Weichao Yuwen
Large Language Model-Powered Conversational Agent Delivering Problem-Solving Therapy (PST) for Family Caregivers: Enhancing Empathy and Therapeutic Alliance Using In-Context Learning
Jun 13, 2025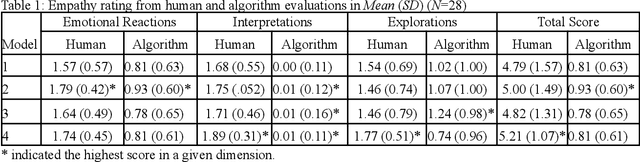
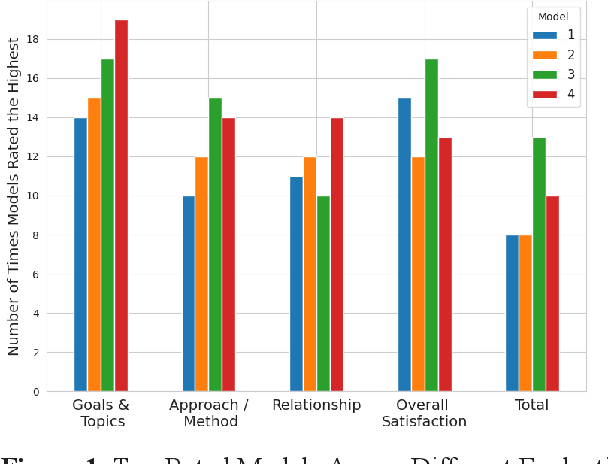
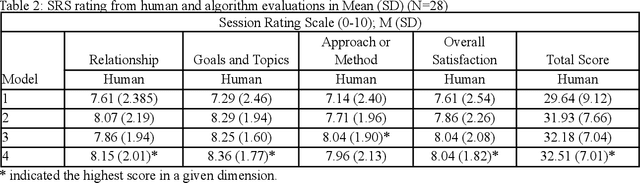
Abstract:Family caregivers often face substantial mental health challenges due to their multifaceted roles and limited resources. This study explored the potential of a large language model (LLM)-powered conversational agent to deliver evidence-based mental health support for caregivers, specifically Problem-Solving Therapy (PST) integrated with Motivational Interviewing (MI) and Behavioral Chain Analysis (BCA). A within-subject experiment was conducted with 28 caregivers interacting with four LLM configurations to evaluate empathy and therapeutic alliance. The best-performing models incorporated Few-Shot and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) prompting techniques, alongside clinician-curated examples. The models showed improved contextual understanding and personalized support, as reflected by qualitative responses and quantitative ratings on perceived empathy and therapeutic alliances. Participants valued the model's ability to validate emotions, explore unexpressed feelings, and provide actionable strategies. However, balancing thorough assessment with efficient advice delivery remains a challenge. This work highlights the potential of LLMs in delivering empathetic and tailored support for family caregivers.
Transforming Tuberculosis Care: Optimizing Large Language Models For Enhanced Clinician-Patient Communication
Feb 28, 2025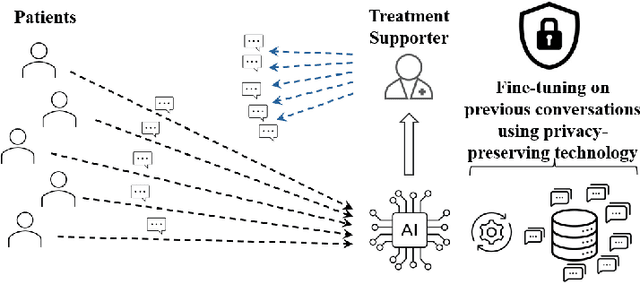
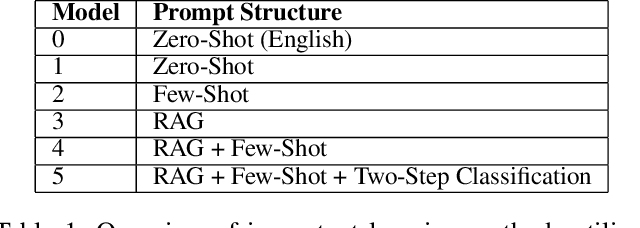
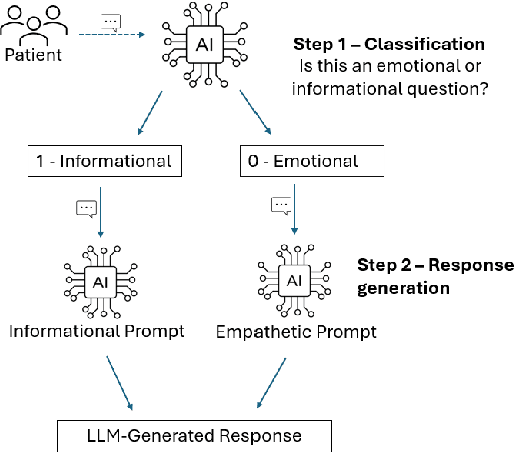
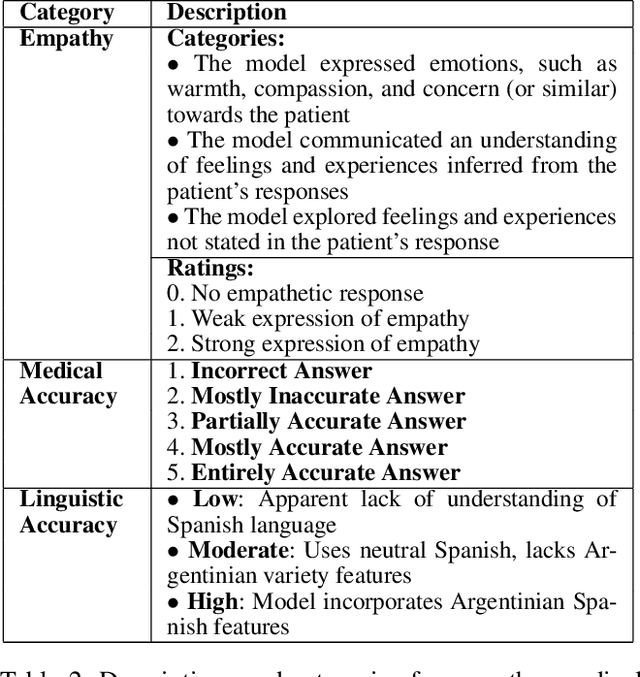
Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death from an infectious disease globally, with the highest burden in low- and middle-income countries. In these regions, limited healthcare access and high patient-to-provider ratios impede effective patient support, communication, and treatment completion. To bridge this gap, we propose integrating a specialized Large Language Model into an efficacious digital adherence technology to augment interactive communication with treatment supporters. This AI-powered approach, operating within a human-in-the-loop framework, aims to enhance patient engagement and improve TB treatment outcomes.
Toward Large Language Models as a Therapeutic Tool: Comparing Prompting Techniques to Improve GPT-Delivered Problem-Solving Therapy
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) are being quickly adapted to many domains, including healthcare, their strengths and pitfalls remain under-explored. In our study, we examine the effects of prompt engineering to guide Large Language Models (LLMs) in delivering parts of a Problem-Solving Therapy (PST) session via text, particularly during the symptom identification and assessment phase for personalized goal setting. We present evaluation results of the models' performances by automatic metrics and experienced medical professionals. We demonstrate that the models' capability to deliver protocolized therapy can be improved with the proper use of prompt engineering methods, albeit with limitations. To our knowledge, this study is among the first to assess the effects of various prompting techniques in enhancing a generalist model's ability to deliver psychotherapy, focusing on overall quality, consistency, and empathy. Exploring LLMs' potential in delivering psychotherapy holds promise with the current shortage of mental health professionals amid significant needs, enhancing the potential utility of AI-based and AI-enhanced care services.
Bridging the Skills Gap: Evaluating an AI-Assisted Provider Platform to Support Care Providers with Empathetic Delivery of Protocolized Therapy
Jan 08, 2024



Abstract:Despite the high prevalence and burden of mental health conditions, there is a global shortage of mental health providers. Artificial Intelligence (AI) methods have been proposed as a way to address this shortage, by supporting providers with less extensive training as they deliver care. To this end, we developed the AI-Assisted Provider Platform (A2P2), a text-based virtual therapy interface that includes a response suggestion feature, which supports providers in delivering protocolized therapies empathetically. We studied providers with and without expertise in mental health treatment delivering a therapy session using the platform with (intervention) and without (control) AI-assistance features. Upon evaluation, the AI-assisted system significantly decreased response times by 29.34% (p=0.002), tripled empathic response accuracy (p=0.0001), and increased goal recommendation accuracy by 66.67% (p=0.001) across both user groups compared to the control. Both groups rated the system as having excellent usability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge