Weijie Hu
Track without Appearance: Learn Box and Tracklet Embedding with Local and Global Motion Patterns for Vehicle Tracking
Aug 13, 2021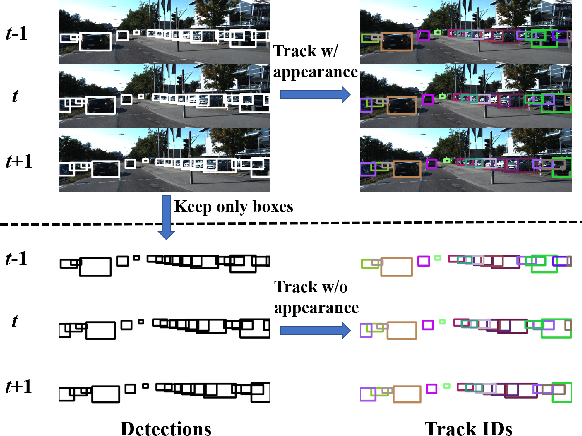
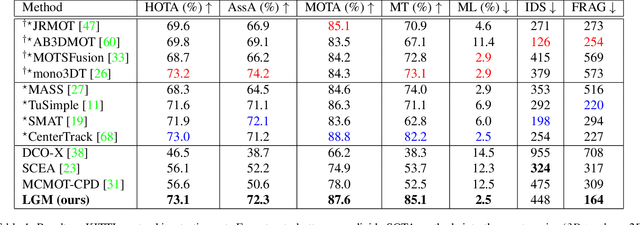
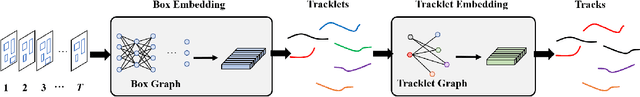
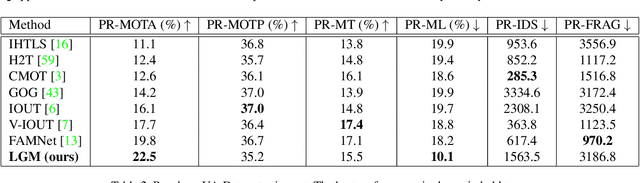
Abstract:Vehicle tracking is an essential task in the multi-object tracking (MOT) field. A distinct characteristic in vehicle tracking is that the trajectories of vehicles are fairly smooth in both the world coordinate and the image coordinate. Hence, models that capture motion consistencies are of high necessity. However, tracking with the standalone motion-based trackers is quite challenging because targets could get lost easily due to limited information, detection error and occlusion. Leveraging appearance information to assist object re-identification could resolve this challenge to some extent. However, doing so requires extra computation while appearance information is sensitive to occlusion as well. In this paper, we try to explore the significance of motion patterns for vehicle tracking without appearance information. We propose a novel approach that tackles the association issue for long-term tracking with the exclusive fully-exploited motion information. We address the tracklet embedding issue with the proposed reconstruct-to-embed strategy based on deep graph convolutional neural networks (GCN). Comprehensive experiments on the KITTI-car tracking dataset and UA-Detrac dataset show that the proposed method, though without appearance information, could achieve competitive performance with the state-of-the-art (SOTA) trackers. The source code will be available at https://github.com/GaoangW/LGMTracker.
Split and Connect: A Universal Tracklet Booster for Multi-Object Tracking
May 06, 2021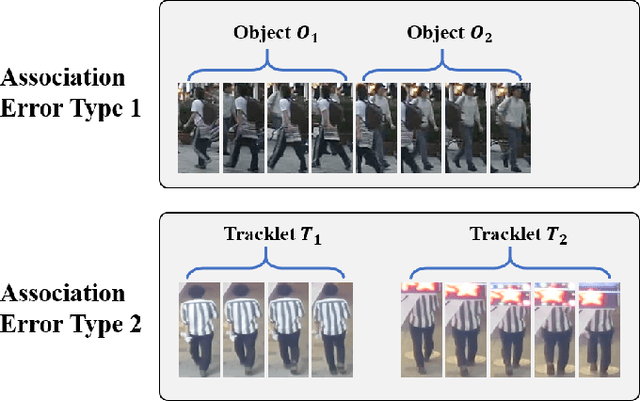
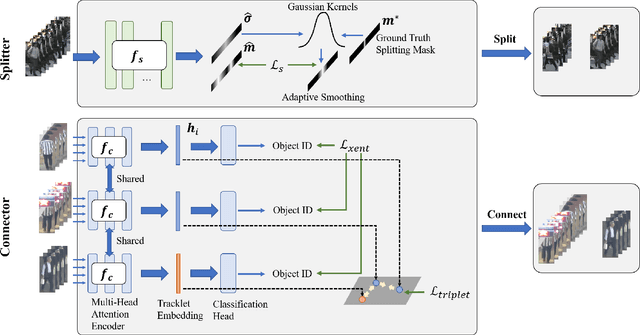
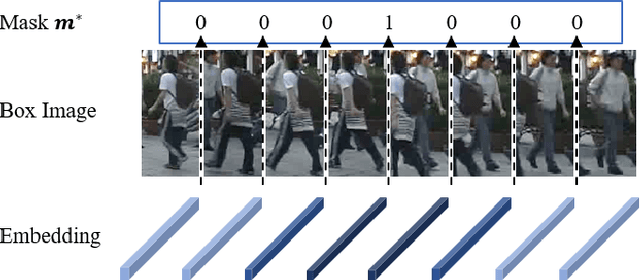
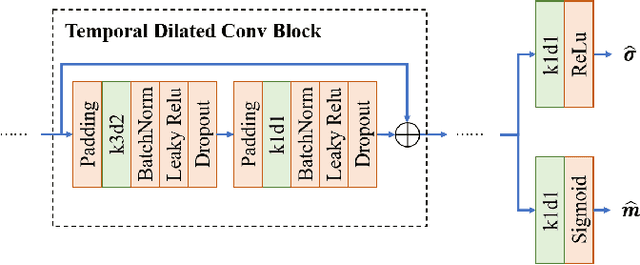
Abstract:Multi-object tracking (MOT) is an essential task in the computer vision field. With the fast development of deep learning technology in recent years, MOT has achieved great improvement. However, some challenges still remain, such as sensitiveness to occlusion, instability under different lighting conditions, non-robustness to deformable objects, etc. To address such common challenges in most of the existing trackers, in this paper, a tracklet booster algorithm is proposed, which can be built upon any other tracker. The motivation is simple and straightforward: split tracklets on potential ID-switch positions and then connect multiple tracklets into one if they are from the same object. In other words, the tracklet booster consists of two parts, i.e., Splitter and Connector. First, an architecture with stacked temporal dilated convolution blocks is employed for the splitting position prediction via label smoothing strategy with adaptive Gaussian kernels. Then, a multi-head self-attention based encoder is exploited for the tracklet embedding, which is further used to connect tracklets into larger groups. We conduct sufficient experiments on MOT17 and MOT20 benchmark datasets, which demonstrates promising results. Combined with the proposed tracklet booster, existing trackers usually can achieve large improvements on the IDF1 score, which shows the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge