Varvara Vetrova
Reducing Smoothness with Expressive Memory Enhanced Hierarchical Graph Neural Networks
Apr 02, 2025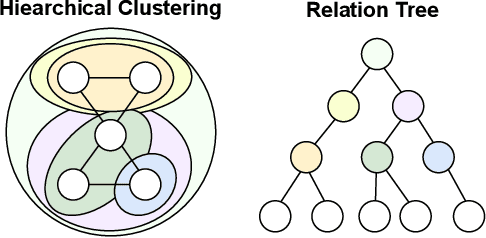
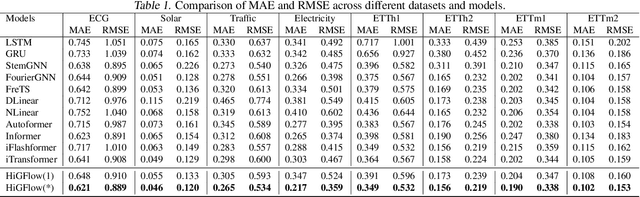
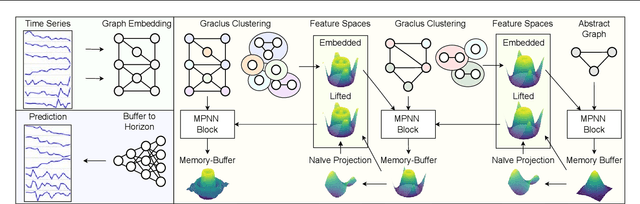
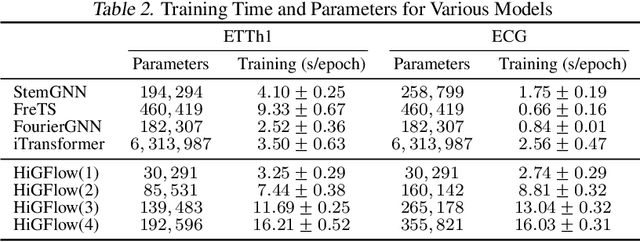
Abstract:Graphical forecasting models learn the structure of time series data via projecting onto a graph, with recent techniques capturing spatial-temporal associations between variables via edge weights. Hierarchical variants offer a distinct advantage by analysing the time series across multiple resolutions, making them particularly effective in tasks like global weather forecasting, where low-resolution variable interactions are significant. A critical challenge in hierarchical models is information loss during forward or backward passes through the hierarchy. We propose the Hierarchical Graph Flow (HiGFlow) network, which introduces a memory buffer variable of dynamic size to store previously seen information across variable resolutions. We theoretically show two key results: HiGFlow reduces smoothness when mapping onto new feature spaces in the hierarchy and non-strictly enhances the utility of message-passing by improving Weisfeiler-Lehman (WL) expressivity. Empirical results demonstrate that HiGFlow outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, including transformer models, by at least an average of 6.1% in MAE and 6.2% in RMSE. Code is available at https://github.com/TB862/ HiGFlow.git.
A Study on Monthly Marine Heatwave Forecasts in New Zealand: An Investigation of Imbalanced Regression Loss Functions with Neural Network Models
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Marine heatwaves (MHWs) are extreme ocean-temperature events with significant impacts on marine ecosystems and related industries. Accurate forecasts (one to six months ahead) of MHWs would aid in mitigating these impacts. However, forecasting MHWs presents a challenging imbalanced regression task due to the rarity of extreme temperature anomalies in comparison to more frequent moderate conditions. In this study, we examine monthly MHW forecasts for 12 locations around New Zealand. We use a fully-connected neural network and compare standard and specialized regression loss functions, including the mean squared error (MSE), the mean absolute error (MAE), the Huber, the weighted MSE, the focal-R, the balanced MSE, and a proposed scaling-weighted MSE. Results show that (i) short lead times (one month) are considerably more predictable than three- and six-month leads, (ii) models trained with the standard MSE or MAE losses excel at forecasting average conditions but struggle to capture extremes, and (iii) specialized loss functions such as the balanced MSE and our scaling-weighted MSE substantially improve forecasting of MHW and suspected MHW events. These findings underscore the importance of tailored loss functions for imbalanced regression, particularly in forecasting rare but impactful events such as MHWs.
Diving Deep: Forecasting Sea Surface Temperatures and Anomalies
Jan 10, 2025Abstract:This overview paper details the findings from the Diving Deep: Forecasting Sea Surface Temperatures and Anomalies Challenge at the European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML PKDD) 2024. The challenge focused on the data-driven predictability of global sea surface temperatures (SSTs), a key factor in climate forecasting, ecosystem management, fisheries management, and climate change monitoring. The challenge involved forecasting SST anomalies (SSTAs) three months in advance using historical data and included a special task of predicting SSTAs nine months ahead for the Baltic Sea. Participants utilized various machine learning approaches to tackle the task, leveraging data from ERA5. This paper discusses the methodologies employed, the results obtained, and the lessons learned, offering insights into the future of climate-related predictive modeling.
Selective nonlinearities removal from digital signals
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:Many instruments performing optical and non-optical imaging and sensing, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging or Fourier-transform spectrometry, produce digital signals containing modulations, sine-like components, which only after Fourier transformation give information about the structure or characteristics of the investigated object. Due to the fundamental physics-related limitations of such methods, the distribution of these signal components is often nonlinear and, when not properly compensated, leads to the resolution, precision or quality drop in the final image. Here, we propose an innovative approach that has the potential to allow cleaning of the signal from the nonlinearities but most of all, it now allows to switch the given order off, leaving all others intact. The latter provides a tool for more in-depth analysis of the nonlinearity-inducing properties of the investigated object, which can lead to applications in early disease detection or more sensitive sensing of chemical compounds. We consider OCT signals and nonlinearities up to the third order. In our approach, we propose two neural networks: one to remove solely the second-order nonlinearity and the other for removing solely the third-order nonlinearity. The input of the networks is a novel two-dimensional data structure with all the information needed for the network to infer a nonlinearity-free signal. We describe the developed networks and present the results for second-order and third-order nonlinearity removal in OCT data representing the images of various objects: a mirror, glass, and fruits.
Towards retrieving dispersion profiles using quantum-mimic Optical Coherence Tomography and Machine Learnin
May 30, 2022



Abstract:Artefacts in quantum-mimic Optical Coherence Tomography are considered detrimental because they scramble the images even for the simplest objects. They are a side effect of autocorrelation which is used in the quantum entanglement mimicking algorithm behind this method. Interestingly, the autocorrelation imprints certain characteristics onto an artefact - it makes its shape and characteristics depend on the amount of dispersion exhibited by the layer that artefact corresponds to. This unique relationship between the artefact and the layer's dispersion can be used to determine Group Velocity Dispersion (GVD) values of object layers and, based on them, build a dispersion-contrasted depth profile. The retrieval of GVD profiles is achieved via Machine Learning. During training, a neural network learns the relationship between GVD and the artefacts' shape and characteristics, and consequently, it is able to provide a good qualitative representation of object's dispersion profile for never-seen-before data: computer-generated single dispersive layers and experimental pieces of glass.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge