Tianxiao Han
Semantic-aware Transmission for Robust Point Cloud Classification
Jun 23, 2023



Abstract:As three-dimensional (3D) data acquisition devices become increasingly prevalent, the demand for 3D point cloud transmission is growing. In this study, we introduce a semantic-aware communication system for robust point cloud classification that capitalizes on the advantages of pre-trained Point-BERT models. Our proposed method comprises four main components: the semantic encoder, channel encoder, channel decoder, and semantic decoder. By employing a two-stage training strategy, our system facilitates efficient and adaptable learning tailored to the specific classification tasks. The results show that the proposed system achieves classification accuracy of over 89\% when SNR is higher than 10 dB and still maintains accuracy above 66.6\% even at SNR of 4 dB. Compared to the existing method, our approach performs at 0.8\% to 48\% better across different SNR values, demonstrating robustness to channel noise. Our system also achieves a balance between accuracy and speed, being computationally efficient while maintaining high classification performance under noisy channel conditions. This adaptable and resilient approach holds considerable promise for a wide array of 3D scene understanding applications, effectively addressing the challenges posed by channel noise.
Generative Model Based Highly Efficient Semantic Communication Approach for Image Transmission
Nov 18, 2022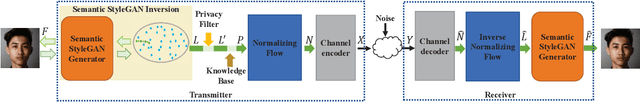
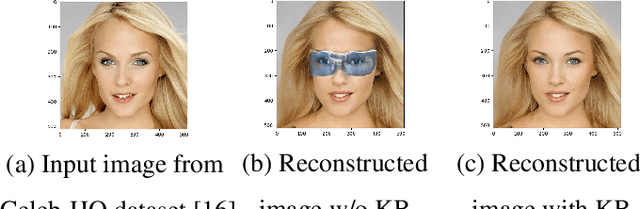
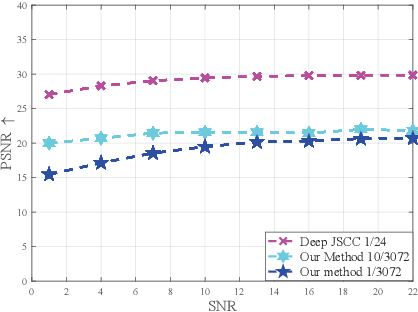
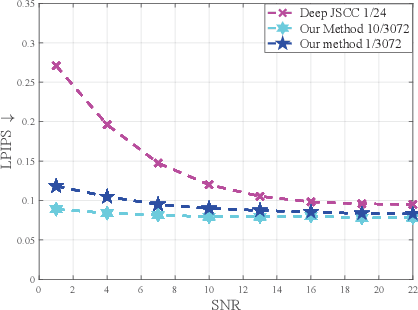
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) based semantic communication methods have been explored to transmit images efficiently in recent years. In this paper, we propose a generative model based semantic communication to further improve the efficiency of image transmission and protect private information. In particular, the transmitter extracts the interpretable latent representation from the original image by a generative model exploiting the GAN inversion method. We also employ a privacy filter and a knowledge base to erase private information and replace it with natural features in the knowledge base. The simulation results indicate that our proposed method achieves comparable quality of received images while significantly reducing communication costs compared to the existing methods.
Semantic-preserved Communication System for Highly Efficient Speech Transmission
May 25, 2022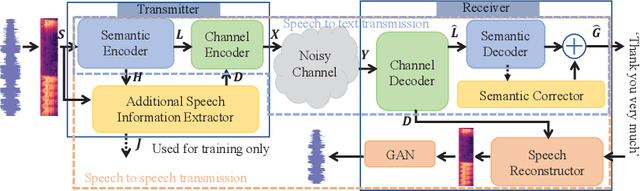
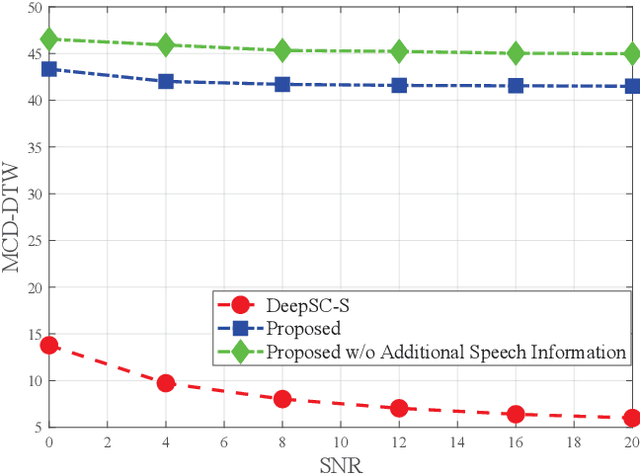
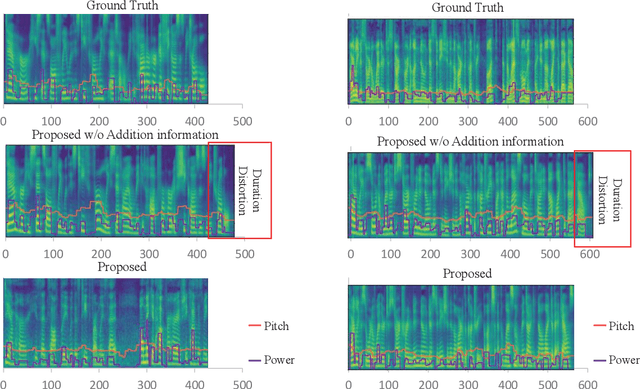
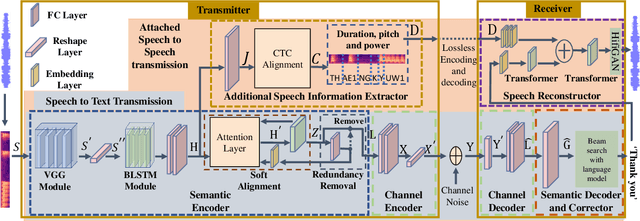
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) based semantic communication methods have been explored for the efficient transmission of images, text, and speech in recent years. In contrast to traditional wireless communication methods that focus on the transmission of abstract symbols, semantic communication approaches attempt to achieve better transmission efficiency by only sending the semantic-related information of the source data. In this paper, we consider semantic-oriented speech transmission which transmits only the semantic-relevant information over the channel for the speech recognition task, and a compact additional set of semantic-irrelevant information for the speech reconstruction task. We propose a novel end-to-end DL-based transceiver which extracts and encodes the semantic information from the input speech spectrums at the transmitter and outputs the corresponding transcriptions from the decoded semantic information at the receiver. For the speech to speech transmission, we further include a CTC alignment module that extracts a small number of additional semantic-irrelevant but speech-related information for the better reconstruction of the original speech signals at the receiver. The simulation results confirm that our proposed method outperforms current methods in terms of the accuracy of the predicted text for the speech to text transmission and the quality of the recovered speech signals for the speech to speech transmission, and significantly improves transmission efficiency. More specifically, the proposed method only sends 16% of the amount of the transmitted symbols required by the existing methods while achieving about 10% reduction in WER for the speech to text transmission. For the speech to speech transmission, it results in an even more remarkable improvement in terms of transmission efficiency with only 0.2% of the amount of the transmitted symbols required by the existing method.
Semantic-aware Speech to Text Transmission with Redundancy Removal
Feb 07, 2022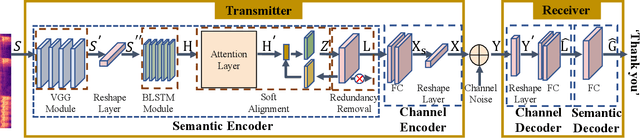
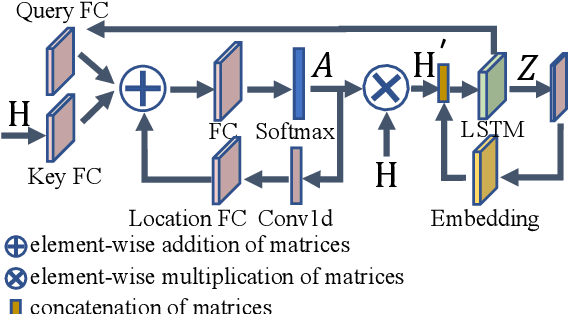
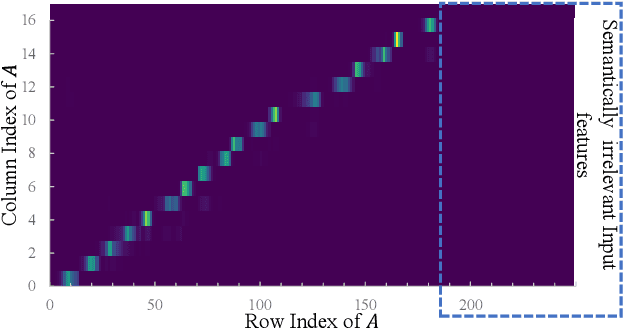
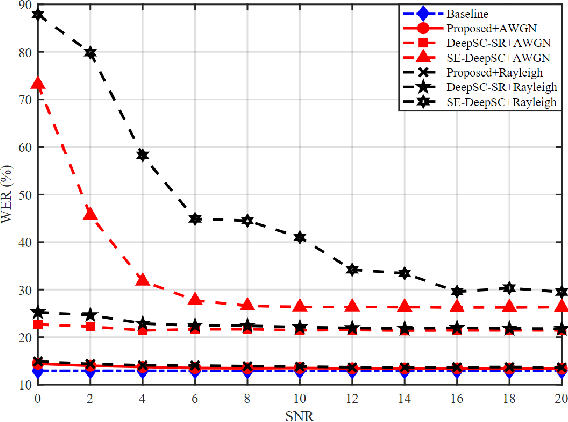
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) based semantic communication methods have been explored for the efficient transmission of images, text, and speech in recent years. In contrast to traditional wireless communication methods that focus on the transmission of abstract symbols, semantic communication approaches attempt to achieve better transmission efficiency by only sending the semantic-related information of the source data. In this paper, we consider semantic-oriented speech to text transmission. We propose a novel end-to-end DL-based transceiver, which includes an attention-based soft alignment module and a redundancy removal module to compress the transmitted data. In particular, the former extracts only the text-related semantic features, and the latter further drops the semantically redundant content, greatly reducing the amount of semantic redundancy compared to existing methods. We also propose a two-stage training scheme, which speeds up the training of the proposed DL model. The simulation results indicate that our proposed method outperforms current methods in terms of the accuracy of the received text and transmission efficiency. Moreover, the proposed method also has a smaller model size and shorter end-to-end runtime.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge