Wenming Guo
MCTS-SQL: An Effective Framework for Text-to-SQL with Monte Carlo Tree Search
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Text-to-SQL is a fundamental and longstanding problem in the NLP area, aiming at converting natural language queries into SQL, enabling non-expert users to operate databases. Recent advances in LLM have greatly improved text-to-SQL performance. However, challenges persist, especially when dealing with complex user queries. Current approaches (e.g., COT prompting and multi-agent frameworks) rely on the ability of models to plan and generate SQL autonomously, but controlling performance remains difficult. In addition, LLMs are still prone to hallucinations. To alleviate these challenges, we designed a novel MCTS-SQL to guide SQL generation iteratively. The approach generates SQL queries through Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) and a heuristic self-refinement mechanism are used to enhance accuracy and reliability. Key components include a schema selector for extracting relevant information and an MCTS-based generator for iterative query refinement. Experimental results from the SPIDER and BIRD benchmarks show that MCTS-SQL achieves state-of-the-art performance. Specifically, on the BIRD development dataset, MCTS-SQL achieves an Execution (EX) accuracy of 69.40% using GPT-4o as the base model and a significant improvement when dealing with challenging tasks, with an EX of 51.48%, which is 3.41% higher than the existing method.
Generalizing Few Data to Unseen Domains Flexibly Based on Label Smoothing Integrated with Distributionally Robust Optimization
Aug 09, 2024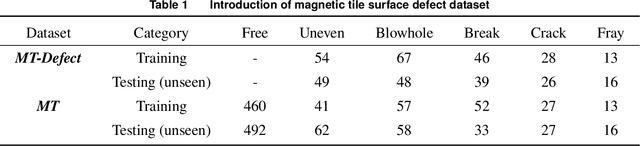


Abstract:Overfitting commonly occurs when applying deep neural networks (DNNs) on small-scale datasets, where DNNs do not generalize well from existing data to unseen data. The main reason resulting in overfitting is that small-scale datasets cannot reflect the situations of the real world. Label smoothing (LS) is an effective regularization method to prevent overfitting, avoiding it by mixing one-hot labels with uniform label vectors. However, LS only focuses on labels while ignoring the distribution of existing data. In this paper, we introduce the distributionally robust optimization (DRO) to LS, achieving shift the existing data distribution flexibly to unseen domains when training DNNs. Specifically, we prove that the regularization of LS can be extended to a regularization term for the DNNs parameters when integrating DRO. The regularization term can be utilized to shift existing data to unseen domains and generate new data. Furthermore, we propose an approximate gradient-iteration label smoothing algorithm (GI-LS) to achieve the findings and train DNNs. We prove that the shift for the existing data does not influence the convergence of GI-LS. Since GI-LS incorporates a series of hyperparameters, we further consider using Bayesian optimization (BO) to find the relatively optimal combinations of these hyperparameters. Taking small-scale anomaly classification tasks as a case, we evaluate GI-LS, and the results clearly demonstrate its superior performance.
ACE-Net: Biomedical Image Segmentation with Augmented Contracting and Expansive Paths
Aug 23, 2019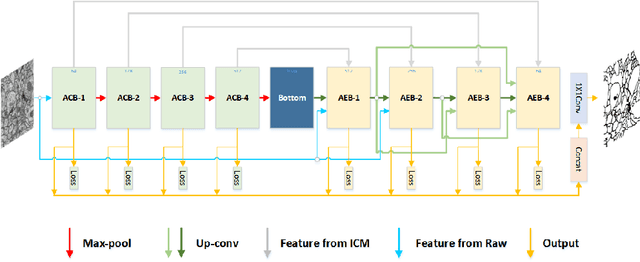
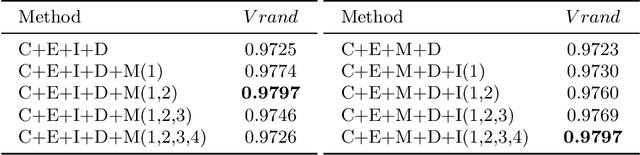
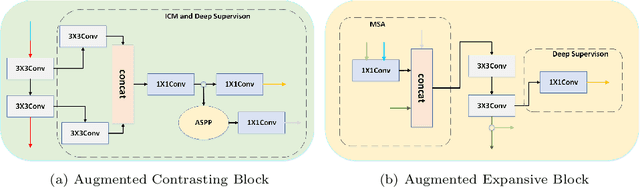
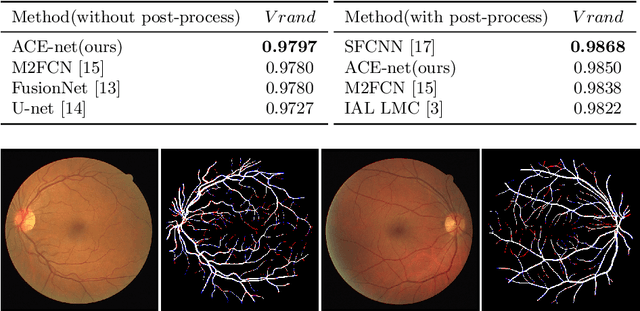
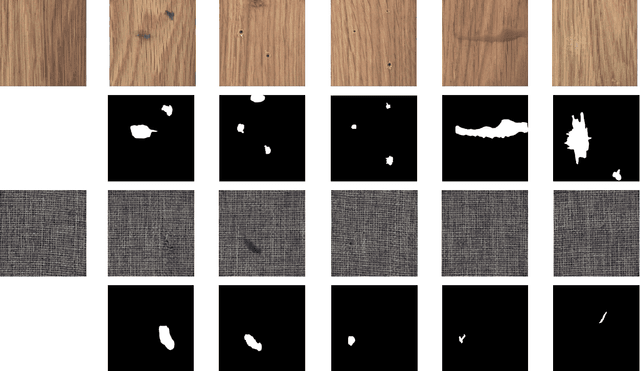
Abstract:Nowadays U-net-like FCNs predominate various biomedical image segmentation applications and attain promising performance, largely due to their elegant architectures, e.g., symmetric contracting and expansive paths as well as lateral skip-connections. It remains a research direction to devise novel architectures to further benefit the segmentation. In this paper, we develop an ACE-net that aims to enhance the feature representation and utilization by augmenting the contracting and expansive paths. In particular, we augment the paths by the recently proposed advanced techniques including ASPP, dense connection and deep supervision mechanisms, and novel connections such as directly connecting the raw image to the expansive side. With these augmentations, ACE-net can utilize features from multiple sources, scales and reception fields to segment while still maintains a relative simple architecture. Experiments on two typical biomedical segmentation tasks validate its effectiveness, where highly competitive results are obtained in both tasks while ACE-net still runs fast at inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge