Gijs Van Dijck
MATCHED: Multimodal Authorship-Attribution To Combat Human Trafficking in Escort-Advertisement Data
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Human trafficking (HT) remains a critical issue, with traffickers increasingly leveraging online escort advertisements (ads) to advertise victims anonymously. Existing detection methods, including Authorship Attribution (AA), often center on text-based analyses and neglect the multimodal nature of online escort ads, which typically pair text with images. To address this gap, we introduce MATCHED, a multimodal dataset of 27,619 unique text descriptions and 55,115 unique images collected from the Backpage escort platform across seven U.S. cities in four geographical regions. Our study extensively benchmarks text-only, vision-only, and multimodal baselines for vendor identification and verification tasks, employing multitask (joint) training objectives that achieve superior classification and retrieval performance on in-distribution and out-of-distribution (OOD) datasets. Integrating multimodal features further enhances this performance, capturing complementary patterns across text and images. While text remains the dominant modality, visual data adds stylistic cues that enrich model performance. Moreover, text-image alignment strategies like CLIP and BLIP2 struggle due to low semantic overlap and vague connections between the modalities of escort ads, with end-to-end multimodal training proving more robust. Our findings emphasize the potential of multimodal AA (MAA) to combat HT, providing LEAs with robust tools to link ads and disrupt trafficking networks.
IDTraffickers: An Authorship Attribution Dataset to link and connect Potential Human-Trafficking Operations on Text Escort Advertisements
Oct 09, 2023Abstract:Human trafficking (HT) is a pervasive global issue affecting vulnerable individuals, violating their fundamental human rights. Investigations reveal that a significant number of HT cases are associated with online advertisements (ads), particularly in escort markets. Consequently, identifying and connecting HT vendors has become increasingly challenging for Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs). To address this issue, we introduce IDTraffickers, an extensive dataset consisting of 87,595 text ads and 5,244 vendor labels to enable the verification and identification of potential HT vendors on online escort markets. To establish a benchmark for authorship identification, we train a DeCLUTR-small model, achieving a macro-F1 score of 0.8656 in a closed-set classification environment. Next, we leverage the style representations extracted from the trained classifier to conduct authorship verification, resulting in a mean r-precision score of 0.8852 in an open-set ranking environment. Finally, to encourage further research and ensure responsible data sharing, we plan to release IDTraffickers for the authorship attribution task to researchers under specific conditions, considering the sensitive nature of the data. We believe that the availability of our dataset and benchmarks will empower future researchers to utilize our findings, thereby facilitating the effective linkage of escort ads and the development of more robust approaches for identifying HT indicators.
VendorLink: An NLP approach for Identifying & Linking Vendor Migrants & Potential Aliases on Darknet Markets
May 04, 2023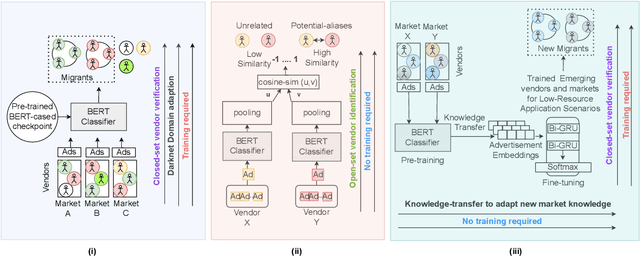
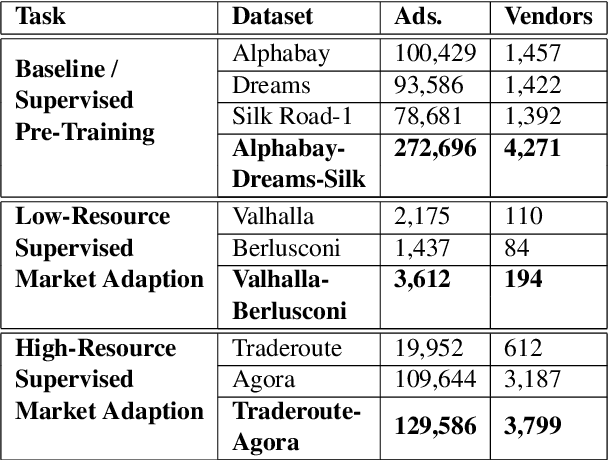
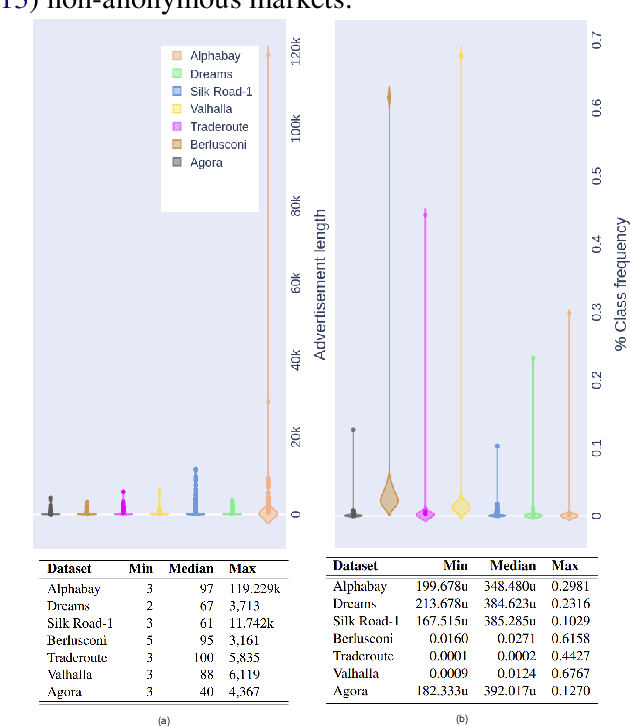
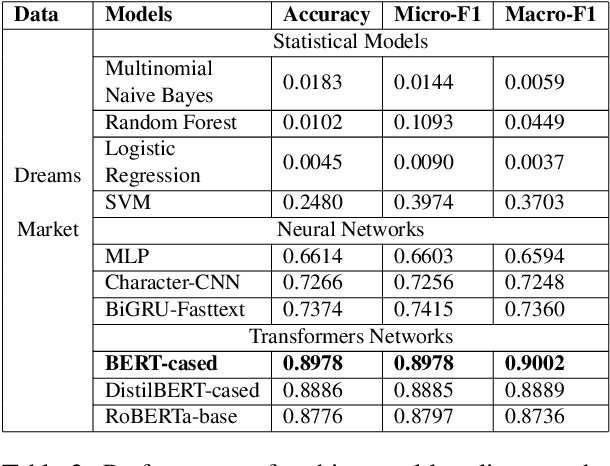
Abstract:The anonymity on the Darknet allows vendors to stay undetected by using multiple vendor aliases or frequently migrating between markets. Consequently, illegal markets and their connections are challenging to uncover on the Darknet. To identify relationships between illegal markets and their vendors, we propose VendorLink, an NLP-based approach that examines writing patterns to verify, identify, and link unique vendor accounts across text advertisements (ads) on seven public Darknet markets. In contrast to existing literature, VendorLink utilizes the strength of supervised pre-training to perform closed-set vendor verification, open-set vendor identification, and low-resource market adaption tasks. Through VendorLink, we uncover (i) 15 migrants and 71 potential aliases in the Alphabay-Dreams-Silk dataset, (ii) 17 migrants and 3 potential aliases in the Valhalla-Berlusconi dataset, and (iii) 75 migrants and 10 potential aliases in the Traderoute-Agora dataset. Altogether, our approach can help Law Enforcement Agencies (LEA) make more informed decisions by verifying and identifying migrating vendors and their potential aliases on existing and Low-Resource (LR) emerging Darknet markets.
A Statutory Article Retrieval Dataset in French
Aug 26, 2021



Abstract:Statutory article retrieval is the task of automatically retrieving law articles relevant to a legal question. While recent advances in natural language processing have sparked considerable interest in many legal tasks, statutory article retrieval remains primarily untouched due to the scarcity of large-scale and high-quality annotated datasets. To address this bottleneck, we introduce the Belgian Statutory Article Retrieval Dataset (BSARD), which consists of 1,100+ French native legal questions labeled by experienced jurists with relevant articles from a corpus of 22,600+ Belgian law articles. Using BSARD, we benchmark several unsupervised information retrieval methods based on term weighting and pooled embeddings. Our best performing baseline achieves 50.8% R@100, which is promising for the feasibility of the task and indicates that there is still substantial room for improvement. By the specificity of the data domain and addressed task, BSARD presents a unique challenge problem for future research on legal information retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge