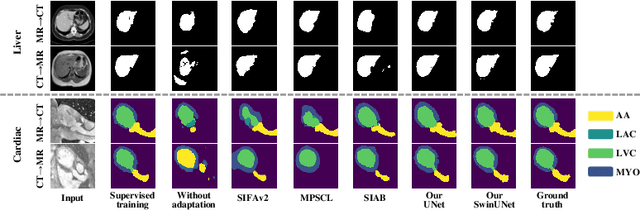
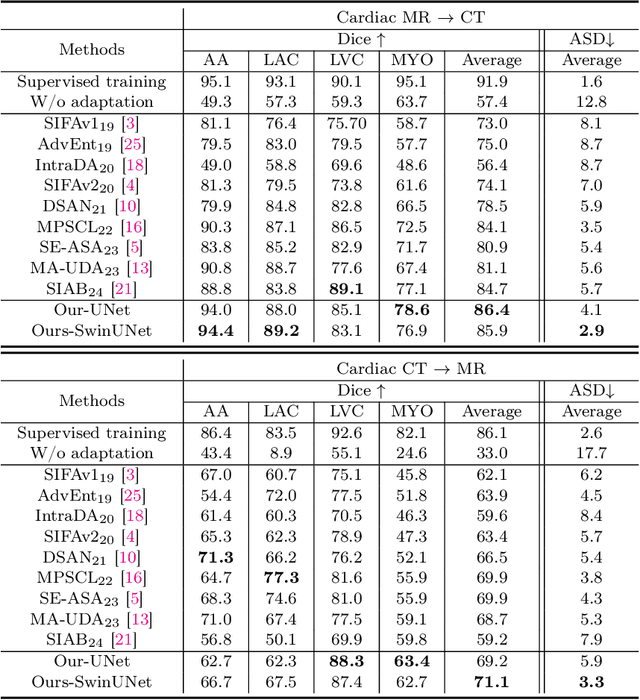
Abstract:This paper addresses the task of cross-modal medical image segmentation by exploring unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) approaches. We propose a model-agnostic UDA framework, LowBridge, which builds on a simple observation that cross-modal images share some similar low-level features (e.g., edges) as they are depicting the same structures. Specifically, we first train a generative model to recover the source images from their edge features, followed by training a segmentation model on the generated source images, separately. At test time, edge features from the target images are input to the pretrained generative model to generate source-style target domain images, which are then segmented using the pretrained segmentation network. Despite its simplicity, extensive experiments on various publicly available datasets demonstrate that \proposed achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming eleven existing UDA approaches under different settings. Notably, further ablation studies show that \proposed is agnostic to different types of generative and segmentation models, suggesting its potential to be seamlessly plugged with the most advanced models to achieve even more outstanding results in the future. The code is available at https://github.com/JoshuaLPF/LowBridge.
Weakly Supervised Segmentation Framework for Thyroid Nodule Based on High-confidence Labels and High-rationality Losses
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Weakly supervised segmentation methods can delineate thyroid nodules in ultrasound images efficiently using training data with coarse labels, but suffer from: 1) low-confidence pseudo-labels that follow topological priors, introducing significant label noise, and 2) low-rationality loss functions that rigidly compare segmentation with labels, ignoring discriminative information for nodules with diverse and complex shapes. To solve these issues, we clarify the objective and references for weakly supervised ultrasound image segmentation, presenting a framework with high-confidence pseudo-labels to represent topological and anatomical information and high-rationality losses to capture multi-level discriminative features. Specifically, we fuse geometric transformations of four-point annotations and MedSAM model results prompted by specific annotations to generate high-confidence box, foreground, and background labels. Our high-rationality learning strategy includes: 1) Alignment loss measuring spatial consistency between segmentation and box label, and topological continuity within the foreground label, guiding the network to perceive nodule location; 2) Contrastive loss pulling features from labeled foreground regions while pushing features from labeled foreground and background regions, guiding the network to learn nodule and background feature distribution; 3) Prototype correlation loss measuring consistency between correlation maps derived by comparing features with foreground and background prototypes, refining uncertain regions to accurate nodule edges. Experimental results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the TN3K and DDTI datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/bluehenglee/MLI-MSC.
Deep Fourier-embedded Network for Bi-modal Salient Object Detection
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:The rapid development of deep learning provides a significant improvement of salient object detection combining both RGB and thermal images. However, existing deep learning-based models suffer from two major shortcomings. First, the computation and memory demands of Transformer-based models with quadratic complexity are unbearable, especially in handling high-resolution bi-modal feature fusion. Second, even if learning converges to an ideal solution, there remains a frequency gap between the prediction and ground truth. Therefore, we propose a purely fast Fourier transform-based model, namely deep Fourier-embedded network (DFENet), for learning bi-modal information of RGB and thermal images. On one hand, fast Fourier transform efficiently fetches global dependencies with low complexity. Inspired by this, we design modal-coordinated perception attention to fuse the frequency gap between RGB and thermal modalities with multi-dimensional representation enhancement. To obtain reliable detailed information during decoding, we design the frequency-decomposed edge-aware module (FEM) to clarify object edges by deeply decomposing low-level features. Moreover, we equip proposed Fourier residual channel attention block in each decoder layer to prioritize high-frequency information while aligning channel global relationships. On the other hand, we propose co-focus frequency loss (CFL) to steer FEM towards minimizing the frequency gap. CFL dynamically weights hard frequencies during edge frequency reconstruction by cross-referencing the bi-modal edge information in the Fourier domain. This frequency-level refinement of edge features further contributes to the quality of the final pixel-level prediction. Extensive experiments on four bi-modal salient object detection benchmark datasets demonstrate our proposed DFENet outperforms twelve existing state-of-the-art models.
Efficient Fourier Filtering Network with Contrastive Learning for UAV-based Unaligned Bi-modal Salient Object Detection
Nov 06, 2024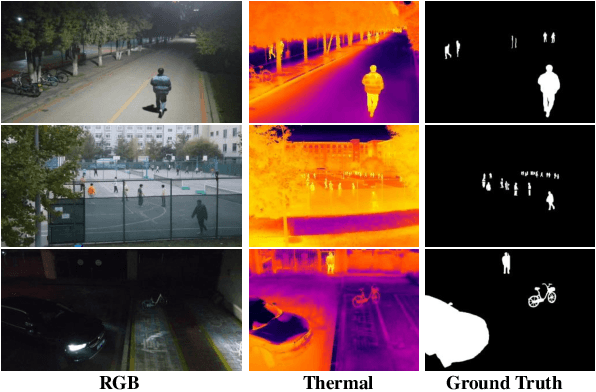
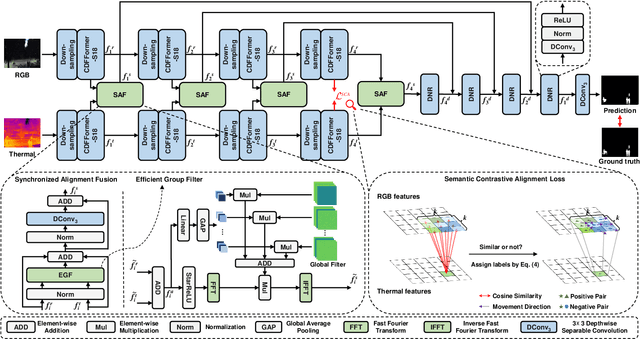
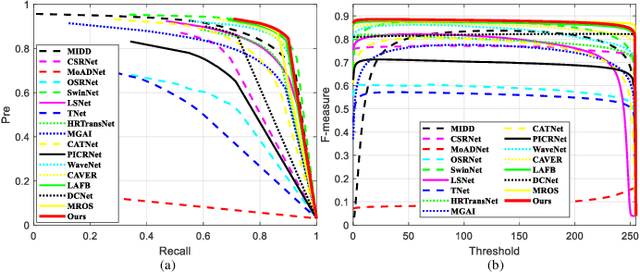

Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based bi-modal salient object detection (BSOD) aims to segment salient objects in a scene utilizing complementary cues in unaligned RGB and thermal image pairs. However, the high computational expense of existing UAV-based BSOD models limits their applicability to real-world UAV devices. To address this problem, we propose an efficient Fourier filter network with contrastive learning that achieves both real-time and accurate performance. Specifically, we first design a semantic contrastive alignment loss to align the two modalities at the semantic level, which facilitates mutual refinement in a parameter-free way. Second, inspired by the fast Fourier transform that obtains global relevance in linear complexity, we propose synchronized alignment fusion, which aligns and fuses bi-modal features in the channel and spatial dimensions by a hierarchical filtering mechanism. Our proposed model, AlignSal, reduces the number of parameters by 70.0%, decreases the floating point operations by 49.4%, and increases the inference speed by 152.5% compared to the cutting-edge BSOD model (i.e., MROS). Extensive experiments on the UAV RGB-T 2400 and three weakly aligned datasets demonstrate that AlignSal achieves both real-time inference speed and better performance and generalizability compared to sixteen state-of-the-art BSOD models across most evaluation metrics. In addition, our ablation studies further verify AlignSal's potential in boosting the performance of existing aligned BSOD models on UAV-based unaligned data. The code is available at: https://github.com/JoshuaLPF/AlignSal.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge