Wanjun Chen
GA-HQS: MRI reconstruction via a generically accelerated unfolding approach
Apr 06, 2023



Abstract:Deep unfolding networks (DUNs) are the foremost methods in the realm of compressed sensing MRI, as they can employ learnable networks to facilitate interpretable forward-inference operators. However, several daunting issues still exist, including the heavy dependency on the first-order optimization algorithms, the insufficient information fusion mechanisms, and the limitation of capturing long-range relationships. To address the issues, we propose a Generically Accelerated Half-Quadratic Splitting (GA-HQS) algorithm that incorporates second-order gradient information and pyramid attention modules for the delicate fusion of inputs at the pixel level. Moreover, a multi-scale split transformer is also designed to enhance the global feature representation. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method surpasses previous ones on single-coil MRI acceleration tasks.
Structure fusion based on graph convolutional networks for semi-supervised classification
Jul 02, 2019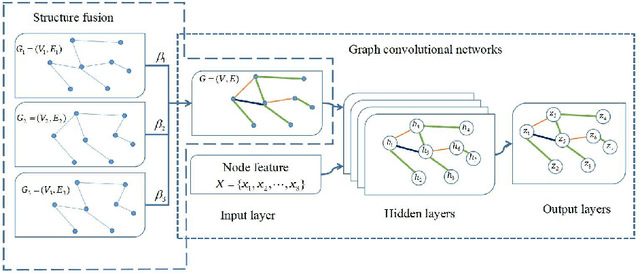
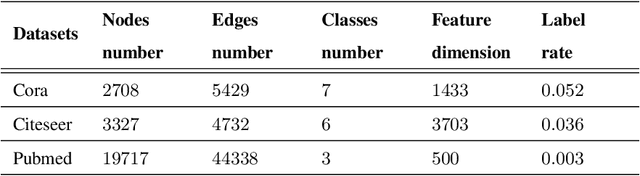
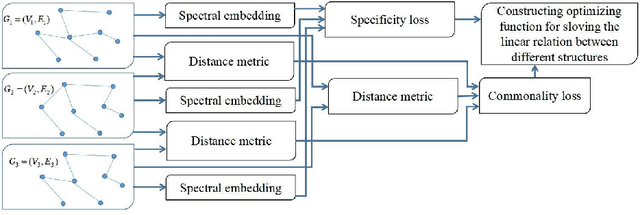
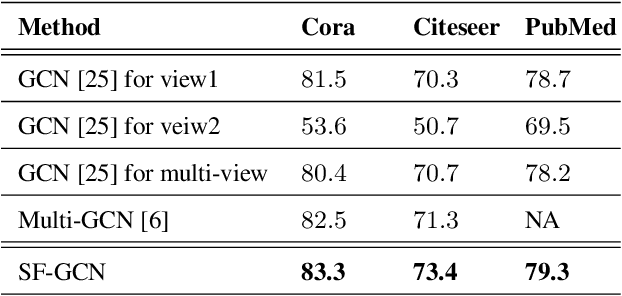
Abstract:Suffering from the multi-view data diversity and complexity for semi-supervised classification, most of existing graph convolutional networks focus on the networks architecture construction or the salient graph structure preservation, and ignore the the complete graph structure for semi-supervised classification contribution. To mine the more complete distribution structure from multi-view data with the consideration of the specificity and the commonality, we propose structure fusion based on graph convolutional networks (SF-GCN) for improving the performance of semi-supervised classification. SF-GCN can not only retain the special characteristic of each view data by spectral embedding, but also capture the common style of multi-view data by distance metric between multi-graph structures. Suppose the linear relationship between multi-graph structures, we can construct the optimization function of structure fusion model by balancing the specificity loss and the commonality loss. By solving this function, we can simultaneously obtain the fusion spectral embedding from the multi-view data and the fusion structure as adjacent matrix to input graph convolutional networks for semi-supervised classification. Experiments demonstrate that the performance of SF-GCN outperforms that of the state of the arts on three challenging datasets, which are Cora,Citeseer and Pubmed in citation networks.
Transfer feature generating networks with semantic classes structure for zero-shot learning
Mar 06, 2019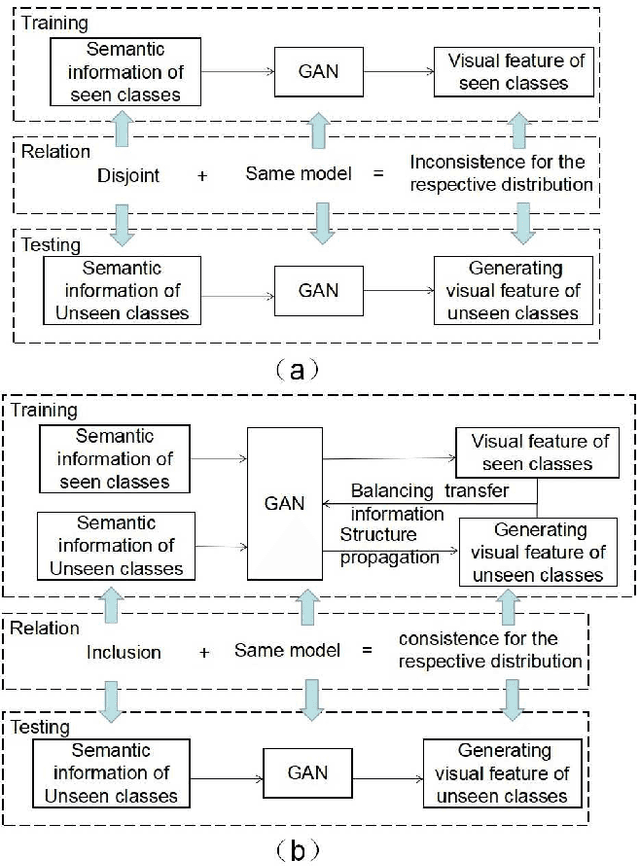
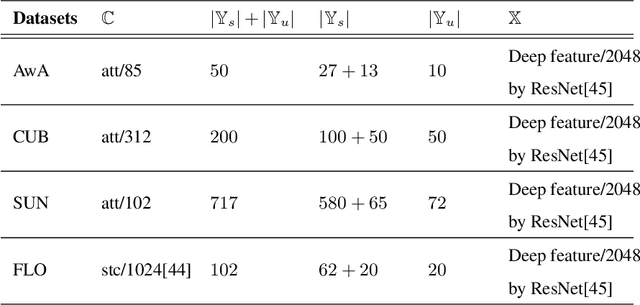
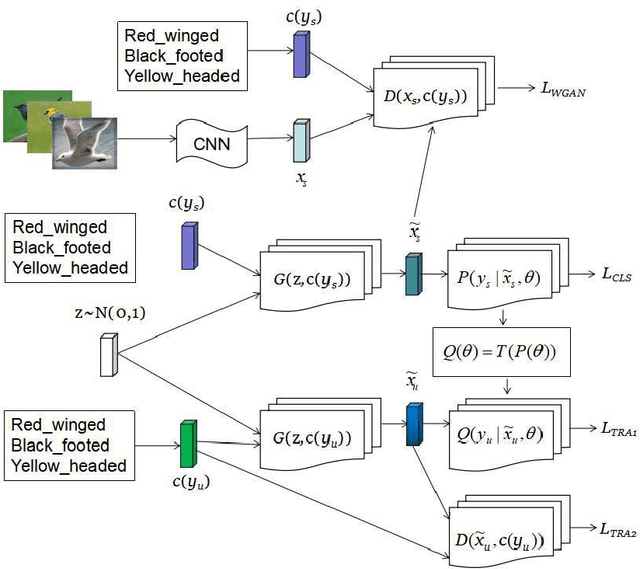
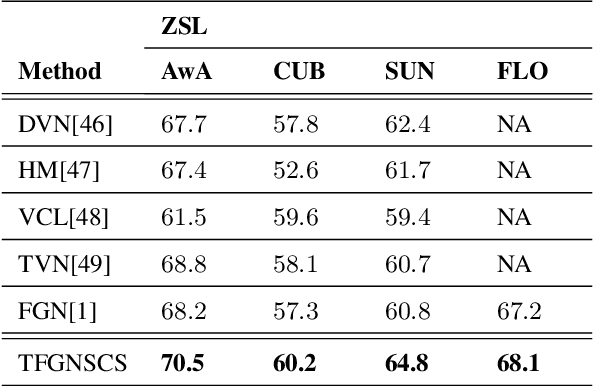
Abstract:Suffering from the generating feature inconsistence of seen classes training model for following the distribution of unseen classes , most of existing feature generating networks difficultly obtain satisfactory performance for the challenging generalization zero-shot learning (GZSL) by adversarial learning the distribution of semantic classes. To alleviate the negative influence of this inconsistence for zero-shot learning (ZSL), transfer feature generating networks with semantic classes structure (TFGNSCS) is proposed to construct networks model for improving the performance of ZSL and GZSL. TFGNSCS can not only consider the semantic structure relationship between seen and unseen classes but also learn the difference of generating features by balancing transfer information between seen and unseen classes in networks. The proposed method can integrate a Wasserstein generative adversarial network with classification loss and transfer loss to generate enough CNN feature, on which softmax classifiers are trained for ZSL and GZSL. Experiments demonstrate that the performance of TFGNSCS outperforms that of the state of the arts on four challenging datasets, which are CUB,FLO,SUN, AWA in GZSL.
Class label autoencoder for zero-shot learning
Jan 25, 2018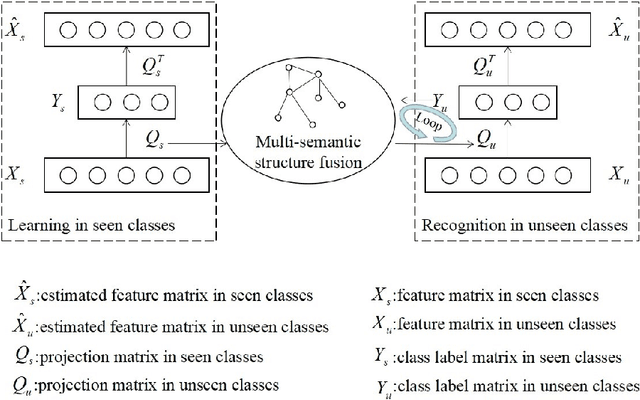
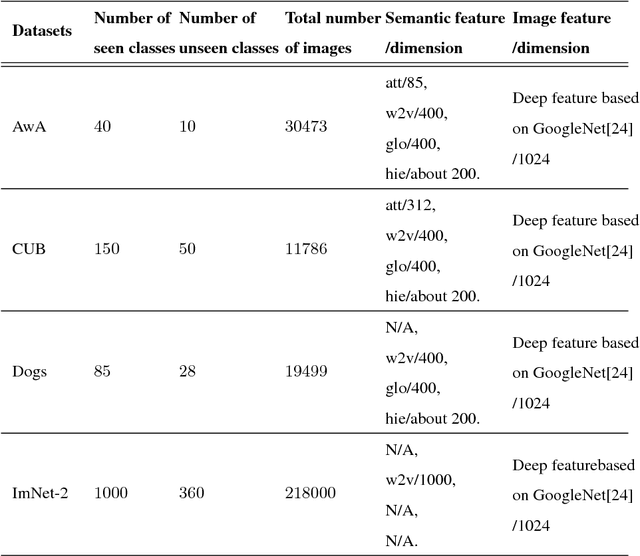
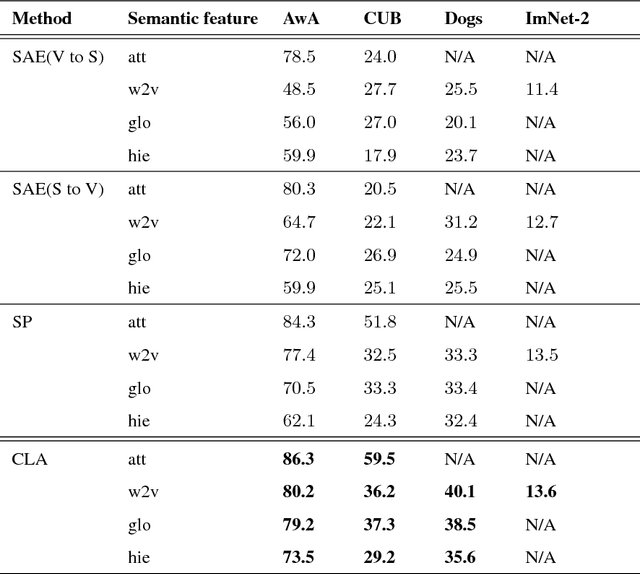
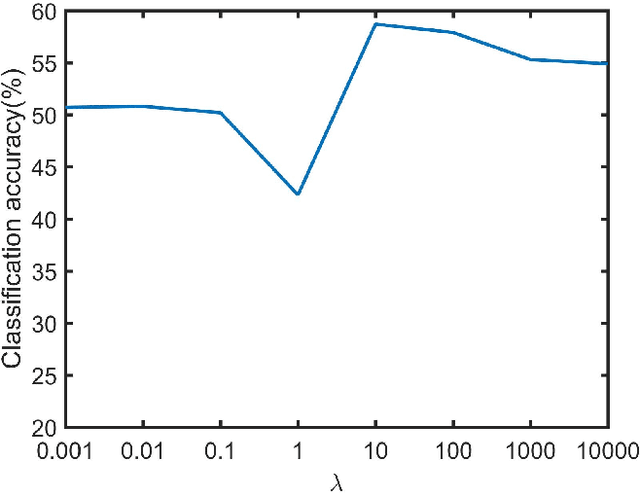
Abstract:Existing zero-shot learning (ZSL) methods usually learn a projection function between a feature space and a semantic embedding space(text or attribute space) in the training seen classes or testing unseen classes. However, the projection function cannot be used between the feature space and multi-semantic embedding spaces, which have the diversity characteristic for describing the different semantic information of the same class. To deal with this issue, we present a novel method to ZSL based on learning class label autoencoder (CLA). CLA can not only build a uniform framework for adapting to multi-semantic embedding spaces, but also construct the encoder-decoder mechanism for constraining the bidirectional projection between the feature space and the class label space. Moreover, CLA can jointly consider the relationship of feature classes and the relevance of the semantic classes for improving zero-shot classification. The CLA solution can provide both unseen class labels and the relation of the different classes representation(feature or semantic information) that can encode the intrinsic structure of classes. Extensive experiments demonstrate the CLA outperforms state-of-art methods on four benchmark datasets, which are AwA, CUB, Dogs and ImNet-2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge