Tinsu Pan
PET image denoising based on denoising diffusion probabilistic models
Sep 14, 2022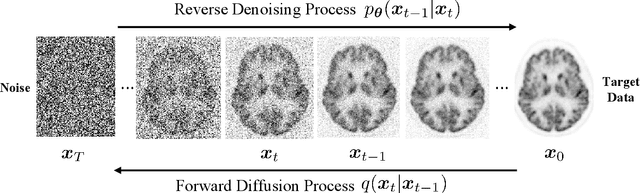
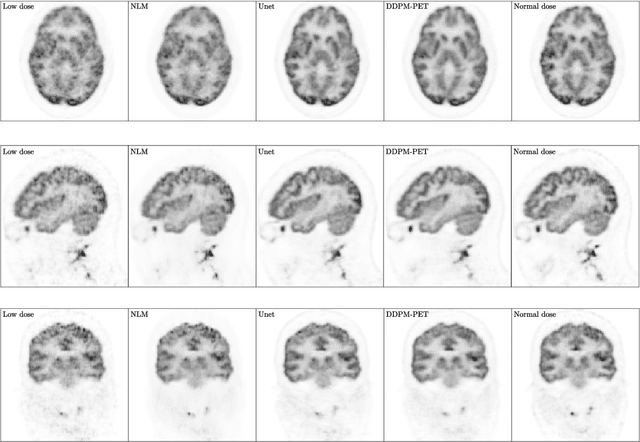
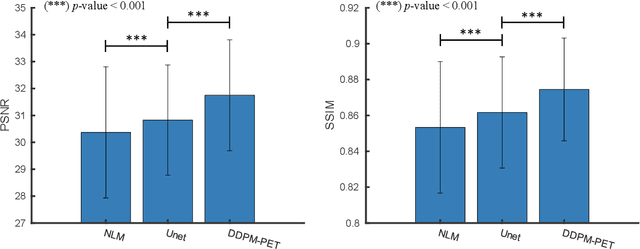
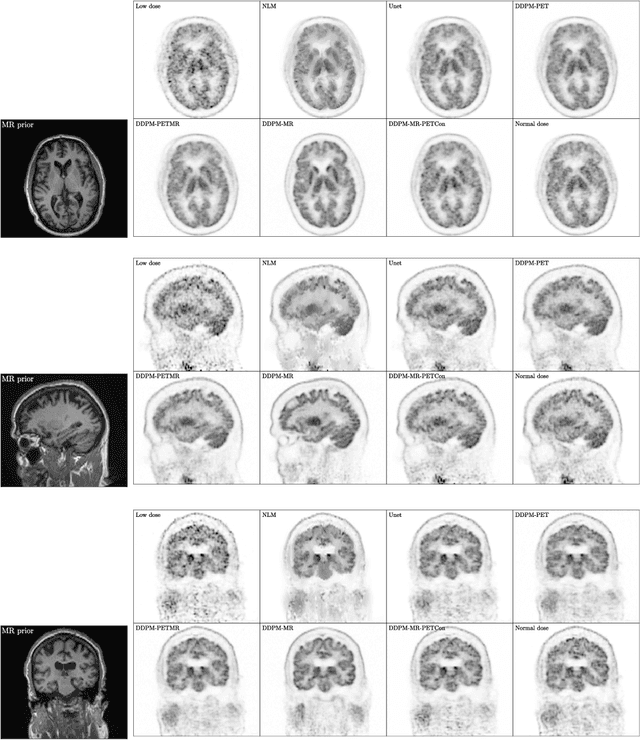
Abstract:Due to various physical degradation factors and limited counts received, PET image quality needs further improvements. The denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPM) are distribution learning-based models, which try to transform a normal distribution into a specific data distribution based on iterative refinements. In this work, we proposed and evaluated different DDPM-based methods for PET image denoising. Under the DDPM framework, one way to perform PET image denoising is to provide the PET image and/or the prior image as the network input. Another way is to supply the prior image as the input with the PET image included in the refinement steps, which can fit for scenarios of different noise levels. 120 18F-FDG datasets and 140 18F-MK-6240 datasets were utilized to evaluate the proposed DDPM-based methods. Quantification show that the DDPM-based frameworks with PET information included can generate better results than the nonlocal mean and Unet-based denoising methods. Adding additional MR prior in the model can help achieve better performance and further reduce the uncertainty during image denoising. Solely relying on MR prior while ignoring the PET information can result in large bias. Regional and surface quantification shows that employing MR prior as the network input while embedding PET image as a data-consistency constraint during inference can achieve the best performance. In summary, DDPM-based PET image denoising is a flexible framework, which can efficiently utilize prior information and achieve better performance than the nonlocal mean and Unet-based denoising methods.
Spach Transformer: Spatial and Channel-wise Transformer Based on Local and Global Self-attentions for PET Image Denoising
Sep 07, 2022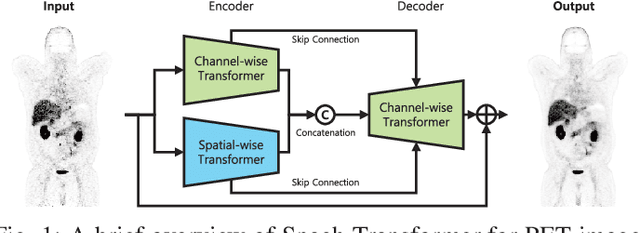
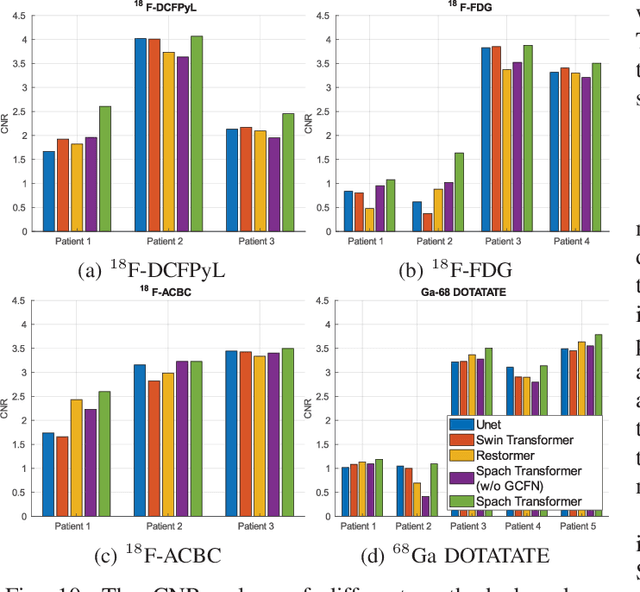
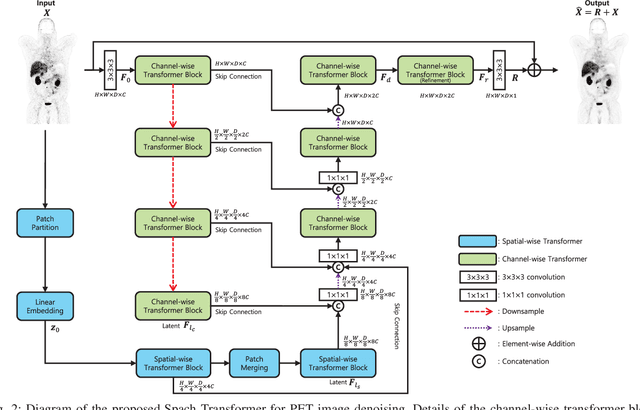
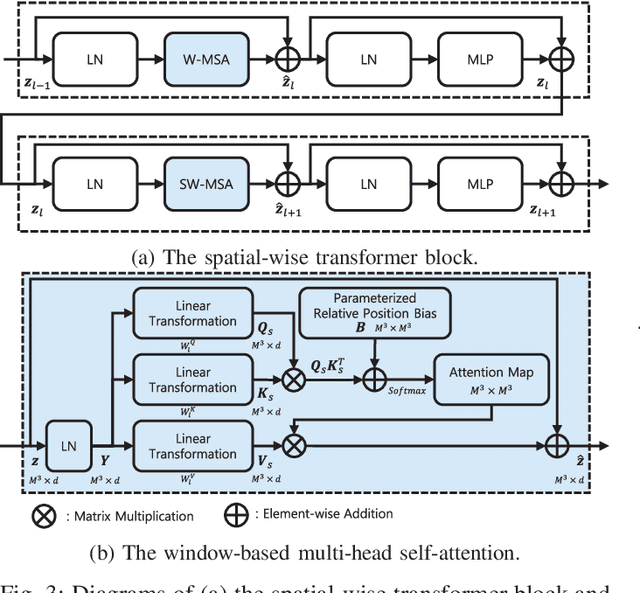
Abstract:Position emission tomography (PET) is widely used in clinics and research due to its quantitative merits and high sensitivity, but suffers from low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Recently convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely used to improve PET image quality. Though successful and efficient in local feature extraction, CNN cannot capture long-range dependencies well due to its limited receptive field. Global multi-head self-attention (MSA) is a popular approach to capture long-range information. However, the calculation of global MSA for 3D images has high computational costs. In this work, we proposed an efficient spatial and channel-wise encoder-decoder transformer, Spach Transformer, that can leverage spatial and channel information based on local and global MSAs. Experiments based on datasets of different PET tracers, i.e., $^{18}$F-FDG, $^{18}$F-ACBC, $^{18}$F-DCFPyL, and $^{68}$Ga-DOTATATE, were conducted to evaluate the proposed framework. Quantitative results show that the proposed Spach Transformer can achieve better performance than other reference methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge