Xavier Thomas
What's in a Latent? Leveraging Diffusion Latent Space for Domain Generalization
Mar 09, 2025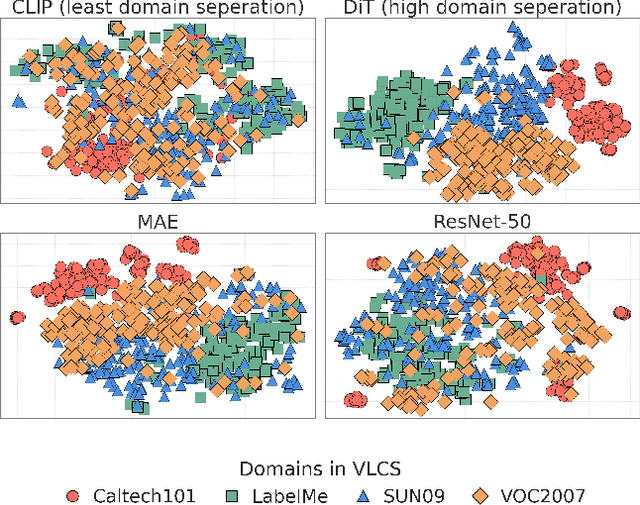


Abstract:Domain Generalization aims to develop models that can generalize to novel and unseen data distributions. In this work, we study how model architectures and pre-training objectives impact feature richness and propose a method to effectively leverage them for domain generalization. Specifically, given a pre-trained feature space, we first discover latent domain structures, referred to as pseudo-domains, that capture domain-specific variations in an unsupervised manner. Next, we augment existing classifiers with these complementary pseudo-domain representations making them more amenable to diverse unseen test domains. We analyze how different pre-training feature spaces differ in the domain-specific variances they capture. Our empirical studies reveal that features from diffusion models excel at separating domains in the absence of explicit domain labels and capture nuanced domain-specific information. On 5 datasets, we show that our very simple framework improves generalization to unseen domains by a maximum test accuracy improvement of over 4% compared to the standard baseline Empirical Risk Minimization (ERM). Crucially, our method outperforms most algorithms that access domain labels during training.
$\textit{Revelio}$: Interpreting and leveraging semantic information in diffusion models
Nov 23, 2024

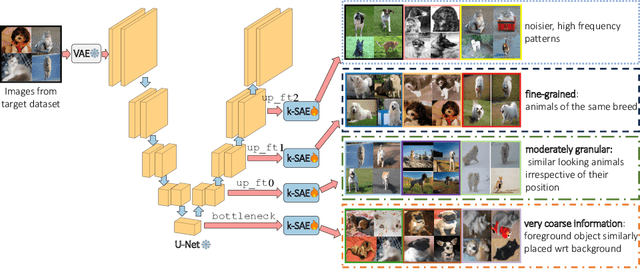

Abstract:We study $\textit{how}$ rich visual semantic information is represented within various layers and denoising timesteps of different diffusion architectures. We uncover monosemantic interpretable features by leveraging k-sparse autoencoders (k-SAE). We substantiate our mechanistic interpretations via transfer learning using light-weight classifiers on off-the-shelf diffusion models' features. On $4$ datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness of diffusion features for representation learning. We provide in-depth analysis of how different diffusion architectures, pre-training datasets, and language model conditioning impacts visual representation granularity, inductive biases, and transfer learning capabilities. Our work is a critical step towards deepening interpretability of black-box diffusion models. Code and visualizations available at: https://github.com/revelio-diffusion/revelio
MAViC: Multimodal Active Learning for Video Captioning
Dec 11, 2022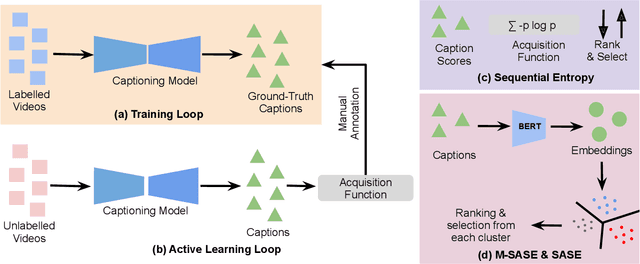

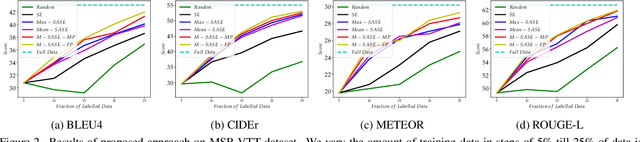
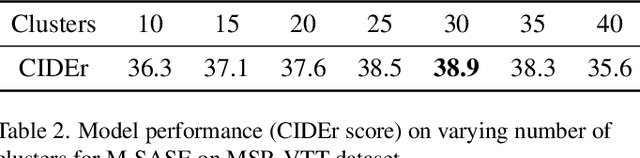
Abstract:A large number of annotated video-caption pairs are required for training video captioning models, resulting in high annotation costs. Active learning can be instrumental in reducing these annotation requirements. However, active learning for video captioning is challenging because multiple semantically similar captions are valid for a video, resulting in high entropy outputs even for less-informative samples. Moreover, video captioning algorithms are multimodal in nature with a visual encoder and language decoder. Further, the sequential and combinatorial nature of the output makes the problem even more challenging. In this paper, we introduce MAViC which leverages our proposed Multimodal Semantics Aware Sequential Entropy (M-SASE) based acquisition function to address the challenges of active learning approaches for video captioning. Our approach integrates semantic similarity and uncertainty of both visual and language dimensions in the acquisition function. Our detailed experiments empirically demonstrate the efficacy of M-SASE for active learning for video captioning and improve on the baselines by a large margin.
Diversity vs. Recognizability: Human-like generalization in one-shot generative models
May 20, 2022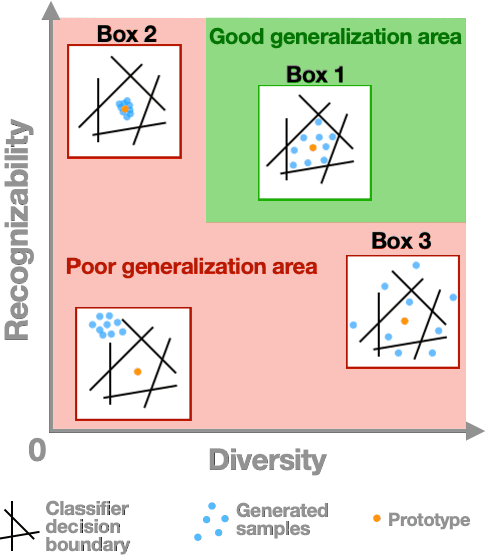

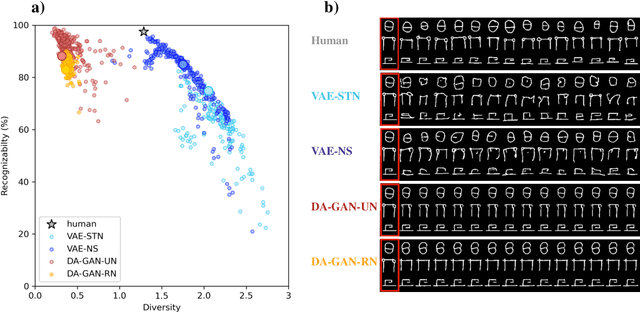
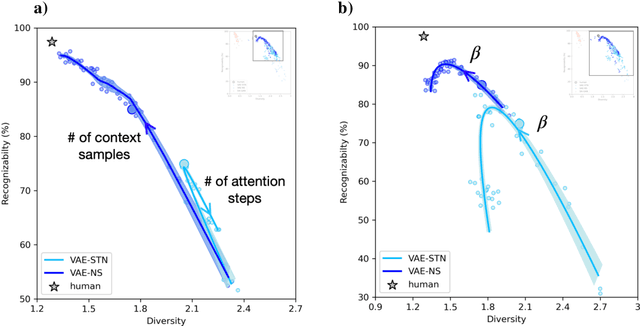
Abstract:Robust generalization to new concepts has long remained a distinctive feature of human intelligence. However, recent progress in deep generative models has now led to neural architectures capable of synthesizing novel instances of unknown visual concepts from a single training example. Yet, a more precise comparison between these models and humans is not possible because existing performance metrics for generative models (i.e., FID, IS, likelihood) are not appropriate for the one-shot generation scenario. Here, we propose a new framework to evaluate one-shot generative models along two axes: sample recognizability vs. diversity (i.e., intra-class variability). Using this framework, we perform a systematic evaluation of representative one-shot generative models on the Omniglot handwritten dataset. We first show that GAN-like and VAE-like models fall on opposite ends of the diversity-recognizability space. Extensive analyses of the effect of key model parameters further revealed that spatial attention and context integration have a linear contribution to the diversity-recognizability trade-off. In contrast, disentanglement transports the model along a parabolic curve that could be used to maximize recognizability. Using the diversity-recognizability framework, we were able to identify models and parameters that closely approximate human data.
Adaptive Methods for Aggregated Domain Generalization
Dec 23, 2021



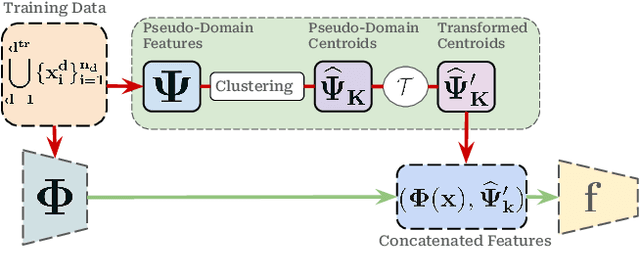
Abstract:Domain generalization involves learning a classifier from a heterogeneous collection of training sources such that it generalizes to data drawn from similar unknown target domains, with applications in large-scale learning and personalized inference. In many settings, privacy concerns prohibit obtaining domain labels for the training data samples, and instead only have an aggregated collection of training points. Existing approaches that utilize domain labels to create domain-invariant feature representations are inapplicable in this setting, requiring alternative approaches to learn generalizable classifiers. In this paper, we propose a domain-adaptive approach to this problem, which operates in two steps: (a) we cluster training data within a carefully chosen feature space to create pseudo-domains, and (b) using these pseudo-domains we learn a domain-adaptive classifier that makes predictions using information about both the input and the pseudo-domain it belongs to. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on a variety of domain generalization benchmarks without using domain labels whatsoever. Furthermore, we provide novel theoretical guarantees on domain generalization using cluster information. Our approach is amenable to ensemble-based methods and provides substantial gains even on large-scale benchmark datasets. The code can be found at: https://github.com/xavierohan/AdaClust_DomainBed
Content-Based Personalized Recommender System Using Entity Embeddings
Oct 24, 2020



Abstract:Recommender systems are a class of machine learning algorithms that provide relevant recommendations to a user based on the user's interaction with similar items or based on the content of the item. In settings where the content of the item is to be preserved, a content-based approach would be beneficial. This paper aims to highlight the advantages of the content-based approach through learned embeddings and leveraging these advantages to provide better and personalised movie recommendations based on user preferences to various movie features such as genre and keyword tags.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge