Ulme Wennberg
Exploring Internal Numeracy in Language Models: A Case Study on ALBERT
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:It has been found that Transformer-based language models have the ability to perform basic quantitative reasoning. In this paper, we propose a method for studying how these models internally represent numerical data, and use our proposal to analyze the ALBERT family of language models. Specifically, we extract the learned embeddings these models use to represent tokens that correspond to numbers and ordinals, and subject these embeddings to Principal Component Analysis (PCA). PCA results reveal that ALBERT models of different sizes, trained and initialized separately, consistently learn to use the axes of greatest variation to represent the approximate ordering of various numerical concepts. Numerals and their textual counterparts are represented in separate clusters, but increase along the same direction in 2D space. Our findings illustrate that language models, trained purely to model text, can intuit basic mathematical concepts, opening avenues for NLP applications that intersect with quantitative reasoning.
Wavebender GAN: An architecture for phonetically meaningful speech manipulation
Feb 22, 2022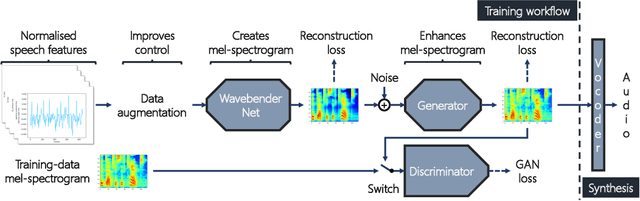
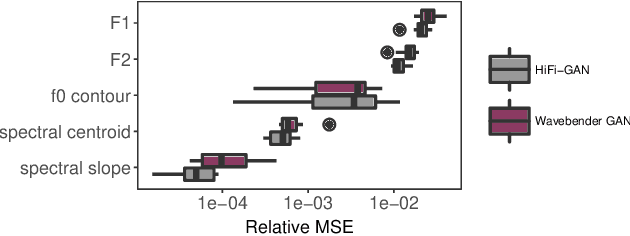
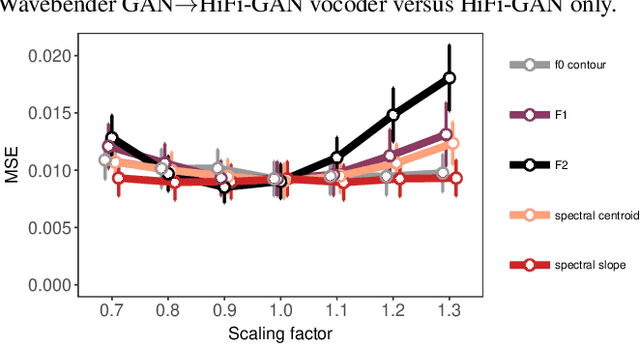
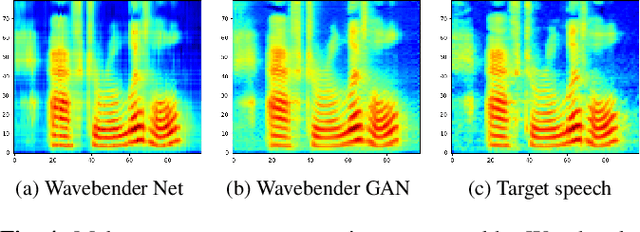
Abstract:Deep learning has revolutionised synthetic speech quality. However, it has thus far delivered little value to the speech science community. The new methods do not meet the controllability demands that practitioners in this area require e.g.: in listening tests with manipulated speech stimuli. Instead, control of different speech properties in such stimuli is achieved by using legacy signal-processing methods. This limits the range, accuracy, and speech quality of the manipulations. Also, audible artefacts have a negative impact on the methodological validity of results in speech perception studies. This work introduces a system capable of manipulating speech properties through learning rather than design. The architecture learns to control arbitrary speech properties and leverages progress in neural vocoders to obtain realistic output. Experiments with copy synthesis and manipulation of a small set of core speech features (pitch, formants, and voice quality measures) illustrate the promise of the approach for producing speech stimuli that have accurate control and high perceptual quality.
The Case for Translation-Invariant Self-Attention in Transformer-Based Language Models
Jun 03, 2021
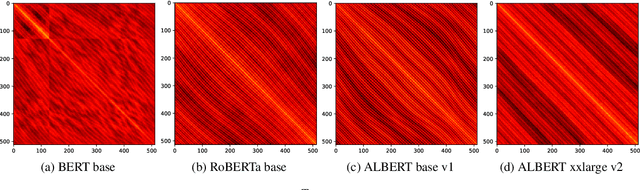

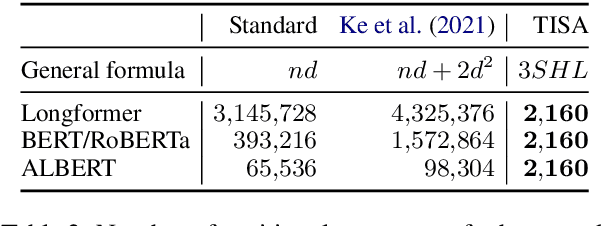
Abstract:Mechanisms for encoding positional information are central for transformer-based language models. In this paper, we analyze the position embeddings of existing language models, finding strong evidence of translation invariance, both for the embeddings themselves and for their effect on self-attention. The degree of translation invariance increases during training and correlates positively with model performance. Our findings lead us to propose translation-invariant self-attention (TISA), which accounts for the relative position between tokens in an interpretable fashion without needing conventional position embeddings. Our proposal has several theoretical advantages over existing position-representation approaches. Experiments show that it improves on regular ALBERT on GLUE tasks, while only adding orders of magnitude less positional parameters.
Entity, Relation, and Event Extraction with Contextualized Span Representations
Sep 10, 2019



Abstract:We examine the capabilities of a unified, multi-task framework for three information extraction tasks: named entity recognition, relation extraction, and event extraction. Our framework (called DyGIE++) accomplishes all tasks by enumerating, refining, and scoring text spans designed to capture local (within-sentence) and global (cross-sentence) context. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art results across all tasks, on four datasets from a variety of domains. We perform experiments comparing different techniques to construct span representations. Contextualized embeddings like BERT perform well at capturing relationships among entities in the same or adjacent sentences, while dynamic span graph updates model long-range cross-sentence relationships. For instance, propagating span representations via predicted coreference links can enable the model to disambiguate challenging entity mentions. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/dwadden/dygiepp and can be easily adapted for new tasks or datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge