Wenhui Fan
Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Zero-Shot Scalable Collaboration
Apr 05, 2024



Abstract:The rise of multi-agent systems, especially the success of multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), is reshaping our future across diverse domains like autonomous vehicle networks. However, MARL still faces significant challenges, particularly in achieving zero-shot scalability, which allows trained MARL models to be directly applied to unseen tasks with varying numbers of agents. In addition, real-world multi-agent systems usually contain agents with different functions and strategies, while the existing scalable MARL methods only have limited heterogeneity. To address this, we propose a novel MARL framework named Scalable and Heterogeneous Proximal Policy Optimization (SHPPO), integrating heterogeneity into parameter-shared PPO-based MARL networks. we first leverage a latent network to adaptively learn strategy patterns for each agent. Second, we introduce a heterogeneous layer for decision-making, whose parameters are specifically generated by the learned latent variables. Our approach is scalable as all the parameters are shared except for the heterogeneous layer, and gains both inter-individual and temporal heterogeneity at the same time. We implement our approach based on the state-of-the-art backbone PPO-based algorithm as SHPPO, while our approach is agnostic to the backbone and can be seamlessly plugged into any parameter-shared MARL method. SHPPO exhibits superior performance over the baselines such as MAPPO and HAPPO in classic MARL environments like Starcraft Multi-Agent Challenge (SMAC) and Google Research Football (GRF), showcasing enhanced zero-shot scalability and offering insights into the learned latent representation's impact on team performance by visualization.
Embodied LLM Agents Learn to Cooperate in Organized Teams
Mar 19, 2024

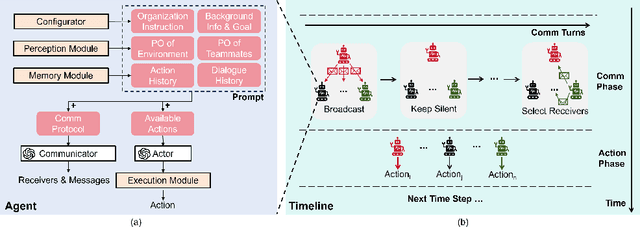

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as integral tools for reasoning, planning, and decision-making, drawing upon their extensive world knowledge and proficiency in language-related tasks. LLMs thus hold tremendous potential for natural language interaction within multi-agent systems to foster cooperation. However, LLM agents tend to over-report and comply with any instruction, which may result in information redundancy and confusion in multi-agent cooperation. Inspired by human organizations, this paper introduces a framework that imposes prompt-based organization structures on LLM agents to mitigate these problems. Through a series of experiments with embodied LLM agents and human-agent collaboration, our results highlight the impact of designated leadership on team efficiency, shedding light on the leadership qualities displayed by LLM agents and their spontaneous cooperative behaviors. Further, we harness the potential of LLMs to propose enhanced organizational prompts, via a Criticize-Reflect process, resulting in novel organization structures that reduce communication costs and enhance team efficiency.
Scalable Communication for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning via Transformer-Based Email Mechanism
Jan 05, 2023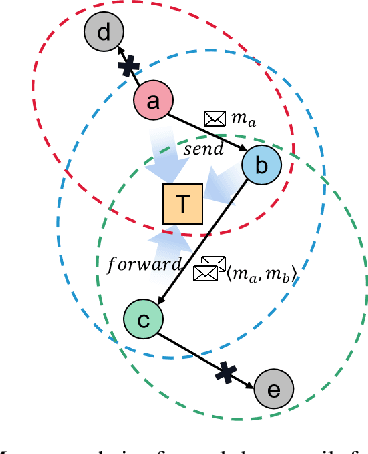
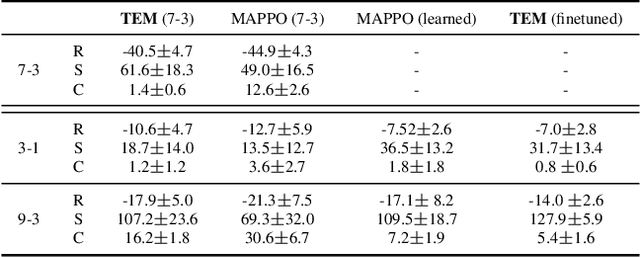
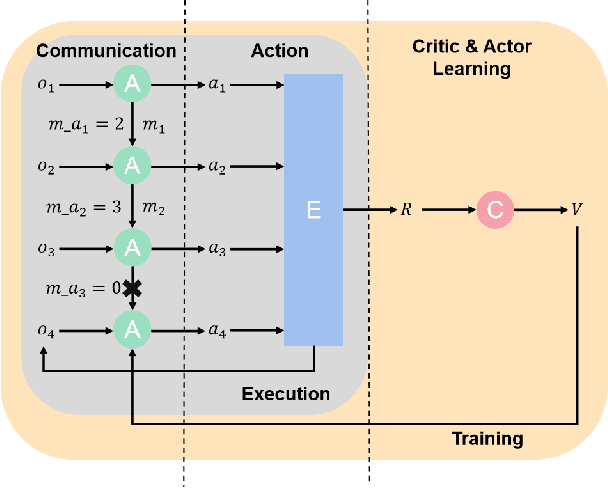
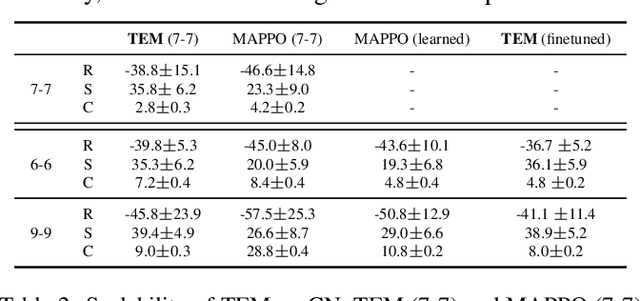
Abstract:Communication can impressively improve cooperation in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL), especially for partially-observed tasks. However, existing works either broadcast the messages leading to information redundancy, or learn targeted communication by modeling all the other agents as targets, which is not scalable when the number of agents varies. In this work, to tackle the scalability problem of MARL communication for partially-observed tasks, we propose a novel framework Transformer-based Email Mechanism (TEM). The agents adopt local communication to send messages only to the ones that can be observed without modeling all the agents. Inspired by human cooperation with email forwarding, we design message chains to forward information to cooperate with the agents outside the observation range. We introduce Transformer to encode and decode the message chain to choose the next receiver selectively. Empirically, TEM outperforms the baselines on multiple cooperative MARL benchmarks. When the number of agents varies, TEM maintains superior performance without further training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge