Warren B. Gefter
Quantitative CT texture-based method to predict diagnosis and prognosis of fibrosing interstitial lung disease patterns
Jun 20, 2022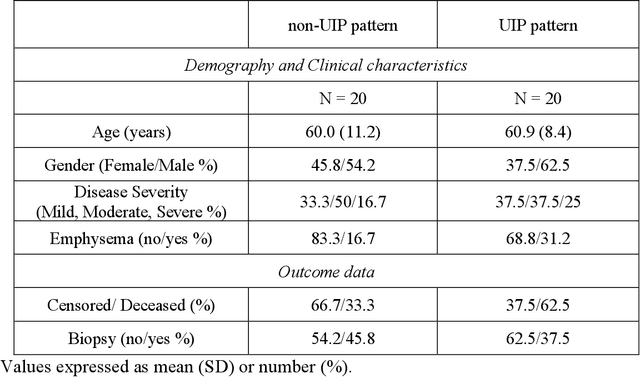
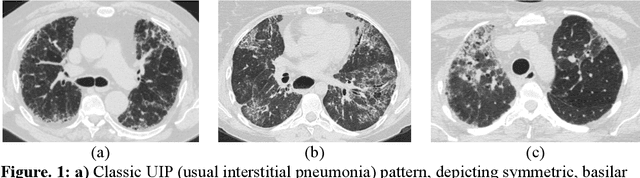
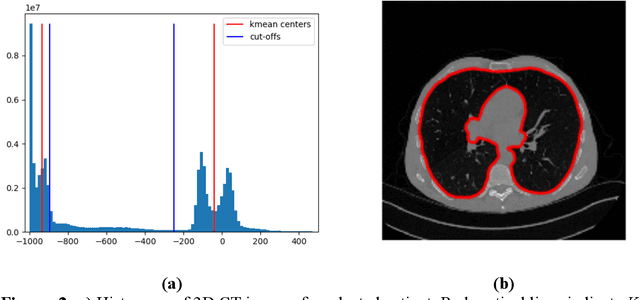
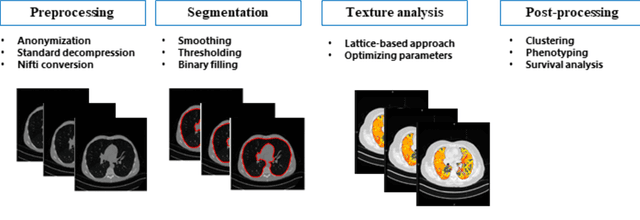
Abstract:Purpose: To utilize high-resolution quantitative CT (QCT) imaging features for prediction of diagnosis and prognosis in fibrosing interstitial lung diseases (ILD). Approach: 40 ILD patients (20 usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), 20 non-UIP pattern ILD) were classified by expert consensus of 2 radiologists and followed for 7 years. Clinical variables were recorded. Following segmentation of the lung field, a total of 26 texture features were extracted using a lattice-based approach (TM model). The TM model was compared with previously histogram-based model (HM) for their abilities to classify UIP vs non-UIP. For prognostic assessment, survival analysis was performed comparing the expert diagnostic labels versus TM metrics. Results: In the classification analysis, the TM model outperformed the HM method with AUC of 0.70. While survival curves of UIP vs non-UIP expert labels in Cox regression analysis were not statistically different, TM QCT features allowed statistically significant partition of the cohort. Conclusions: TM model outperformed HM model in distinguishing UIP from non-UIP patterns. Most importantly, TM allows for partitioning of the cohort into distinct survival groups, whereas expert UIP vs non-UIP labeling does not. QCT TM models may improve diagnosis of ILD and offer more accurate prognostication, better guiding patient management.
Automated detection and quantification of COVID-19 airspace disease on chest radiographs: A novel approach achieving radiologist-level performance using a CNN trained on digital reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) from CT-based ground-truth
Aug 13, 2020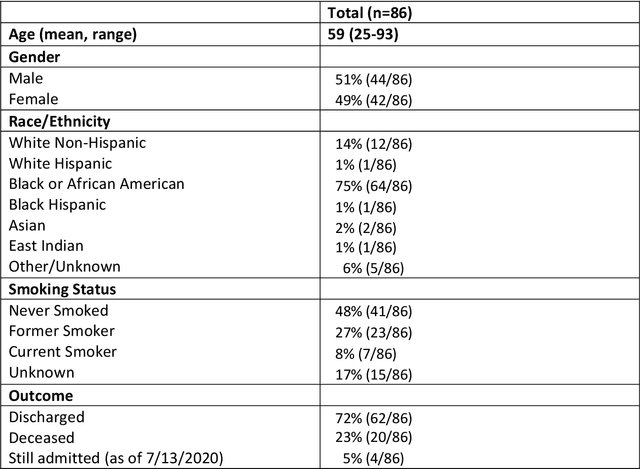
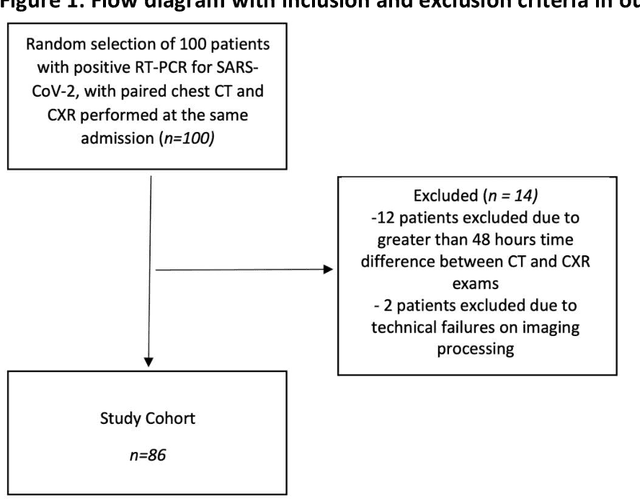
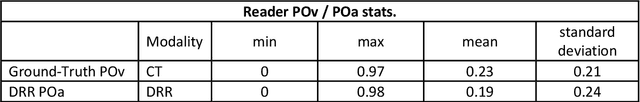
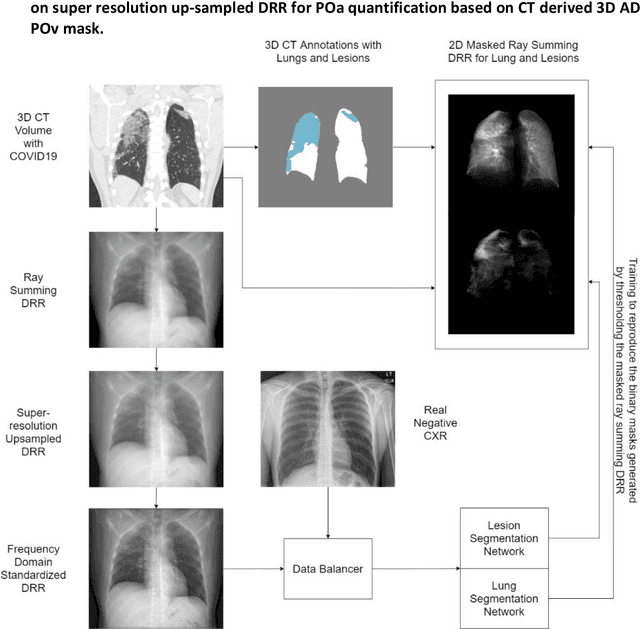
Abstract:Purpose: To leverage volumetric quantification of airspace disease (AD) derived from a superior modality (CT) serving as ground truth, projected onto digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) to: 1) train a convolutional neural network to quantify airspace disease on paired CXRs; and 2) compare the DRR-trained CNN to expert human readers in the CXR evaluation of patients with confirmed COVID-19. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively selected a cohort of 86 COVID-19 patients (with positive RT-PCR), from March-May 2020 at a tertiary hospital in the northeastern USA, who underwent chest CT and CXR within 48 hrs. The ground truth volumetric percentage of COVID-19 related AD (POv) was established by manual AD segmentation on CT. The resulting 3D masks were projected into 2D anterior-posterior digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRR) to compute area-based AD percentage (POa). A convolutional neural network (CNN) was trained with DRR images generated from a larger-scale CT dataset of COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients, automatically segmenting lungs, AD and quantifying POa on CXR. CNN POa results were compared to POa quantified on CXR by two expert readers and to the POv ground-truth, by computing correlations and mean absolute errors. Results: Bootstrap mean absolute error (MAE) and correlations between POa and POv were 11.98% [11.05%-12.47%] and 0.77 [0.70-0.82] for average of expert readers, and 9.56%-9.78% [8.83%-10.22%] and 0.78-0.81 [0.73-0.85] for the CNN, respectively. Conclusion: Our CNN trained with DRR using CT-derived airspace quantification achieved expert radiologist level of accuracy in the quantification of airspace disease on CXR, in patients with positive RT-PCR for COVID-19.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge