Vivek Pradeep
ImagePairs: Realistic Super Resolution Dataset via Beam Splitter Camera Rig
Apr 18, 2020
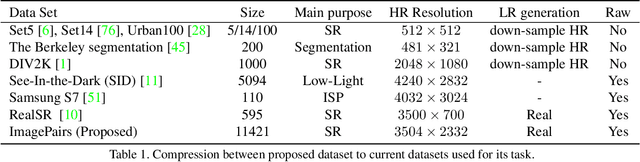
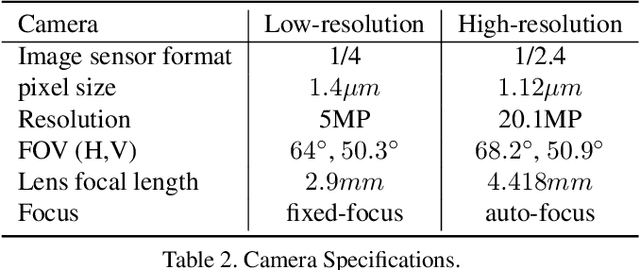
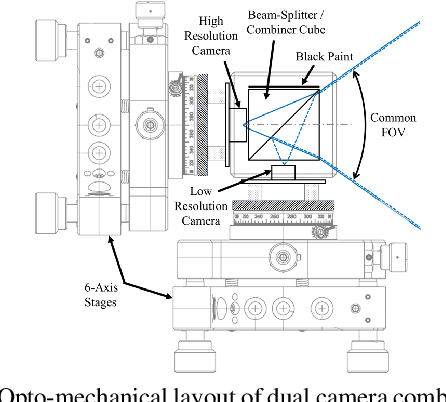
Abstract:Super Resolution is the problem of recovering a high-resolution image from a single or multiple low-resolution images of the same scene. It is an ill-posed problem since high frequency visual details of the scene are completely lost in low-resolution images. To overcome this, many machine learning approaches have been proposed aiming at training a model to recover the lost details in the new scenes. Such approaches include the recent successful effort in utilizing deep learning techniques to solve super resolution problem. As proven, data itself plays a significant role in the machine learning process especially deep learning approaches which are data hungry. Therefore, to solve the problem, the process of gathering data and its formation could be equally as vital as the machine learning technique used. Herein, we are proposing a new data acquisition technique for gathering real image data set which could be used as an input for super resolution, noise cancellation and quality enhancement techniques. We use a beam-splitter to capture the same scene by a low resolution camera and a high resolution camera. Since we also release the raw images, this large-scale dataset could be used for other tasks such as ISP generation. Unlike current small-scale dataset used for these tasks, our proposed dataset includes 11,421 pairs of low-resolution high-resolution images of diverse scenes. To our knowledge this is the most complete dataset for super resolution, ISP and image quality enhancement. The benchmarking result shows how the new dataset can be successfully used to significantly improve the quality of real-world image super resolution.
DIY Human Action Data Set Generation
Mar 29, 2018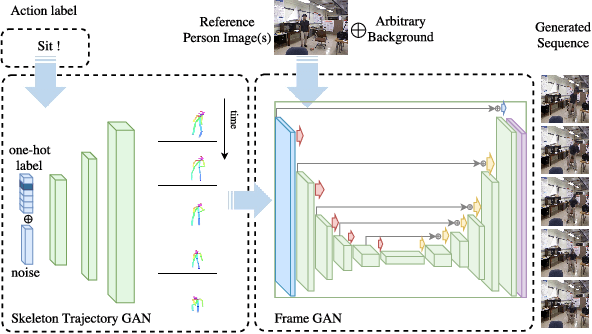
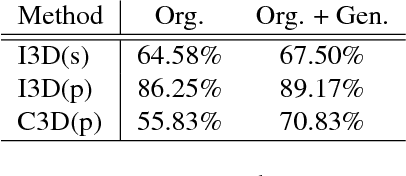
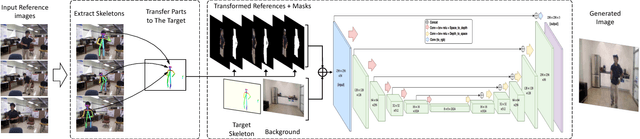
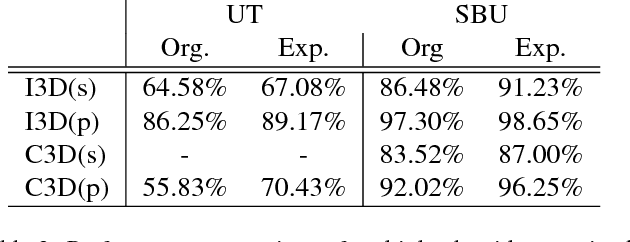
Abstract:The recent successes in applying deep learning techniques to solve standard computer vision problems has aspired researchers to propose new computer vision problems in different domains. As previously established in the field, training data itself plays a significant role in the machine learning process, especially deep learning approaches which are data hungry. In order to solve each new problem and get a decent performance, a large amount of data needs to be captured which may in many cases pose logistical difficulties. Therefore, the ability to generate de novo data or expand an existing data set, however small, in order to satisfy data requirement of current networks may be invaluable. Herein, we introduce a novel way to partition an action video clip into action, subject and context. Each part is manipulated separately and reassembled with our proposed video generation technique. Furthermore, our novel human skeleton trajectory generation along with our proposed video generation technique, enables us to generate unlimited action recognition training data. These techniques enables us to generate video action clips from an small set without costly and time-consuming data acquisition. Lastly, we prove through extensive set of experiments on two small human action recognition data sets, that this new data generation technique can improve the performance of current action recognition neural nets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge