Varun Mithal
TE2Rules: Extracting Rule Lists from Tree Ensembles
Jun 30, 2022

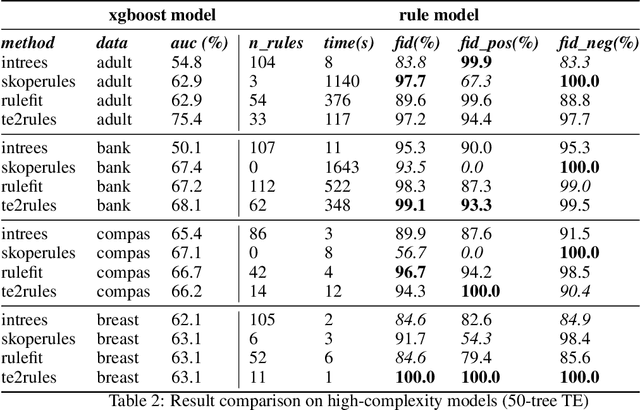

Abstract:Tree Ensemble (TE) models (e.g. Gradient Boosted Trees and Random Forests) often provide higher prediction performance compared to single decision trees. However, TE models generally lack transparency and interpretability, as humans have difficulty understanding their decision logic. This paper presents a novel approach to convert a TE trained for a binary classification task, to a rule list (RL) that is a global equivalent to the TE and is comprehensible for a human. This RL captures all necessary and sufficient conditions for decision making by the TE. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that, compared to state-of-the-art methods, (i) predictions from the RL generated by TE2Rules have high fidelity with respect to the original TE, (ii) the RL from TE2Rules has high interpretability measured by the number and the length of the decision rules, (iii) the run-time of TE2Rules algorithm can be reduced significantly at the cost of a slightly lower fidelity, and (iv) the RL is a fast alternative to the state-of-the-art rule-based instance-level outcome explanation techniques.
Semi-supervised Classification using Attention-based Regularization on Coarse-resolution Data
Jan 03, 2020



Abstract:Many real-world phenomena are observed at multiple resolutions. Predictive models designed to predict these phenomena typically consider different resolutions separately. This approach might be limiting in applications where predictions are desired at fine resolutions but available training data is scarce. In this paper, we propose classification algorithms that leverage supervision from coarser resolutions to help train models on finer resolutions. The different resolutions are modeled as different views of the data in a multi-view framework that exploits the complementarity of features across different views to improve models on both views. Unlike traditional multi-view learning problems, the key challenge in our case is that there is no one-to-one correspondence between instances across different views in our case, which requires explicit modeling of the correspondence of instances across resolutions. We propose to use the features of instances at different resolutions to learn the correspondence between instances across resolutions using an attention mechanism.Experiments on the real-world application of mapping urban areas using satellite observations and sentiment classification on text data show the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
An Attentive Survey of Attention Models
Apr 05, 2019
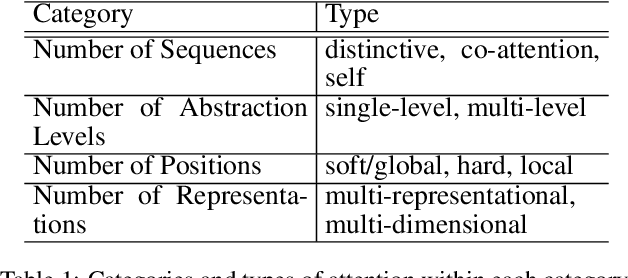
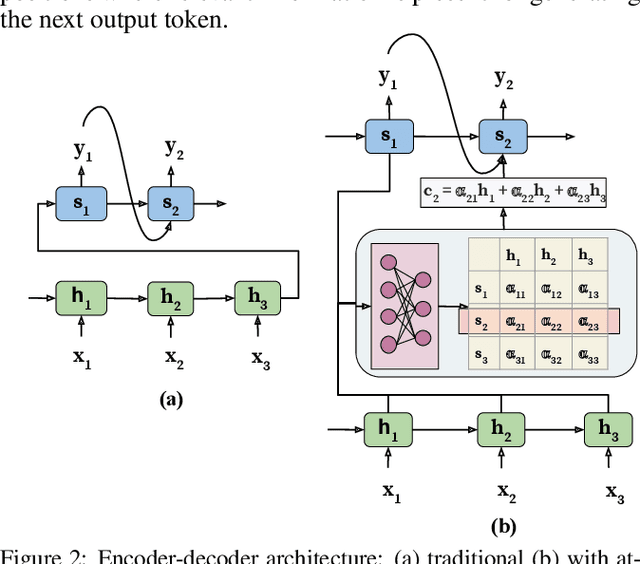
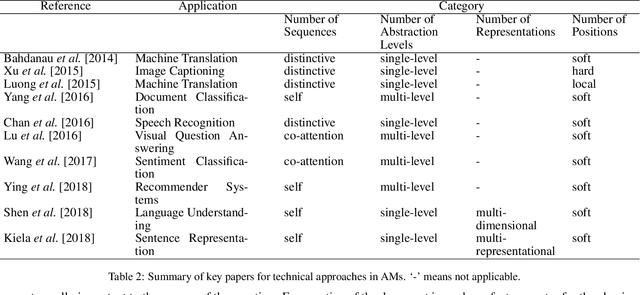
Abstract:Attention Model has now become an important concept in neural networks that has been researched within diverse application domains. This survey provides a structured and comprehensive overview of the developments in modeling attention. In particular, we propose a taxonomy which groups existing techniques into coherent categories. We review the different neural architectures in which attention has been incorporated, and also show how attention improves interpretability of neural models. Finally, we discuss some applications in which modeling attention has a significant impact. We hope this survey will provide a succinct introduction to attention models and guide practitioners while developing approaches for their applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge