Wuttikorn Ponwitayarat
SEA-BED: Southeast Asia Embedding Benchmark
Aug 17, 2025
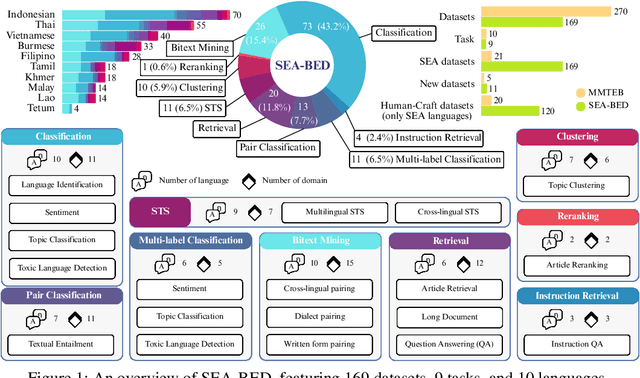


Abstract:Sentence embeddings are essential for NLP tasks such as semantic search, re-ranking, and textual similarity. Although multilingual benchmarks like MMTEB broaden coverage, Southeast Asia (SEA) datasets are scarce and often machine-translated, missing native linguistic properties. With nearly 700 million speakers, the SEA region lacks a region-specific embedding benchmark. We introduce SEA-BED, the first large-scale SEA embedding benchmark with 169 datasets across 9 tasks and 10 languages, where 71% are formulated by humans, not machine generation or translation. We address three research questions: (1) which SEA languages and tasks are challenging, (2) whether SEA languages show unique performance gaps globally, and (3) how human vs. machine translations affect evaluation. We evaluate 17 embedding models across six studies, analyzing task and language challenges, cross-benchmark comparisons, and translation trade-offs. Results show sharp ranking shifts, inconsistent model performance among SEA languages, and the importance of human-curated datasets for low-resource languages like Burmese.
Assessing Thai Dialect Performance in LLMs with Automatic Benchmarks and Human Evaluation
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:Large language models show promising results in various NLP tasks. Despite these successes, the robustness and consistency of LLMs in underrepresented languages remain largely unexplored, especially concerning local dialects. Existing benchmarks also focus on main dialects, neglecting LLMs' ability on local dialect texts. In this paper, we introduce a Thai local dialect benchmark covering Northern (Lanna), Northeastern (Isan), and Southern (Dambro) Thai, evaluating LLMs on five NLP tasks: summarization, question answering, translation, conversation, and food-related tasks. Furthermore, we propose a human evaluation guideline and metric for Thai local dialects to assess generation fluency and dialect-specific accuracy. Results show that LLM performance declines significantly in local Thai dialects compared to standard Thai, with only proprietary models like GPT-4o and Gemini2 demonstrating some fluency
Space Decomposition for Sentence Embedding
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Determining sentence pair similarity is crucial for various NLP tasks. A common technique to address this is typically evaluated on a continuous semantic textual similarity scale from 0 to 5. However, based on a linguistic observation in STS annotation guidelines, we found that the score in the range [4,5] indicates an upper-range sample, while the rest are lower-range samples. This necessitates a new approach to treating the upper-range and lower-range classes separately. In this paper, we introduce a novel embedding space decomposition method called MixSP utilizing a Mixture of Specialized Projectors, designed to distinguish and rank upper-range and lower-range samples accurately. The experimental results demonstrate that MixSP decreased the overlap representation between upper-range and lower-range classes significantly while outperforming competitors on STS and zero-shot benchmarks.
An Efficient Self-Supervised Cross-View Training For Sentence Embedding
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Self-supervised sentence representation learning is the task of constructing an embedding space for sentences without relying on human annotation efforts. One straightforward approach is to finetune a pretrained language model (PLM) with a representation learning method such as contrastive learning. While this approach achieves impressive performance on larger PLMs, the performance rapidly degrades as the number of parameters decreases. In this paper, we propose a framework called Self-supervised Cross-View Training (SCT) to narrow the performance gap between large and small PLMs. To evaluate the effectiveness of SCT, we compare it to 5 baseline and state-of-the-art competitors on seven Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) benchmarks using 5 PLMs with the number of parameters ranging from 4M to 340M. The experimental results show that STC outperforms the competitors for PLMs with less than 100M parameters in 18 of 21 cases.
Typo-Robust Representation Learning for Dense Retrieval
Jun 17, 2023



Abstract:Dense retrieval is a basic building block of information retrieval applications. One of the main challenges of dense retrieval in real-world settings is the handling of queries containing misspelled words. A popular approach for handling misspelled queries is minimizing the representations discrepancy between misspelled queries and their pristine ones. Unlike the existing approaches, which only focus on the alignment between misspelled and pristine queries, our method also improves the contrast between each misspelled query and its surrounding queries. To assess the effectiveness of our proposed method, we compare it against the existing competitors using two benchmark datasets and two base encoders. Our method outperforms the competitors in all cases with misspelled queries. Our code and models are available at https://github. com/panuthept/DST-DenseRetrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge