Vageesh Saxena
Understanding and Analyzing Model Robustness and Knowledge-Transfer in Multilingual Neural Machine Translation using TX-Ray
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Neural networks have demonstrated significant advancements in Neural Machine Translation (NMT) compared to conventional phrase-based approaches. However, Multilingual Neural Machine Translation (MNMT) in extremely low-resource settings remains underexplored. This research investigates how knowledge transfer across languages can enhance MNMT in such scenarios. Using the Tatoeba translation challenge dataset from Helsinki NLP, we perform English-German, English-French, and English-Spanish translations, leveraging minimal parallel data to establish cross-lingual mappings. Unlike conventional methods relying on extensive pre-training for specific language pairs, we pre-train our model on English-English translations, setting English as the source language for all tasks. The model is fine-tuned on target language pairs using joint multi-task and sequential transfer learning strategies. Our work addresses three key questions: (1) How can knowledge transfer across languages improve MNMT in extremely low-resource scenarios? (2) How does pruning neuron knowledge affect model generalization, robustness, and catastrophic forgetting? (3) How can TX-Ray interpret and quantify knowledge transfer in trained models? Evaluation using BLEU-4 scores demonstrates that sequential transfer learning outperforms baselines on a 40k parallel sentence corpus, showcasing its efficacy. However, pruning neuron knowledge degrades performance, increases catastrophic forgetting, and fails to improve robustness or generalization. Our findings provide valuable insights into the potential and limitations of knowledge transfer and pruning in MNMT for extremely low-resource settings.
MATCHED: Multimodal Authorship-Attribution To Combat Human Trafficking in Escort-Advertisement Data
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Human trafficking (HT) remains a critical issue, with traffickers increasingly leveraging online escort advertisements (ads) to advertise victims anonymously. Existing detection methods, including Authorship Attribution (AA), often center on text-based analyses and neglect the multimodal nature of online escort ads, which typically pair text with images. To address this gap, we introduce MATCHED, a multimodal dataset of 27,619 unique text descriptions and 55,115 unique images collected from the Backpage escort platform across seven U.S. cities in four geographical regions. Our study extensively benchmarks text-only, vision-only, and multimodal baselines for vendor identification and verification tasks, employing multitask (joint) training objectives that achieve superior classification and retrieval performance on in-distribution and out-of-distribution (OOD) datasets. Integrating multimodal features further enhances this performance, capturing complementary patterns across text and images. While text remains the dominant modality, visual data adds stylistic cues that enrich model performance. Moreover, text-image alignment strategies like CLIP and BLIP2 struggle due to low semantic overlap and vague connections between the modalities of escort ads, with end-to-end multimodal training proving more robust. Our findings emphasize the potential of multimodal AA (MAA) to combat HT, providing LEAs with robust tools to link ads and disrupt trafficking networks.
ColBERT-XM: A Modular Multi-Vector Representation Model for Zero-Shot Multilingual Information Retrieval
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:State-of-the-art neural retrievers predominantly focus on high-resource languages like English, which impedes their adoption in retrieval scenarios involving other languages. Current approaches circumvent the lack of high-quality labeled data in non-English languages by leveraging multilingual pretrained language models capable of cross-lingual transfer. However, these models require substantial task-specific fine-tuning across multiple languages, often perform poorly in languages with minimal representation in the pretraining corpus, and struggle to incorporate new languages after the pretraining phase. In this work, we present a novel modular dense retrieval model that learns from the rich data of a single high-resource language and effectively zero-shot transfers to a wide array of languages, thereby eliminating the need for language-specific labeled data. Our model, ColBERT-XM, demonstrates competitive performance against existing state-of-the-art multilingual retrievers trained on more extensive datasets in various languages. Further analysis reveals that our modular approach is highly data-efficient, effectively adapts to out-of-distribution data, and significantly reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions. By demonstrating its proficiency in zero-shot scenarios, ColBERT-XM marks a shift towards more sustainable and inclusive retrieval systems, enabling effective information accessibility in numerous languages. We publicly release our code and models for the community.
IDTraffickers: An Authorship Attribution Dataset to link and connect Potential Human-Trafficking Operations on Text Escort Advertisements
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Human trafficking (HT) is a pervasive global issue affecting vulnerable individuals, violating their fundamental human rights. Investigations reveal that a significant number of HT cases are associated with online advertisements (ads), particularly in escort markets. Consequently, identifying and connecting HT vendors has become increasingly challenging for Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs). To address this issue, we introduce IDTraffickers, an extensive dataset consisting of 87,595 text ads and 5,244 vendor labels to enable the verification and identification of potential HT vendors on online escort markets. To establish a benchmark for authorship identification, we train a DeCLUTR-small model, achieving a macro-F1 score of 0.8656 in a closed-set classification environment. Next, we leverage the style representations extracted from the trained classifier to conduct authorship verification, resulting in a mean r-precision score of 0.8852 in an open-set ranking environment. Finally, to encourage further research and ensure responsible data sharing, we plan to release IDTraffickers for the authorship attribution task to researchers under specific conditions, considering the sensitive nature of the data. We believe that the availability of our dataset and benchmarks will empower future researchers to utilize our findings, thereby facilitating the effective linkage of escort ads and the development of more robust approaches for identifying HT indicators.
VendorLink: An NLP approach for Identifying & Linking Vendor Migrants & Potential Aliases on Darknet Markets
May 04, 2023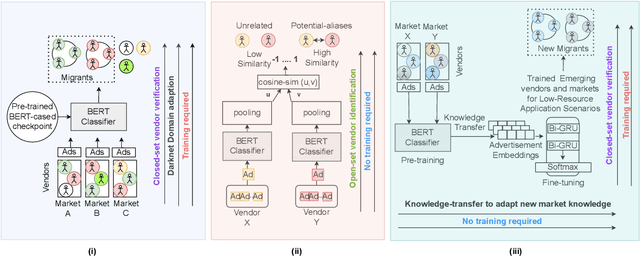
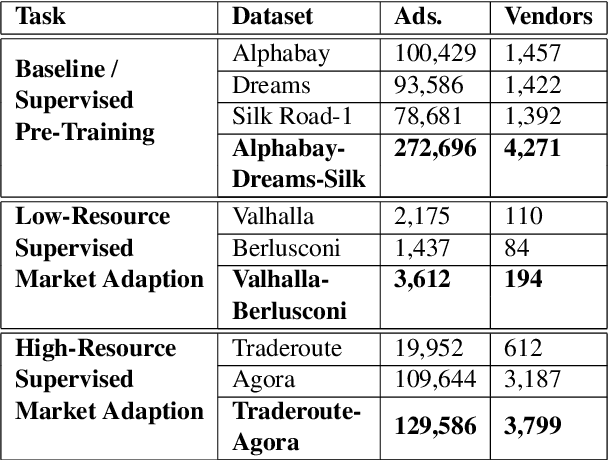
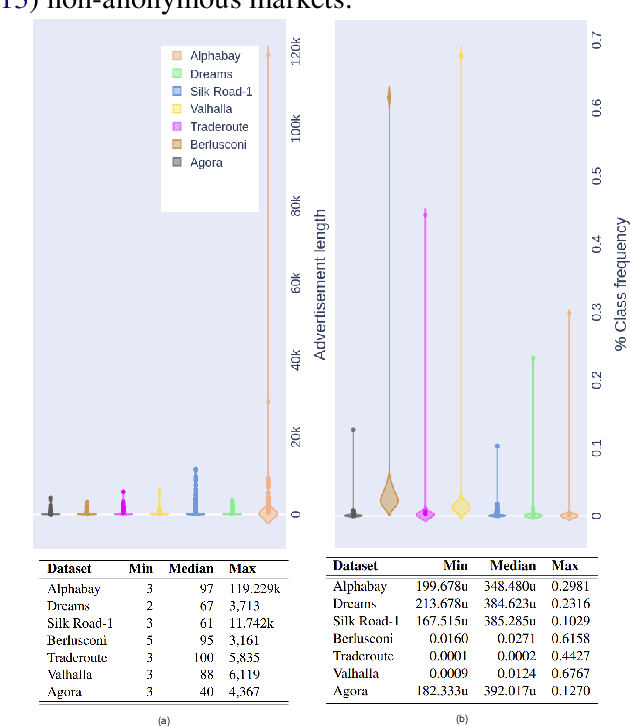
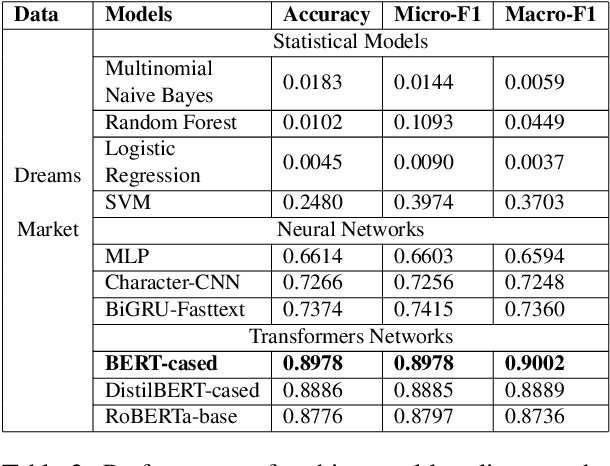
Abstract:The anonymity on the Darknet allows vendors to stay undetected by using multiple vendor aliases or frequently migrating between markets. Consequently, illegal markets and their connections are challenging to uncover on the Darknet. To identify relationships between illegal markets and their vendors, we propose VendorLink, an NLP-based approach that examines writing patterns to verify, identify, and link unique vendor accounts across text advertisements (ads) on seven public Darknet markets. In contrast to existing literature, VendorLink utilizes the strength of supervised pre-training to perform closed-set vendor verification, open-set vendor identification, and low-resource market adaption tasks. Through VendorLink, we uncover (i) 15 migrants and 71 potential aliases in the Alphabay-Dreams-Silk dataset, (ii) 17 migrants and 3 potential aliases in the Valhalla-Berlusconi dataset, and (iii) 75 migrants and 10 potential aliases in the Traderoute-Agora dataset. Altogether, our approach can help Law Enforcement Agencies (LEA) make more informed decisions by verifying and identifying migrating vendors and their potential aliases on existing and Low-Resource (LR) emerging Darknet markets.
Video Action Classification Using PredNet
Jun 14, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we evaluate the PredNet \cite{lotter16} on the Something-something action data set \cite{farzaneh18} and implement the PredNet+, which we train in a multi-task fashion to output both classification labels and predictions. Our idea is to condition video prediction and action classification on each other. We discuss a series of observations about the PredNet and conclude that it does not completely follow the principles of the predictive coding framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge