Xiangfu Song
LicenseGPT: A Fine-tuned Foundation Model for Publicly Available Dataset License Compliance
Dec 30, 2024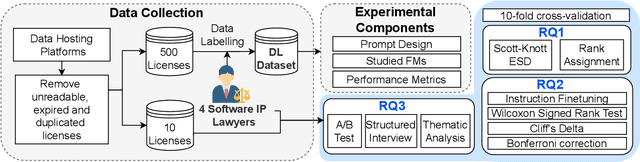
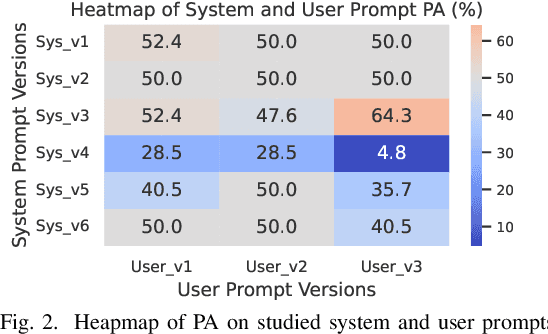

Abstract:Dataset license compliance is a critical yet complex aspect of developing commercial AI products, particularly with the increasing use of publicly available datasets. Ambiguities in dataset licenses pose significant legal risks, making it challenging even for software IP lawyers to accurately interpret rights and obligations. In this paper, we introduce LicenseGPT, a fine-tuned foundation model (FM) specifically designed for dataset license compliance analysis. We first evaluate existing legal FMs (i.e., FMs specialized in understanding and processing legal texts) and find that the best-performing model achieves a Prediction Agreement (PA) of only 43.75%. LicenseGPT, fine-tuned on a curated dataset of 500 licenses annotated by legal experts, significantly improves PA to 64.30%, outperforming both legal and general-purpose FMs. Through an A/B test and user study with software IP lawyers, we demonstrate that LicenseGPT reduces analysis time by 94.44%, from 108 seconds to 6 seconds per license, without compromising accuracy. Software IP lawyers perceive LicenseGPT as a valuable supplementary tool that enhances efficiency while acknowledging the need for human oversight in complex cases. Our work underscores the potential of specialized AI tools in legal practice and offers a publicly available resource for practitioners and researchers.
Beyond Statistical Estimation: Differentially Private Individual Computation in the Shuffle Model
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:The shuffle model of differential privacy (DP) has recently emerged as a powerful one for decentralized computation without fully trustable parties. Since it anonymizes and permutes messages from clients through a shuffler, the privacy can be amplified and utility can be improved. However, the shuffling procedure in turn restricts its applications only to statistical tasks that are permutation-invariant. This work explores the feasibility of shuffle privacy amplification for prevalent non-statistical computations: spatial crowdsourcing, combinatorial optimization, location-based social systems, and federated learning with incentives, which suffer either computationally intractability or intolerable utility loss in existing approaches (e.g., secure MPC and local DP). We proposes a new paradigm of shuffle model that can provide critical security functionalities like message authorization and result access control, meanwhile maintaining the most of privacy amplification effects. It incurs almost the same computation/communication costs as the non-private setting, and permits the server to run arbitrary algorithms on (noisy) client information in plaintext. Our novel technique is introducing statistically random identity into DP and force identical random distribution on all clients, so as to support secure functionalities even after message shuffling and to maintain privacy amplification simultaneously. Given that existing DP randomizers fails in the new shuffle model, we also propose a new mechanism and prove its optimality therein. Experimental results on spatial crowdsourcing, location-based social system, and federated learning with incentives, show that our paradigm and mechanism is fast as non-private settings, while reducing up to 90% error and increasing utility performance indicates by 100%-300% relatively, and can be practical under reasonable privacy budget.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge